diff --git a/docs/hardware/gpsmodule.mdx b/docs/1.2-End-of-life/hardware/gpsmodule.mdx
similarity index 100%
rename from docs/hardware/gpsmodule.mdx
rename to docs/1.2-End-of-life/hardware/gpsmodule.mdx
diff --git a/docs/1.2-End-of-life/hardware/heltec.mdx b/docs/1.2-End-of-life/hardware/heltec.mdx
index b860b996..16f223fe 100644
--- a/docs/1.2-End-of-life/hardware/heltec.mdx
+++ b/docs/1.2-End-of-life/hardware/heltec.mdx
@@ -1,46 +1,36 @@
---
-id: techo
-title: LILYGO® TTGO T-Echo devices
-sidebar_label: LILYGO® T-Echo
-sidebar_position: 2
+id: heltec
+title: Heltec device
+sidebar_label: Heltec
+sidebar_position: 6
---
-The T-Echo is the latest device to be release by LILYGO® supporting a low power consumption microcontroller.
+## WiFi LoRa 32 (V2) * Not Recommended - Support may be dropped
-### Features
+It continues to be a struggle to support this very old ESP32 chip, not officially supported in 1.3 / 2.0 and support may be dropped completely.
-- nRF52840 - Bluetooth BLE 5.0, NFC and very low power consumption
-- SX1262 - LoRa transceiver
-- 1.54" eInk display
-- L76K - GNSS receiver - Supporting GPS, BeiDou, GLONASS & QZSS
-- Reset, Program and capacitive touch buttons
+Using this device with a battery is not recommended.
+
+- ESP32 - Wifi & Bluetooth
+- SX127x - LoRa Transceiver
+- Frequency options:
+ - 433 MHz
+ - 470-510 MHz
+ - 863-870 MHz
+ - 902-928 MHz
+- Built in 0.96 inch OLED display
- U.FL antenna connector
-- Optional BME280 - Humidity and Pressure Sensor
-- Comes with a case and battery
+- Reset and Program switches
+- No GPS
-### Resources
+- Firmware file: `firmware-heltec-1.x.x.bin`
-- Firmware file: `firmware-t-echo-2.x.x.uf2`
-- [Purchase link](https://www.aliexpress.com/item/1005002842456390.html)
-- TTGO's [GitHub page](https://github.com/Xinyuan-LilyGO/LilyGO-T-Echo) for the T-Echo
+[](/img/hardware/heltec-v2.png)
-
+[](/img/hardware/heltec_v2_pinmap.png)
-### T-Echo button functions
+There are two versions of the Heltec (V2). Below is a picture highlighting the visual differences:
-- Capacitive top button
- - A short press refreshes the current screen
-- Button 1
- - A single press resets the device
- - A double press puts the device into bootloader mode ready to receive a new firmware
-- Button 2
- - A single press changes the page displayed on the device
- - A double press turns the screen backlight on/off
- - A long press turns the device off
+[](/img/hardware/heltec_v2_vs_v21.png)
-
-[](/img/hardware/t-echo-lilygo.jpg)
+- See [hardware update log](https://docs.heltec.org/en/node/esp32/dev-board/hardware_update_log.html) for more details
diff --git a/docs/1.2-End-of-life/settings/range-test-module.mdx b/docs/1.2-End-of-life/settings/range-test-module.mdx
index f07c97c7..5a0a24e0 100644
--- a/docs/1.2-End-of-life/settings/range-test-module.mdx
+++ b/docs/1.2-End-of-life/settings/range-test-module.mdx
@@ -179,7 +179,7 @@ Be sure to turn off either the plugin configured as a sender or the device where
Also be mindful of your space usage on the file system. It has protections from filling up the space but it's best to delete old range test results.
:::note
-Leaving this plugin on can slow down your mesh. Currently, the messages are sent using the same `TEXT_MESSAGE_APP` [port that all other messages](/docs/developers/protobufs/api#portnumsproto) are sent on.
+Leaving this plugin on can slow down your mesh. Currently, the messages are sent using the same `TEXT_MESSAGE_APP` [port that all other messages](/docs/development/firmware/portnum) are sent on.
:::
```plaintext title="Example URLs"
diff --git a/docs/1.2-End-of-life/settings/store-and-forward-module.mdx b/docs/1.2-End-of-life/settings/store-and-forward-module.mdx
index f8c5e87c..7911d1ed 100644
--- a/docs/1.2-End-of-life/settings/store-and-forward-module.mdx
+++ b/docs/1.2-End-of-life/settings/store-and-forward-module.mdx
@@ -291,7 +291,7 @@ Initial Requirements:
### Meshtastic channel configuration
-Don't use this on the "Long Range / Slow" or "Long Range / Fast" channel settings. You're welcome to try and report back, but those channels have a [very low bitrate](/docs/developers/firmware/radio-settings#pre-defined).
+Don't use this on the "Long Range / Slow" or "Long Range / Fast" channel settings. You're welcome to try and report back, but those channels have a [very low bitrate](/docs/about/overview/radio-settings#pre-defined).
Either use a custom channel configuration with at an at least 1kbit data rate or use "Medium Range / Fast".
diff --git a/docs/1.2-End-of-life/software/mqtt.mdx b/docs/1.2-End-of-life/software/mqtt.mdx
index 7a07460c..0cba7c7f 100644
--- a/docs/1.2-End-of-life/software/mqtt.mdx
+++ b/docs/1.2-End-of-life/software/mqtt.mdx
@@ -36,7 +36,7 @@ The payload is a raw protobuf. Looking at the MQTT traffic with a program like `
ShortFast !937bed1c
```
-Packets from the following [port numbers](/docs/developers/Firmware/portnum) are serialized to JSON and then forwarded to the `msh/1/json/CHANNELID/DEVICEID` topic: `TEXT_MESSAGE_APP`, `ENVIRONMENTAL_MEASUREMENT_APP`, `NODEINFO_APP` and `POSITION_APP`.
+Packets from the following [port numbers](/docs/development/firmware/portnum) are serialized to JSON and then forwarded to the `msh/1/json/CHANNELID/DEVICEID` topic: `TEXT_MESSAGE_APP`, `ENVIRONMENTAL_MEASUREMENT_APP`, `NODEINFO_APP` and `POSITION_APP`.
An example of a received `NODEINFO_APP` message:
@@ -147,7 +147,7 @@ FIXME - explain this more, talk about how useful for users and security domains.
## On device API
-For information on the related on-device API see [here](/docs/developers/firmware/device-api).
+For information on the related on-device API see [here](/docs/developers/protobufs/api).
## MQTT transport
diff --git a/docs/developers/Firmware/_category_.yml b/docs/about/_category_.yml
similarity index 69%
rename from docs/developers/Firmware/_category_.yml
rename to docs/about/_category_.yml
index 3b3d54bd..7042440b 100644
--- a/docs/developers/Firmware/_category_.yml
+++ b/docs/about/_category_.yml
@@ -1,7 +1,7 @@
-
position: 1 # float position is supported
-label: 'Firmware'
+label: About
collapsible: true # make the category collapsible
link:
type: generated-index
- title: Firmware
\ No newline at end of file
+ title: About Meshtastic
+ slug: /about
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/docs/developers/contributing.mdx b/docs/about/contributing.mdx
similarity index 93%
rename from docs/developers/contributing.mdx
rename to docs/about/contributing.mdx
index adcee6b0..06c9d272 100644
--- a/docs/developers/contributing.mdx
+++ b/docs/about/contributing.mdx
@@ -1,11 +1,10 @@
---
-id: contributing
-title: Contributing
-slug: /developers/contributing
+title: Community Guide
+sidebar_label: Contributing
+slug: /contributing
+sidebar_position: 3
---
-# How to Help
-
Meshtastic is a team of volunteers, and as such there is always plenty of ways to help. This project gets great contributions from people in their off hours. Those contributors work on the features they are interested in. It is a very open and welcoming developer community, and we are always looking for help to improve Meshtastic.
- If you're a developer, there's plenty stuff to do. Dig in!
@@ -38,7 +37,7 @@ The [meshtastic/Meshtastic-python](https://github.com/meshtastic/Meshtastic-pyth
## Web Application
-The [meshtastic/web](https://github.com/meshtastic/web) repository is where the hosted web server on the ESP32 devices in Typescript is developed. See the [Web interface overview](/docs/software/web) for more details.
+The [meshtastic/web](https://github.com/meshtastic/web) repository is where the hosted web server on the ESP32 devices in Typescript is developed. See the [Web interface overview](/docs/software/web-client) for more details.
The [meshtastic/meshtastic.js](https://github.com/meshtastic/meshtastic.js) repository is a JavaScript library that provides an interface for Meshtastic devices.
@@ -53,7 +52,7 @@ The [meshtastic/meshtastic.js](https://github.com/meshtastic/meshtastic.js) repo
There are two phone apps that interact with the Meshtastic devices:
-- The [meshtastic/Meshtastic-Android](https://github.com/meshtastic/Meshtastic-Android) repository repo contains the Kotlin code for Android based interactions with Meshtastic devices. See [here](/docs/developers/android/build-app) for how to build/create a development environment for the Meshtastic Android App.
+- The [meshtastic/Meshtastic-Android](https://github.com/meshtastic/Meshtastic-Android) repository repo contains the Kotlin code for Android based interactions with Meshtastic devices. See [here](/docs/development/android) for how to build/create a development environment for the Meshtastic Android App.
- The iOS app is in the process of a complete re-write in Swift and will have the new repo published soon. Note: There are a couple of earlier implementations.
## Documentation
diff --git a/docs/faq/index.mdx b/docs/about/faq.mdx
similarity index 91%
rename from docs/faq/index.mdx
rename to docs/about/faq.mdx
index 9f92e8fc..0ff71476 100644
--- a/docs/faq/index.mdx
+++ b/docs/about/faq.mdx
@@ -2,35 +2,14 @@
id: faq
title: FAQs
slug: /faq
-sidebar_position: 8
+sidebar_position: 3
---
-
-
-## Overview
-
-### What is Meshtastic?
-
-Meshtastic is the most awesome long range, low power communications service on the planet earth! That's not even an exaggeration!
### Where can I get additional help, ask questions, or bond with the Meshtastic community?
-This site (which has a great search function) is the preferred place for up to date documentation. Many of our users and developers hang out on the [Meshtastic Discord](https://discord.gg/ktMAKGBnBs) server where you may connect with like-minded people.
+This site (which has a great search function) is the preferred place for up-to-date documentation. Many of our users and developers hang out on the [Meshtastic Discord](https://discord.gg/ktMAKGBnBs) server where you may connect with like-minded people.
### How can I contribute to Meshtastic?
@@ -65,7 +44,7 @@ The now-in-beta iOS app requires iOS v15.
### How do I get the Meshtastic iOS App?
-See [iOS App](/docs/software/apple)
+See [iOS App](/docs/category/apple-apps)
### After updating firmware, my node is not connecting via Bluetooth. What should I do?
@@ -119,7 +98,7 @@ Push the left PWR button for about 1 second.
### Where do I purchase the device hardware?
-Each [supported device](/docs/hardware/supported/tbeam) has a "Purchase Link".
+Each [supported device](/docs/hardware/devices/tbeam) has a "Purchase Link".
### I have my hardware. How do I install the firmware and any required drivers?
@@ -226,4 +205,4 @@ A list of available modules is available [here](/docs/settings/moduleconfig).
### I'd like to write a module. How do I get started?
-API documentation for creating modules is available [here](/docs/developers/firmware/module-api).
+API documentation for creating modules is available [here](/docs/development/device/module-api).
diff --git a/docs/about/index.mdx b/docs/about/introduction.mdx
similarity index 63%
rename from docs/about/index.mdx
rename to docs/about/introduction.mdx
index 6ee9c2d3..40fa3002 100644
--- a/docs/about/index.mdx
+++ b/docs/about/introduction.mdx
@@ -1,7 +1,7 @@
---
title: Introduction
-sidebar_label: About
-slug: /about
+sidebar_label: Introduction
+slug: /introduction
sidebar_position: 1
---
@@ -11,28 +11,32 @@ Meshtastic® is a project that enables you to use inexpensive LoRa radios as a l
### Features
-- No phone required for node to node communication.
+- Long range ([_166km record by Puzzled Pancake_](/docs/about/overview/range-test#current-record))
+- No phone required for mesh communication
- Encrypted communication
-- Excellent battery life (LoRa radios have a very low power draw)
-- Send and recieve text messages between members of the mesh
-- Enable optional GPS based location features
+- Excellent battery life
+- Send and receive text messages between members of the mesh
+- Optional GPS based location features
- And more!
## How it works
-The underlying technology, LoRa is a long range radio protocol that is available to most regions without needing certification like HAM operators.
+The underlying technology, LoRa, is a long range radio protocol available to most regions without requiring certification like HAM operators.
The radios automatically rebroadcast messages they receive in order to create a mesh network so that everyone in the group can receive messages - even from the furthest member. Depending on settings used, the Meshtastic mesh can sustain up to 80 device nodes.
Radios can be paired to a single phone so that your friends and family are able to address a message to your specific radio. Each device supports a connection from a single user at a time.
-
+
+
+ Overview
+
+
## Contributors
diff --git a/docs/developers/Firmware/encryption.mdx b/docs/about/overview/encryption.mdx
similarity index 99%
rename from docs/developers/Firmware/encryption.mdx
rename to docs/about/overview/encryption.mdx
index 16a50456..4a75720d 100644
--- a/docs/developers/Firmware/encryption.mdx
+++ b/docs/about/overview/encryption.mdx
@@ -1,7 +1,8 @@
---
id: encryption
-title: Meshtastic encryption
+title: Meshtastic Encryption
sidebar_label: Encryption
+sidebar_position: 2
---
Cryptography is tricky, so we've tried to 'simply' apply standard crypto solutions to our implementation. However, the project developers are not cryptography experts. Therefore we ask two things:
diff --git a/docs/about/overview/index.mdx b/docs/about/overview/index.mdx
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..f72799eb
--- /dev/null
+++ b/docs/about/overview/index.mdx
@@ -0,0 +1,14 @@
+---
+title: Overview
+sidebar_label: Overview
+slug: /overview
+sidebar_position: 2
+---
+
+## How it works
+
+When you send a message on your Meshtastic companion app, it is relayed to the radio using Bluetooth. That message is then broadcast by the radio three times over a certain interval in order to create redundancy for lost packets.
+
+When a receiving radio captures a packet, it checks to see if it has heard that message before. If it has it ignores the message. If it hasn't heard the message, it will rebroadcast it at a certain interval three times.
+
+For each message a radio rebroadcasts, it marks the "hop limit" down by one. When a radio receives a packet with a hop limit of zero, it will not rebroadcast the message.
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/docs/developers/Firmware/mesh-alg.mdx b/docs/about/overview/mesh-alg.mdx
similarity index 63%
rename from docs/developers/Firmware/mesh-alg.mdx
rename to docs/about/overview/mesh-alg.mdx
index 2be5d802..8b89fd9a 100644
--- a/docs/developers/Firmware/mesh-alg.mdx
+++ b/docs/about/overview/mesh-alg.mdx
@@ -1,23 +1,24 @@
---
id: mesh-alg
-title: Mesh broadcast algorithm
-sidebar_label: Mesh algorithm
+title: Mesh Broadcast Algorithm
+sidebar_label: Mesh Algorithm
+sidebar_position: 1
---
## Current Algorithm
-The routing protocol for Meshtastic is really quite simple (and suboptimal). If you want to test its theoretical performance, you can have a look at the [simulator](https://github.com/GUVWAF/Meshtasticator). The protocol is heavily influenced by the mesh routing algorithm used in [RadioHead](https://www.airspayce.com/mikem/arduino/RadioHead) (which was used in very early versions of this project). It has four conceptual layers.
+The routing protocol for Meshtastic is really quite simple (and sub-optimal). If you want to test its theoretical performance, you can have a look at the [simulator](https://github.com/GUVWAF/Meshtasticator). The protocol is heavily influenced by the mesh routing algorithm used in [RadioHead](https://www.airspayce.com/mikem/arduino/RadioHead) (which was used in very early versions of this project). It has four conceptual layers.
### A Note About Protocol Buffers
Because we want our devices to work across various vendors and implementations, we use [Protocol Buffers](https://github.com/meshtastic/protobufs) pervasively. For purposes of this document you mostly only
-need to consider the MeshPacket and Subpacket message types.
+need to consider the MeshPacket and Sub-packet message types.
### Layer 0: LoRa Radio
All data is converted into LoRa symbols which are sent to the radio for transmission. The details are described elsewhere, but it is worth noting that in addition to the converted packet bytes described below, there is also a preamble sent at the start of any data packet.
-This preamble allows receiving radios to synchronize clocks and start framing. We use a preable length of 32, which is longer than the minimum preamble length of 8, to maximize the amount of time the LoRa receivers can stay asleep, which dramatically lowers power consumption.
+This preamble allows receiving radios to synchronize clocks and start framing. We use a preamble length of 32, which is longer than the minimum preamble length of 8, to maximize the amount of time the LoRa receivers can stay asleep, which dramatically lowers power consumption.
### Layer 1: Unreliable Zero Hop Messaging
@@ -45,15 +46,15 @@ This layer is conventional non-reliable LoRa packet transmission. The transmitte
- **Packet Header:** is described directly by the `PacketHeader` class in the C++ source code. But indirectly it matches the first portion of the `MeshPacket` protobuf definition. Note that the packet header is not encoded using a protobuf, but is sent as raw bytes. This both saves airtime and allows receiving radio hardware to optionally filter packets before waking the main CPU.
-- **Packet Header - NodeIDs:** are constructed from the bottom four bytes of the MAC address of the Bluetooth address. Because the OUI is assigned by the IEEE, and we currently only support a few CPU manufacturers, the upper byte is defacto guaranteed unique for each vendor. The bottom 3 bytes are guaranteed unique by that vendor.
+- **Packet Header - NodeIDs:** are constructed from the bottom four bytes of the MAC address of the Bluetooth address. Because the OUI is assigned by the IEEE, and we currently only support a few CPU manufacturers, the upper byte is de-facto guaranteed unique for each vendor. The bottom 3 bytes are guaranteed unique by that vendor.
- **Packet Header - Unique ID:** The ID is a large, 32 bit ID to ensure there is enough unique state to protect an encrypted payload from attack.
-- **Payload:** An encrypted and packed protobuf encoding of the SubPacket protobuf. Only the SubPacket is encrypted, while headers are not. This allows the option of eventually allowing nodes to route packets without knowing anything about the encrypted payload. For more information, see the [encryption](/docs/developers/firmware/encryption) and [protobufs](/docs/developers/protobufs/api) documentation. Any data past the maximum length is truncated.
+- **Payload:** An encrypted and packed protobuf encoding of the SubPacket protobuf. Only the SubPacket is encrypted, while headers are not. This allows the option of eventually allowing nodes to route packets without knowing anything about the encrypted payload. For more information, see the [encryption](/docs/about/overview/encryption) and [protobufs](/docs/developers/protobufs/api) documentation. Any data past the maximum length is truncated.
#### Carrier-Sense Multiple Access with Collision Avoidance (CSMA/CA)
-Meshtastic adopts CSMA/CA, similar as to what is used in Wi-Fi. This means that all transmitters must perform Channel Activity Detection (CAD) before attempting to transmit. If the channel is considered busy, the node will wait until it is not anymore. Since once the channel becomes idle multiple nodes might want to start transmitting, a node has to wait a random multiple of slot times. The slot time is the time needed to reliably perform CAD. The amount of slot times to wait is randomly picked from a contention window (CW), which size depends on the current channel utilization. The contention window is larger for a higher channel utilization, in order to limit the chance of collisions.
+Meshtastic adopts CSMA/CA, similar as to what is used in WiFi. This means that all transmitters must perform Channel Activity Detection (CAD) before attempting to transmit. If the channel is considered busy, the node will wait until it is not anymore. Since once the channel becomes idle multiple nodes might want to start transmitting, a node has to wait a random multiple of slot times. The slot time is the time needed to reliably perform CAD. The amount of slot times to wait is randomly picked from a contention window (CW), which size depends on the current channel utilization. The contention window is larger for a higher channel utilization, in order to limit the chance of collisions.
### Layer 2: Reliable Zero Hop Messaging
@@ -64,15 +65,15 @@ The default messaging provided by Layer 1 is extended by setting the `WantAck` f
> This packet is being sent as a reliable message, we would prefer it to arrive at the destination. We would like to receive an ACK packet in response.
>
> Broadcast messages treat this flag specially: Since ACKs for broadcasts would rapidly flood the channel, the normal ACK behavior is suppressed. Instead, the original sender listens to see if at least one node is rebroadcasting this
-> packet (because naive flooding algorithm). If it hears that, the odds (given typical LoRa topologies) are very high that every node should eventually receive the message. So FloodingRouter.cpp generates an implicit ACK which is delivered to the original sender. If after some time we don't hear anyone rebroadcast our packet, we will timeout and retransmit, using the regular resend logic.
+> packet (because naive flooding algorithm). If it hears that, the odds (given typical LoRa topology) are very high that every node should eventually receive the message. So FloodingRouter.cpp generates an implicit ACK which is delivered to the original sender. If after some time we don't hear anyone rebroadcast our packet, we will timeout and re-transmit, using the regular resend logic.
-If a transmitting node does not receive an ACK (or NAK) packet after a certain expiration time, it will use Layer 1 to attempt a retransmission of the sent packet. A reliable packet (at this 'zero hop' level) will be resent a maximum of three times. If no ACK or NAK has been received by then the local node will internally generate a NAK (either for local consumption or use by higher layers of the protocol). The retransmission expiration time is based on the maximum time it would take to receive an (implicit) ACK, taking the airtime of the sent packet and any processing delay into account.
+If a transmitting node does not receive an ACK (or NAK) packet after a certain expiration time, it will use Layer 1 to attempt a re-transmission of the sent packet. A reliable packet (at this 'zero hop' level) will be resent a maximum of three times. If no ACK or NAK has been received by then the local node will internally generate a NAK (either for local consumption or use by higher layers of the protocol). The re-transmission expiration time is based on the maximum time it would take to receive an (implicit) ACK, taking the airtime of the sent packet and any processing delay into account.
### Layer 3: (Naive) Flooding for Multi-Hop Messaging
-Given our use-case for the initial release, most of our protocol is built around [flooding](). The implementation is currently 'naive' and doesn't try to optimize flooding, except by abandoning retransmission once a node has seen a nearby receiver ACK the packet it's trying to flood. This means that up to N retransmissions of a packet could occur in an N node mesh.
+Given our use-case for the initial release, most of our protocol is built around [flooding](). The implementation is currently 'naive' and doesn't try to optimize flooding, except by abandoning re-transmission once a node has seen a nearby receiver ACK the packet it's trying to flood. This means that up to N re-transmissions of a packet could occur in an N node mesh.
-If any mesh node sees a packet with a HopLimit other than zero, it will decrement that HopLimit and attempt retransmission on behalf of the original sending node. In order to promote letting nodes that are further away flood the message, such that the message eventually reaches farther, the contention window (see Layer 1) for a flooding message depends on the Signal-to-Noise Ratio (SNR) of the received packet. The CW size is small for a low SNR, such that nodes that are further away are more likely to flood first and closer nodes that hear this will refrain from flooding.
+If any mesh node sees a packet with a HopLimit other than zero, it will decrement that HopLimit and attempt re-transmission on behalf of the original sending node. In order to promote letting nodes that are further away flood the message, such that the message eventually reaches farther, the contention window (see Layer 1) for a flooding message depends on the Signal-to-Noise Ratio (SNR) of the received packet. The CW size is small for a low SNR, such that nodes that are further away are more likely to flood first and closer nodes that hear this will refrain from flooding.
### Example
diff --git a/docs/developers/Firmware/radio-settings.mdx b/docs/about/overview/radio-settings.mdx
similarity index 98%
rename from docs/developers/Firmware/radio-settings.mdx
rename to docs/about/overview/radio-settings.mdx
index 7f32d71d..154c71a2 100644
--- a/docs/developers/Firmware/radio-settings.mdx
+++ b/docs/about/overview/radio-settings.mdx
@@ -2,10 +2,11 @@
id: radio-settings
title: Radio Settings
sidebar_label: Radio Settings
+sidebar_position: 3
---
We use the same channel maps as LoRaWAN (though this is not LoRaWAN).
-(Note, not the same channel map as TTN for US frequences.)
+(Note, not the same channel map as TTN for US frequencies.)

@@ -69,7 +70,7 @@ We have six predefined channels. These are the most common settings and have bee
| Long Range / Slow | Long Slow | 0.18 kbps | 12 / 4096 | 4/8 | 125 | 154dB |
| Very Long Range - Slow | Very Long Slow | 0.05 kbps | 12 / 4096 | 4/8 | 31.25 | 160.1dB |
-Note: The link budget used by these calculations assumes a transmit power of 17dBm and an antenna with 0dB gain. Adjust your link budget assumptions based on your actual devices. Data-rate in this table is actual measured but doesn't count mesh overhead, hops and retransmissions.
+Note: The link budget used by these calculations assumes a transmit power of 17dBm and an antenna with 0dB gain. Adjust your link budget assumptions based on your actual devices. Data-rate in this table is actual measured but doesn't count mesh overhead, hops and re-transmissions.
### Custom Settings
diff --git a/docs/about/overview/range-test.mdx b/docs/about/overview/range-test.mdx
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..bacdb967
--- /dev/null
+++ b/docs/about/overview/range-test.mdx
@@ -0,0 +1,25 @@
+---
+title: Range Tests
+sidebar_label: Range Tests
+sidebar_position: 1
+---
+
+## Current Record
+
+- **Range:** 166km (103 miles)
+- **Record Holder:** _Puzzled Pancake_
+- **Firmware Version:** 1.2
+- **Frequency:** 868MHz
+- **Bandwidth:** 125
+- **Spread Factor:** 12
+- **Coding Rate:** 4/8
+- **Device A:** [LILYGO TTGO T-Beam w/ SX1262](/docs/hardware/devices/tbeam)
+ - **Antenna:** Omnidirectional
+- **Device B:** [LILYGO TTGO T-Beam w/ SX1262](/docs/hardware/devices/tbeam)
+ - **Antenna:** Omnidirectional
+
+
+
+
+
+
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/docs/blocks/_lora-regions.mdx b/docs/blocks/_lora-regions.mdx
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..cc38a110
--- /dev/null
+++ b/docs/blocks/_lora-regions.mdx
@@ -0,0 +1,15 @@
+| Region Code | Description |
+| :-------: | :--------: |
+| `UNSET` | Unset |
+| `US` | United States |
+| `EU_433` | European Union 433MHz |
+| `EU_868` | European Union 868MHz |
+| `CN` | China |
+| `JP` | Japan |
+| `ANZ` | Australia & New Zealand |
+| `KR` | Korea |
+| `TW` | Taiwan |
+| `RU` | Russia |
+| `IN` | India |
+| `NZ_865` | New Zealand 865MHz |
+| `TH` | Thailand |
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/docs/configuration/_category_.yml b/docs/configuration/_category_.yml
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..d86396a5
--- /dev/null
+++ b/docs/configuration/_category_.yml
@@ -0,0 +1,7 @@
+label: Configuration
+collapsible: true
+position: 4
+link:
+ type: generated-index
+ title: Configuration
+ slug: /settings
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/docs/settings/config/bluetooth.mdx b/docs/configuration/device-config/bluetooth.mdx
similarity index 85%
rename from docs/settings/config/bluetooth.mdx
rename to docs/configuration/device-config/bluetooth.mdx
index d2136f29..3ff89fad 100644
--- a/docs/settings/config/bluetooth.mdx
+++ b/docs/configuration/device-config/bluetooth.mdx
@@ -1,19 +1,20 @@
---
id: bluetooth
title: Bluetooth Settings
+slug: /settings/config/bluetooth
sidebar_label: Bluetooth
---
import Tabs from '@theme/Tabs';
import TabItem from '@theme/TabItem';
-The bluetooth config options are: Enabled, Pairing Mode and Fixed PIN Value. Bluetooth config uses an admin message sending a `Config.Bluetooth` protobuf.
+The Bluetooth config options are: Enabled, Pairing Mode and Fixed PIN Value. Bluetooth config uses an admin message sending a `Config.Bluetooth` protobuf.
## Bluetooth Config Values
### Enabled
-Enables bluetooth
+Enables Bluetooth
### Pairing Mode
@@ -49,13 +50,13 @@ Bluetooth module config is not available for Android.
:::info
-All bluetooth config values are available on iOS, iPadOS and macOS at Settings > Radio Configuration > Position.
+All Bluetooth config values are available on iOS, iPadOS and macOS at Settings > Radio Configuration > Position.
:::
-All bluetooth module config options are available in the python CLI. Example commands are below:
+All Bluetooth module config options are available in the python CLI. Example commands are below:
| Setting | Acceptable Values | Default |
| :-----------------------: | :-----------------: | :-----: |
@@ -76,7 +77,7 @@ meshtastic --set bluetooth.fixed_pin 111111
:::info
-All bluetooth module config options are available for the Web UI.
+All Bluetooth module config options are available for the Web UI.
:::
diff --git a/docs/settings/config/channels.mdx b/docs/configuration/device-config/channels.mdx
similarity index 94%
rename from docs/settings/config/channels.mdx
rename to docs/configuration/device-config/channels.mdx
index 5875c3be..50084432 100644
--- a/docs/settings/config/channels.mdx
+++ b/docs/configuration/device-config/channels.mdx
@@ -1,6 +1,7 @@
---
id: channels
title: Channel Configuration
+slug: /settings/config/channels
sidebar_label: Channels
---
@@ -37,7 +38,7 @@ _Indexing_ can not be modified.
| 7 | 8 | `DISABLED` | User defined |
:::note
-You can **not** have `DISABLED` channels inbetween active channels such as `PRIMARY` and `SECONDARY`. Active channels must be consecutive.
+You can **not** have `DISABLED` channels in-between active channels such as `PRIMARY` and `SECONDARY`. Active channels must be consecutive.
:::
### Role
@@ -49,14 +50,14 @@ Each channel is assigned one of 3 roles:
- Only one primary channel can exist and can not be disabled.
- Direct messages are only available on this channel.
2. `SECONDARY` or `2`
- - Can modify the encryption key (psk).
+ - Can modify the encryption key (PSK).
3. `DISABLED` or `0`
- The channel is no longer available for use.
- The channel settings are set to default.
## Channel Settings Values
-The Channel Settings options are: ID, Name, PSK, Downlink Enabled, and Uplink Enabled. Channel settings are embeded in the `Channel` protobuf as a `ChannelSettings` protobuf and sent as an admin message.
+The Channel Settings options are: ID, Name, PSK, Downlink Enabled, and Uplink Enabled. Channel settings are embedded in the `Channel` protobuf as a `ChannelSettings` protobuf and sent as an admin message.
:::note
The full globally unique ID will be constructed from the Name and ID (`.`) where ID is base36 encoded. Assuming that the number of Meshtastic users is below 20K (true for a long time) the chance of this 64 bit random number colliding with anyone else is super low. The penalty for collision is low as well.
diff --git a/docs/settings/config/device.mdx b/docs/configuration/device-config/device.mdx
similarity index 98%
rename from docs/settings/config/device.mdx
rename to docs/configuration/device-config/device.mdx
index cdb63e9c..1c0316af 100644
--- a/docs/settings/config/device.mdx
+++ b/docs/configuration/device-config/device.mdx
@@ -1,6 +1,7 @@
---
id: device
title: Device Configuration
+slug: /settings/config/device
sidebar_label: Device
---
diff --git a/docs/settings/config/display.mdx b/docs/configuration/device-config/display.mdx
similarity index 98%
rename from docs/settings/config/display.mdx
rename to docs/configuration/device-config/display.mdx
index 28a90520..06dbec3c 100644
--- a/docs/settings/config/display.mdx
+++ b/docs/configuration/device-config/display.mdx
@@ -1,6 +1,7 @@
---
id: display
title: Display Configuration
+slug: /settings/config/display
sidebar_label: Display
---
diff --git a/docs/configuration/device-config/index.mdx b/docs/configuration/device-config/index.mdx
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..44c19e32
--- /dev/null
+++ b/docs/configuration/device-config/index.mdx
@@ -0,0 +1,21 @@
+---
+id: config
+title: Device Configuration
+sidebar_label: Device Config
+slug: /settings/config
+sidebar_position: 1
+---
+
+There are several config sections in the Meshtastic firmware, these are broken out so they can be sent as small admin messages over the mesh.
+
+| Name | Description |
+|:----:|:-----------:|
+| [Bluetooth](/docs/settings/config/bluetooth) | Bluetooth config options are: Enabled, Pairing Mode and Fixed PIN. |
+| [Channels](/docs/settings/config/channels) | Channels config options are: Index, Role and Settings. |
+| [Device](/docs/settings/config/device) | Device config options are: Device Role, Serial Output, Debug Log and Factory Reset. |
+| [Display](/docs/settings/config/display) | Display config options are: Screen On Duration, Auto Carousel Interval, Always Point North, and GPS Format. |
+| [LoRa](/docs/settings/config/lora) | The LoRa config options are: Region, Modem Preset, Max Hops, Transmit Power, Bandwidth, Spread Factor, Coding Rate, Frequency Offset, Transmit Disabled and Ignore Incoming Array. |
+| [Network](/docs/settings/config/network) | Network config options are: WiFi Enabled, WiFi SSID, WiFi PSK, WiFi Mode and NTP Server. |
+| [Position](/docs/settings/config/position) | Position config options are: GPS Enabled, GPS Update Interval, GPS Attempt Time, Fixed Position, Smart Broadcast, Broadcast Interval and Position Packet Flags. |
+| [Power](/docs/settings/config/power) | Power config options are: Charge Current, Power Saving, Shutdown after losing power, ADC Multiplier Override Wait Bluetooth Interval, Mesh Super Deep Sleep Timeout, Super Deep Sleep Interval, Light Sleep Interval and Minimum Wake Interval. |
+| [User](/docs/settings/config/user) | The user config options are: Long Name, Short Name, and Is Licensed |
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/docs/settings/config/lora.mdx b/docs/configuration/device-config/lora.mdx
similarity index 81%
rename from docs/settings/config/lora.mdx
rename to docs/configuration/device-config/lora.mdx
index f3634907..c222f028 100644
--- a/docs/settings/config/lora.mdx
+++ b/docs/configuration/device-config/lora.mdx
@@ -1,11 +1,13 @@
---
id: lora
title: LoRa Configuration
+slug: /settings/config/lora
sidebar_label: LoRa
---
import Tabs from '@theme/Tabs';
import TabItem from '@theme/TabItem';
+import LoRaRegions from '../../blocks/_lora-regions.mdx';
The LoRa config options are: Region, Modem Preset, Max Hops, Transmit Power, Bandwidth, Spread Factor, Coding Rate, Frequency Offset, Transmit Enabled and Ignore Incoming Array. LoRa config uses an admin message sending a `Config.LoRa` protobuf.
@@ -18,22 +20,7 @@ You must set your device's `lora.region` setting. This will ensure that you are
### Region
Sets the region for your node. Default is `unset`.
-| Region Code | Description |
-| :-------: | :---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------: |
-| `UNSET` | Unset |
-| `US` | United States |
-| `EU_433` | European Union 433MHz |
-| `EU_868` | European Union 868MHz |
-| `CN` | China |
-| `JP` | Japan |
-| `ANZ` | Australia & New Zealand |
-| `KR` | Korea |
-| `TW` | Taiwan |
-| `RU` | Russia |
-| `IN` | India |
-| `NZ_865` | New Zealand 865MHz |
-| `TH` | Thailand |
-
+
### Modem Preset
@@ -114,14 +101,14 @@ LoRa config commands are available in the python CLI. Example commands are below
:::info
-No lora config options are available in the Flasher.
+No LoRa config options are available in the Flasher.
:::
:::info
-All lora config options are available in the Web UI.
+All LoRa config options are available in the Web UI.
:::
diff --git a/docs/settings/config/network.mdx b/docs/configuration/device-config/network.mdx
similarity index 97%
rename from docs/settings/config/network.mdx
rename to docs/configuration/device-config/network.mdx
index b6065377..fc6e8ad7 100644
--- a/docs/settings/config/network.mdx
+++ b/docs/configuration/device-config/network.mdx
@@ -1,6 +1,7 @@
---
id: network
title: Network Configuration
+slug: /settings/config/network
sidebar_label: Network
---
@@ -10,7 +11,7 @@ import TabItem from '@theme/TabItem';
The Network config options are: WiFi Enabled, WiFi SSID, WiFi PSK, and NTP Server. Network config uses an admin message sending a `Config.Network` protobuf.
:::info
-Enabling WiFi will disable bluetooth. Only one connection method will work at a time.
+Enabling WiFi will disable Bluetooth. Only one connection method will work at a time.
:::
ESP32 devices have the ability to connect to WiFi as a client. SoftAP mode is not supported by the Meshtastic firmware.
diff --git a/docs/settings/config/position.mdx b/docs/configuration/device-config/position.mdx
similarity index 99%
rename from docs/settings/config/position.mdx
rename to docs/configuration/device-config/position.mdx
index 0161be7e..1f474cb5 100644
--- a/docs/settings/config/position.mdx
+++ b/docs/configuration/device-config/position.mdx
@@ -1,6 +1,7 @@
---
id: position
title: Position Configuration
+slug: /settings/config/position
sidebar_label: Position
---
diff --git a/docs/settings/config/power.mdx b/docs/configuration/device-config/power.mdx
similarity index 99%
rename from docs/settings/config/power.mdx
rename to docs/configuration/device-config/power.mdx
index cba3a6c1..9ec89042 100644
--- a/docs/settings/config/power.mdx
+++ b/docs/configuration/device-config/power.mdx
@@ -1,6 +1,7 @@
---
id: power
title: Power Configuration
+slug: /settings/config/power
sidebar_label: Power
---
diff --git a/docs/settings/config/user.mdx b/docs/configuration/device-config/user.mdx
similarity index 97%
rename from docs/settings/config/user.mdx
rename to docs/configuration/device-config/user.mdx
index 4dd9757a..a80ec458 100644
--- a/docs/settings/config/user.mdx
+++ b/docs/configuration/device-config/user.mdx
@@ -1,6 +1,7 @@
---
id: user
title: User Configuration
+slug: /settings/config/user
sidebar_label: User
---
@@ -13,7 +14,7 @@ The user config options are: Long Name, Short Name, and Is Licensed. User config
### Long Name
-A personalised name for your device.
+A personalized name for your device.
Auto-generated by default.
@@ -81,7 +82,6 @@ meshtastic --set-owner-short 'NODE'
meshtastic --set-ham 'CALLSIGN'
```
-
diff --git a/docs/settings/moduleconfig/canned-message.mdx b/docs/configuration/module-config/canned-message.mdx
similarity index 98%
rename from docs/settings/moduleconfig/canned-message.mdx
rename to docs/configuration/module-config/canned-message.mdx
index 870c3f67..13d47292 100644
--- a/docs/settings/moduleconfig/canned-message.mdx
+++ b/docs/configuration/module-config/canned-message.mdx
@@ -1,6 +1,7 @@
---
id: canned-message
title: Canned Message Module Configuration
+slug: /settings/moduleconfig/canned-message
sidebar_label: Canned Message
---
@@ -61,11 +62,11 @@ GPIO Pin Value (1-39) For encoder Press port
### Input Broker Event Clockwise
-Generate the rotary cloockwise event.
+Generate the rotary clockwise event.
### Input Broker Event Counter Clockwise
-Generate the rotary counter cloockwise event.
+Generate the rotary counter clockwise event.
### Input Broker Event Press
diff --git a/docs/settings/moduleconfig/external-notification.mdx b/docs/configuration/module-config/external-notification.mdx
similarity index 91%
rename from docs/settings/moduleconfig/external-notification.mdx
rename to docs/configuration/module-config/external-notification.mdx
index 259076cd..63c01f73 100644
--- a/docs/settings/moduleconfig/external-notification.mdx
+++ b/docs/configuration/module-config/external-notification.mdx
@@ -1,6 +1,7 @@
---
id: external-notification
title: External Notification Module Configuration
+slug: /settings/moduleconfig/external-notification
sidebar_label: External Notification
---
@@ -32,7 +33,7 @@ Specifies whether the external circuit is triggered when the device's GPIO is lo
Specifies the GPIO that your external circuit is attached to on the device.
:::info
-on ESP32 based boards, GPIOs 34 to 39 are GPIs – input only pins. These pins don’t have internal pull-up or pull-down resistors. They can’t be used as outputs, so you can NOT use these pins as outputs.
+On ESP32 based boards, GPIOs 34 to 39 are GPIs – input only pins. These pins do not have internal pull-up or pull-down resistors. They can not be used as outputs, so you can NOT use these pins as outputs.
:::
### How long monitored GPIO is triggered
@@ -69,7 +70,7 @@ All external notification module config options are available on iOS, iPadOS and
-All external noftification module config options are available in the python CLI. Example commands are below:
+All external notification module config options are available in the python CLI. Example commands are below:
| Setting | Acceptable Values | Default |
| :----------------------------: | :----------------------: | :-----: |
@@ -90,7 +91,7 @@ meshtastic --set external_notification.alert_bell true
meshtastic --set external_notification.alert_bell false
```
-```shell title="Set GPIO active high / low (defalut of false is low)"
+```shell title="Set GPIO active high / low (default of false is low)"
meshtastic --set external_notification.active false
meshtastic --set external_notification.active true
```
diff --git a/docs/configuration/module-config/index.mdx b/docs/configuration/module-config/index.mdx
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..d7b575db
--- /dev/null
+++ b/docs/configuration/module-config/index.mdx
@@ -0,0 +1,18 @@
+---
+id: module-config
+title: Module Configuration
+sidebar_label: Module Config
+slug: /settings/moduleconfig
+sidebar_position: 3
+---
+
+Modules are included in the firmware and allow users to extend the functionality of their mesh or device.
+
+| Name | Description |
+|:----:|:-----------:|
+| [Canned Message](/docs/settings/moduleconfig/canned-message) | Set a number of predefined messages to send out directly from the device with the use of an input device like a rotary encoder. |
+| [External Notification](/docs/settings/moduleconfig/external-notification) | Incoming messages are able to alert you using circuits you attach to the device (LEDs, Buzzers, etc) |
+| [MQTT](/docs/settings/moduleconfig/mqtt) | Forward packets along to an MQTT server. This allows users on the local mesh to communicate with users on another mesh over the internet. |
+| [Range Test](/docs/settings/moduleconfig/range-test) | Send messages with GPS location at an interval to test the distance your devices can communicate. Requires (at least) one device set up as a sender and one as a receiver. The receiver(s) will log all incoming messages to a CSV. |
+| [Serial Module](/docs/settings/moduleconfig/serial) | Send messages across the mesh by sending strings over a serial port. |
+| [Telemetry](/docs/settings/moduleconfig/telemetry) | Attach sensors to the device and transmit readings on a regular interval to the mesh. |
diff --git a/docs/settings/moduleconfig/mqtt.mdx b/docs/configuration/module-config/mqtt.mdx
similarity index 80%
rename from docs/settings/moduleconfig/mqtt.mdx
rename to docs/configuration/module-config/mqtt.mdx
index 5606b537..cfbf9ba4 100644
--- a/docs/settings/moduleconfig/mqtt.mdx
+++ b/docs/configuration/module-config/mqtt.mdx
@@ -1,6 +1,7 @@
---
id: mqtt
title: MQTT Module Configuration
+slug: /settings/moduleconfig/mqtt
sidebar_label: MQTT
---
@@ -25,15 +26,15 @@ The server to use for MQTT. If not set, the default server public will be used.
### Username
-MQTT Server username to use (most useful for a custom MQTT server). If using a custom server, this will be honoured even if empty. If using the default public server, this will only be honoured if set, otherwise the device will use the default username.
+MQTT Server username to use (most useful for a custom MQTT server). If using a custom server, this will be honored even if empty. If using the default public server, this will only be honored if set, otherwise the device will use the default username.
### Password
-MQTT password to use (most useful for a custom MQTT server). If using a custom server, this will be honoured even if empty. If using the default server, this will only be honoured if set, otherwise the device will use the default password
+MQTT password to use (most useful for a custom MQTT server). If using a custom server, this will be honored even if empty. If using the default server, this will only be honored if set, otherwise the device will use the default password
### Encryption Enabled
-Whether to send encrypted or decrypted packets to MQTT. This parameter is only honoured if you also set server (the default official mqtt.meshtastic.org server can handle encrypted packets) Decrypted packets may be useful for external systems that want to consume meshtastic packets.
+Whether to send encrypted or decrypted packets to MQTT. This parameter is only honored if you also set server (the default official mqtt.meshtastic.org server can handle encrypted packets) Decrypted packets may be useful for external systems that want to consume meshtastic packets.
### JSON Enabled
diff --git a/docs/settings/moduleconfig/range-test.mdx b/docs/configuration/module-config/range-test.mdx
similarity index 99%
rename from docs/settings/moduleconfig/range-test.mdx
rename to docs/configuration/module-config/range-test.mdx
index c9d2145e..f2d1b117 100644
--- a/docs/settings/moduleconfig/range-test.mdx
+++ b/docs/configuration/module-config/range-test.mdx
@@ -1,6 +1,7 @@
---
id: range-test
title: Range Test Module Configuration
+slug: /settings/moduleconfig/range-test
sidebar_label: Range Test
---
diff --git a/docs/settings/moduleconfig/serial.mdx b/docs/configuration/module-config/serial.mdx
similarity index 99%
rename from docs/settings/moduleconfig/serial.mdx
rename to docs/configuration/module-config/serial.mdx
index c6f99e8d..97d73831 100644
--- a/docs/settings/moduleconfig/serial.mdx
+++ b/docs/configuration/module-config/serial.mdx
@@ -1,6 +1,7 @@
---
id: serial
title: Serial Module Configuration
+slug: /settings/moduleconfig/serial
sidebar_label: Serial
---
diff --git a/docs/settings/moduleconfig/telemetry.mdx b/docs/configuration/module-config/telemetry.mdx
similarity index 91%
rename from docs/settings/moduleconfig/telemetry.mdx
rename to docs/configuration/module-config/telemetry.mdx
index d888a006..4ce8aa84 100644
--- a/docs/settings/moduleconfig/telemetry.mdx
+++ b/docs/configuration/module-config/telemetry.mdx
@@ -1,17 +1,18 @@
---
id: telemetry
title: Telemetry Module Configuration
+slug: /settings/moduleconfig/telemetry
sidebar_label: Telemetry
---
import Tabs from '@theme/Tabs';
import TabItem from '@theme/TabItem';
-The Telemetry Module provides two types of data over the mesh. Device metrics (Battery Level, Voltage, Channel Utilization and Airtime) from your meshtastic device and Environement Metrics from attached I2C sensors.
+The Telemetry Module provides two types of data over the mesh. Device metrics (Battery Level, Voltage, Channel Utilization and Airtime) from your meshtastic device and Environment Metrics from attached I2C sensors.
-Supported sensors connected to the I2C bus of the device will be automattically detected at startup. Environement Telemetry must be enabled for them to be instrumented and their readings sent over the mesh.
+Supported sensors connected to the I2C bus of the device will be automatically detected at startup. Environment Telemetry must be enabled for them to be instrumented and their readings sent over the mesh.
-The telemetry module config options are: Device Metrics Update Interval, Environment Metrics Update Interval, Environement Telemetry Enabled, Show on Device Screen, and Display Fahrenheit.
+The telemetry module config options are: Device Metrics Update Interval, Environment Metrics Update Interval, Environment Telemetry Enabled, Show on Device Screen, and Display Fahrenheit.
### Currently Supported Sensor Types
@@ -178,7 +179,7 @@ And examine the serial logs for Telemetry diagnostic information.
### Environment Metrics
-The environment metrics in the telemetry module supports a limited amount of fields as they are stored in memory on the device. Support for sensors that provide one or more of the following fields can potentially be added to the main firmare provided there is a GPL licensed library for us to include to support it, and the libary size is not prohibitive.
+The environment metrics in the telemetry module supports a limited amount of fields as they are stored in memory on the device. Support for sensors that provide one or more of the following fields can potentially be added to the main firmware provided there is a GPL licensed library for us to include to support it, and the library size is not prohibitive.
* Temperature
* Relative Humidity
diff --git a/docs/software/device/remote-admin.mdx b/docs/configuration/remote-admin.mdx
similarity index 98%
rename from docs/software/device/remote-admin.mdx
rename to docs/configuration/remote-admin.mdx
index afd33a58..9df67777 100644
--- a/docs/software/device/remote-admin.mdx
+++ b/docs/configuration/remote-admin.mdx
@@ -1,7 +1,7 @@
---
-id: device-remote-admin
-title: Remote node administration
-sidebar_label: Remote node administration
+id: remote-admin
+title: Remote Node Administration
+sidebar_label: Remote Nodes
---
This feature will allow you to use the multiple channels feature to enable remote administration of Meshtastic nodes. This will let you talk through the mesh to some far away node and change that node's settings. This is an advanced feature that (currently) few users would need. Also, keep in mind it is possible (if you are not careful) to assign settings to that remote node that cause it to completely drop off of your mesh. We advise network admins have a test node to test settings with before applying changes to a remote node to prevent this.
diff --git a/docs/developers/Firmware/documents.mdx b/docs/developers/Firmware/documents.mdx
deleted file mode 100644
index 660e83b0..00000000
--- a/docs/developers/Firmware/documents.mdx
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,9 +0,0 @@
----
-id: documents
-title: Useful Documents
-sidebar_label: Useful Documents
----
-
-## LoRa
-
-[LoRa Design Guide](/documents/LoRa_Design_Guide.pdf)
diff --git a/docs/developers/_category_.yml b/docs/developers/_category_.yml
deleted file mode 100644
index d4feb728..00000000
--- a/docs/developers/_category_.yml
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,8 +0,0 @@
-
-position: 6 # float position is supported
-label: 'Developers'
-collapsible: true # make the category collapsible
-link:
- type: generated-index
- title: Developers
- slug: /developers
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/docs/developers/android/_category_.yml b/docs/developers/android/_category_.yml
deleted file mode 100644
index eae5f472..00000000
--- a/docs/developers/android/_category_.yml
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,7 +0,0 @@
-
-position: 3 # float position is supported
-label: 'Android'
-collapsible: true # make the category collapsible
-link:
- type: generated-index
- title: Android
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/docs/developers/api.mdx b/docs/developers/api.mdx
deleted file mode 100644
index eeba902c..00000000
--- a/docs/developers/api.mdx
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,36 +0,0 @@
----
-id: api
-title: APIs
-sidebar_label: APIs
----
-
-## General
-
-:::note
-
-Currently there are three methods of interfacing with devices: `HTTP`, `BLE`, and `Serial`.
-
-Whilst each method has it's own ways sending and receiving data, the underlying protobuf transport medium remains the same.
-:::
-
-## HTTP
-
-### Endpoints
-
-#### `PUT` /api/v1/toradio
-
-#### `GET` /api/v1/fromradio&all=`boolean`
-
-## BLE
-
-:::important
-UUID for the service: `6ba1b218-15a8-461f-9fa8-5dcae273eafd`
-:::
-
-## Serial
-
-:::important
-
-You can communicate with devices with a baud rate of `921600`bps
-
-:::
diff --git a/docs/developers/documentation/docusaurus.mdx b/docs/developers/documentation/docusaurus.mdx
deleted file mode 100644
index f41d3e4d..00000000
--- a/docs/developers/documentation/docusaurus.mdx
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,13 +0,0 @@
----
-id: docusaurus
-title: Docusaurus
-sidebar_label: Docusaurus
----
-
-## Overview
-
-Meshtastic's documentation is set up using [Docusaurus](https://docusaurus.io). It is highly encouraged to look at [their documentation](https://docusaurus.io/docs) when looking for a solution to a problem with our docs. They most likely have thought of the use case you've discovered.
-
-## Known Issues
-
-- Admonitions within a `TabItem` component need to be completely unindented to show up correctly.
diff --git a/docs/developers/documentation/github.mdx b/docs/developers/documentation/github.mdx
deleted file mode 100644
index dc56777e..00000000
--- a/docs/developers/documentation/github.mdx
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,14 +0,0 @@
----
-id: github
-title: GitHub
-sidebar_label: GitHub
----
-
-## Overview
-
-All of Meshtastic's code and documentation is hosted on GitHub. If you would like to contribute to the project, having a GitHub account is an important step to doing so.
-
-## Set up GitHub account
-
-- Go to [github.com](https://github.com)
-- Click `Sign Up`
diff --git a/docs/developers/documentation/vercel.mdx b/docs/developers/documentation/vercel.mdx
deleted file mode 100644
index a0e3c3f9..00000000
--- a/docs/developers/documentation/vercel.mdx
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,37 +0,0 @@
----
-id: vercel
-title: Vercel
-sidebar_label: Vercel
----
-
-## Overview
-
-Setting up a Vercel account is an optional step that can help you view your changes to the documentation in a server environment just like the actual docs. This can be helpful to include when submitting a pull request so that developers can review your changes and visually check that things look correct.
-
-## Set up Vercel account
-
-- Go to [vercel.com](https://vercel.com)
-- Login with your GitHub account, click `Continue with GitHub`
-
-## Link your fork of the project
-
-- Click `New Project`
-- Under `Import Git Repository` select `+ Add GitHub Account`
- You'll be redirected to GitHub to allow access to select repositories.
-- Select your fork of the project: `username/Meshtastic`
-
-## Configure project
-
-Configure project:
-
-- Set a name for the project
-- Select a framework preset: `Docusaurus 2`
-- Click `Deploy`
-
-That's it! You should now see your project with a green or orange status dot showing that your fork of the project has been compiled. There will be a commit-specific url that you can share to view your changes. There also will be a branch-specific url that you can view. If there are any errors it will show up red and include the logs for you to figure out what has gone wrong.
-
-:::tip
-There is a limited number of branch urls that you will be able to view. If you notice that option has disappeared, you can delete unused branches on your fork and that will enable that feature again.
-
-Branch urls are helpful in PRs because they will remain constant, and you won't need to resubmit a new url for review each new commit if changes are requested.
-:::
diff --git a/docs/development/_category_.yml b/docs/development/_category_.yml
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..ef7b07c9
--- /dev/null
+++ b/docs/development/_category_.yml
@@ -0,0 +1,7 @@
+label: Development
+collapsible: true
+position: 7
+link:
+ type: generated-index
+ title: Developers
+ slug: /developers
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/docs/developers/android/build.mdx b/docs/development/android.mdx
similarity index 73%
rename from docs/developers/android/build.mdx
rename to docs/development/android.mdx
index e735268a..f6e31bf2 100644
--- a/docs/developers/android/build.mdx
+++ b/docs/development/android.mdx
@@ -1,7 +1,8 @@
---
-id: build-app
-title: Creating a build/development environment for the Android App
-sidebar_label: Building Android App
+id: android
+title: Building the Android App
+sidebar_label: Android
+sidebar_position: 1
---
## Build instructions
@@ -11,12 +12,11 @@ If you would like to develop this application we'd love your help! These build i
- Use Android Studio to build/debug
- Use `git submodule update --init --recursive` to pull in the various submodules we depend on
- There are a few config files which you'll need to copy from templates included in the project. Run the following commands to do so:
-
-```
- rm ./app/google-services.json
- cp ./app/google-services-example.json ./app/google-services.json
- rm ./app/src/main/res/values/curfirmwareversion.xml
- cp ./app/special/curfirmwareversion.xml ./app/src/main/res/values/
+```sh
+rm ./app/google-services.json
+cp ./app/google-services-example.json ./app/google-services.json
+rm ./app/src/main/res/values/curfirmwareversion.xml
+cp ./app/special/curfirmwareversion.xml ./app/src/main/res/values/
```
- Now you should be able to select "Run / Run" in the IDE and it will happily start running on your phone or the emulator.
@@ -30,14 +30,14 @@ The emulators don't support Bluetooth, so some features can not be used in that
- Analytics are included but can be disabled by the user on the settings screen
- On dev devices
-```shell
+```sh
adb shell setprop debug.firebase.analytics.app com.geeksville.mesh
adb shell setprop log.tag.FirebaseCrashlytics DEBUG
```
for verbose logging:
-```shell
+```sh
adb shell setprop log.tag.FA VERBOSE
```
diff --git a/docs/development/device/_category_.yml b/docs/development/device/_category_.yml
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..d8de1354
--- /dev/null
+++ b/docs/development/device/_category_.yml
@@ -0,0 +1,7 @@
+label: Device
+collapsible: true
+position: 1
+link:
+ slug: /development/device
+ type: generated-index
+ title: Device
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/docs/developers/Firmware/device-api.mdx b/docs/development/device/client-api.mdx
similarity index 92%
rename from docs/developers/Firmware/device-api.mdx
rename to docs/development/device/client-api.mdx
index 0b3a98a3..08ccf623 100644
--- a/docs/developers/Firmware/device-api.mdx
+++ b/docs/development/device/client-api.mdx
@@ -1,18 +1,19 @@
---
-id: device-api
-title: Bluetooth/serial/TCP protocol API
-sidebar_label: Device API
+id: client-api
+title: Client API (Serial/TCP/BLE)
+sidebar_label: Client API
+sidebar_position: 1
---
-This document describes the protocol for external API clients using our devices. If you are interested in running your own code on the device itself, see the [module API](module-api) documentation instead.
+This document describes the protocol for external API clients using our devices. If you are interested in running your own code on the device itself, see the [module API](/docs/development/device/module-api) documentation instead.
-The Device API is design to have only a simple stream of ToRadio and FromRadio packets and all polymorphism comes from the flexible set of Google Protocol Buffers which are sent over the wire. We use protocol buffers extensively both for the Bluetooth API and for packets inside the mesh or when providing packets to other applications on the phone.
+The Device API is designed to have only a simple stream of ToRadio and FromRadio packets and all polymorphism comes from the flexible set of Google Protocol Buffers which are sent over the wire. We use protocol buffers extensively both for the Bluetooth API and for packets inside the mesh or when providing packets to other applications on the phone.
## Streaming version
This protocol is **almost** identical when it is deployed over BLE, Serial/USB, or TCP (our three currently supported transports for connecting to phone/PC). Most of this document is in terms of the original BLE version, but this section describes the small changes when this API is exposed over a Streaming (non datagram) transport. The streaming version has the following changes:
-- We assume the stream is reliable (though the protocol will resynchronize if bytes are lost or corrupted). i.e. we do not include CRCs or error correction codes.
+- We assume the stream is reliable (though the protocol will re-synchronize if bytes are lost or corrupted). i.e. we do not include CRCs or error correction codes.
- Packets always have a four byte header (described below) prefixed before each packet. This header provides framing characters and length.
- The stream going towards the radio is only a series of ToRadio packets (with the extra 4 byte headers)
- The stream going towards the PC is a stream of FromRadio packets (with the 4 byte headers), or if the receiver state machine does not see valid header bytes it can (optionally) print those bytes as the debug console from the radio. This allows the device to emit regular serial debugging messages (which can be understood by a terminal program) but also switch to a more structured set of protobufs once it sees that the PC client has sent a protobuf towards it.
@@ -26,7 +27,8 @@ The 4 byte header is constructed to both provide framing and to not look line 'n
The receiver will validate length and if >512 it will assume the packet is corrupted and return to looking for START1. While looking for START1 any other characters are printed as "debug output". For small example implementation of this reader see the python implementation.
-## MeshBluetoothService (the BLE API)
+
+## Bluetooth (MeshBluetoothService)
This is the main Bluetooth service for the device and provides the API your app should use to get information about the mesh, send packets, or provision the radio.
diff --git a/docs/software/device/critical-faults.mdx b/docs/development/device/error-codes.mdx
similarity index 96%
rename from docs/software/device/critical-faults.mdx
rename to docs/development/device/error-codes.mdx
index 2bc2e524..16031db8 100644
--- a/docs/software/device/critical-faults.mdx
+++ b/docs/development/device/error-codes.mdx
@@ -1,7 +1,8 @@
---
-id: critical-error-codes
-title: Critical error codes
-sidebar_label: Critical error codes
+id: error-codes
+title: Critical Error Codes
+sidebar_label: Error Codes
+sidebar_position: 4
---
The device might report these fault codes on the screen, but it will also be outputted on the device serial output. If you encounter a fault code, please post on the forum and we'll try to help.
diff --git a/docs/developers/Firmware/http-api.mdx b/docs/development/device/http-api.mdx
similarity index 99%
rename from docs/developers/Firmware/http-api.mdx
rename to docs/development/device/http-api.mdx
index 62ff9b60..72ca9c42 100644
--- a/docs/developers/Firmware/http-api.mdx
+++ b/docs/development/device/http-api.mdx
@@ -2,6 +2,7 @@
id: http-api
title: HTTP API
sidebar_label: HTTP API
+sidebar_position: 2
---
:::info
diff --git a/docs/developers/Firmware/module-api.mdx b/docs/development/device/module-api.mdx
similarity index 96%
rename from docs/developers/Firmware/module-api.mdx
rename to docs/development/device/module-api.mdx
index d2eb9d9a..53abdb5b 100644
--- a/docs/developers/Firmware/module-api.mdx
+++ b/docs/development/device/module-api.mdx
@@ -2,6 +2,7 @@
id: module-api
title: Module API
sidebar_label: Module API
+sidebar_position: 3
---
This is a tutorial on how to write small modules which run on the device. Modules are bits of regular 'Arduino' code that can send and receive packets to other nodes/apps/PCs using our mesh.
@@ -41,14 +42,14 @@ A number of [key services](http://github.com/meshtastic/firmware/tree/master/src
- [TextMessageModule](http://github.com/meshtastic/firmware/tree/master/src/modules/TextMessageModule.h) - receives text messages and displays them on the LCD screen/stores them in the local DB
- [NodeInfoModule](http://github.com/meshtastic/firmware/tree/master/src/modules/NodeInfoModule.h) - receives/sends User information to other nodes so that usernames are available in the databases
-- [RemoteHardwareModule](http://github.com/meshtastic/firmware/tree/master/src/modules/RemoteHardwareModule.h) - a module that provides easy remote access to device hardware (for things like turning GPIOs on or off). Intended to be a more extensive example and provide a useful feature of its own. See [remote-hardware](/docs/software/device/remote-hardware-service) for details.
+- [RemoteHardwareModule](http://github.com/meshtastic/firmware/tree/master/src/modules/RemoteHardwareModule.h) - a module that provides easy remote access to device hardware (for things like turning GPIOs on or off). Intended to be a more extensive example and provide a useful feature of its own. See [remote-hardware](/docs/hardware/peripheral/#remote-hardware) for details.
- [ReplyModule](http://github.com/meshtastic/firmware/tree/master/src/modules/ReplyModule.h) - a simple module that just replies to any packet it receives (provides a 'ping' service).
## Getting started
The easiest way to get started is:
-- [Build and install](/docs/developers/firmware/build) the standard codebase from GitHub.
+- [Build and install](/docs/development/firmware/build) the standard codebase from GitHub.
- Copy [src/modules/ReplyModule.\*](http://github.com/meshtastic/firmware/tree/master/src/modules/ReplyModule.cpp) into src/modules/YourModule.*. Then change the port number from *PortNum_REPLY_APP* to *PortNum_PRIVATE_APP\*.
- Edit moduless/Moduless.cpp:setupModules() to add a call to create an instance of your module (see comment at head of that function)
- Rebuild with your new messaging goodness and install on the device
@@ -72,7 +73,7 @@ If you are making a new app using meshtastic, please send in a pull request to a
- **0-63** Core Meshtastic use; do not use for third party apps
- **64-127** Registered 3rd party apps. Send in a pull request that adds a new entry to portnums.proto to register your application
- **256-511** Use one of these portnums for your private applications that you don't want to register publicly
-- **1024-66559** Are reserved for use by IP tunneling (see [here](/docs/developers/firmware/portnum) for more information)
+- **1024-66559** Are reserved for use by IP tunneling (see [here](/docs/development/firmware/portnum) for more information)
All other values are reserved.
diff --git a/docs/developers/documentation/index.mdx b/docs/development/documentation/index.mdx
similarity index 86%
rename from docs/developers/documentation/index.mdx
rename to docs/development/documentation/index.mdx
index b9c7b5fd..6e7bc0ef 100644
--- a/docs/developers/documentation/index.mdx
+++ b/docs/development/documentation/index.mdx
@@ -1,19 +1,20 @@
---
-id: documentation
+id: docs
title: Maintaining Documentation
-sidebar_label: Documentation
-sidebar_position: 6
+slug: /development/docs
+sidebar_label: Docs
+sidebar_position: 9
---
Meshtastic documentation is an important ingredient to the overall project. We want users to hit the ground running with the information they need right at their finger tips. This section will discuss the documentation software stack, file organization, and style guides.
## Software Stack
-All of our documentation resides on GitHub. Instructions for setting up your GitHub account are located [here](github).
+All of our documentation resides on GitHub. Instructions for setting up your GitHub account are located [here](/docs/development/reference/github).
-Our documentation is powered by [Docusaurus](https://docusaurus.io) — a documentation platform built on React that utilizes markdown files. Because markdown files are easy to edit, most content changes should be fairly simple. Instructions for setting up your instance of Docusaurus are located [here](docusaurus).
+Our documentation is powered by [Docusaurus](https://docusaurus.io) — a documentation platform built on React that utilizes markdown files. Because markdown files are easy to edit, most content changes should be fairly simple.
-Another component that we use is [Vercel](https://vercel.com) — a platform for frontend frameworks and static sites. Instructions for setting up your instance of Vercel are located [here](vercel).
+Another component that we use is [Vercel](https://vercel.com) — a platform for front-end frameworks and static sites. Instructions for setting up your instance of Vercel are located [here](/docs/development/documentation/publish#publish-to-vercel).
## Documentation Organization
@@ -23,15 +24,15 @@ Another component that we use is [Vercel](https://vercel.com) — a platform for
| Meshtastic Software | `docs/software` | Current bulk of documentation running through each Meshtastic project. |
| Getting Started | `docs/getting-started` | Instructions on how to get the Meshtastic firmware onto a users device. |
| Device Settings | `docs/software/settings` | Details each user setting and provides explanations for what the setting does and how to configure the device using the various clients available (Android, CLI, iOS, Web) |
-| Hardware Details | `docs/hardware` | Any hardware related content. Any time a user is attaching a peripheral accessory to their device. That includes 3d printed cases, antennas, buttons, chimes, rotary encoders, and screens. |
-| Radio Mesh Details | `docs/mesh` | This section discusses everything relating to the Meshtastic mesh. Mesh health metrics will be discussed here as well as topics such as signal strength, range and anyting else pertaining to "over the air". |
+| Hardware Details | `docs/hardware` | Any hardware related content. Any time a user is attaching a peripheral accessory to their device. That includes 3D printed cases, antennas, buttons, chimes, rotary encoders, and screens. |
+| Radio Mesh Details | `docs/mesh` | This section discusses everything relating to the Meshtastic mesh. Mesh health metrics will be discussed here as well as topics such as signal strength, range and anything else pertaining to "over the air". |
| Contribute to Meshtastic | `docs/developers` | Details each of the projects and how they work together to give a developer an idea of how the Meshtastic ecosystem operates. |
| About the Documentation | `docs/maintaining-documentation` | This section explains how our documentation is organized, how to make edits to the documentation, view a local copy of your fork of the project. Style guides and tips will also be included here. |
| Legal | `docs/legal` | Any legal information. Most changes here will be handled by developers actually working on the projects that require any legal disclosures. Examples include: the Meshtastic trademark, terms of service, and privacy policy. |
## Quick Start
-Assuming you have the [prerequisites installed](serve-docs-locally#prerequisites), running a local instance of Docusaurus takes three steps:
+Assuming you have the [prerequisites installed](/docs/development/documentation/local-dev#prerequisites), running a local instance of Docusaurus takes three steps:
1. Fork/Clone the [meshtastic/meshtastic](https://github.com/meshtastic/meshtastic) repository and navigate to the root directory of the project.
diff --git a/docs/developers/documentation/serve-docs-locally.mdx b/docs/development/documentation/local-dev.mdx
similarity index 95%
rename from docs/developers/documentation/serve-docs-locally.mdx
rename to docs/development/documentation/local-dev.mdx
index dfb1d810..65988f2c 100644
--- a/docs/developers/documentation/serve-docs-locally.mdx
+++ b/docs/development/documentation/local-dev.mdx
@@ -1,7 +1,7 @@
---
-id: serve-docs-locally
-title: Setting up Local Documentation
-sidebar_label: Serve Docs Locally
+id: local-dev
+title: Serving Docs Locally for Development
+sidebar_label: Local Development
---
:::note
diff --git a/docs/developers/publish.mdx b/docs/development/documentation/publish.mdx
similarity index 62%
rename from docs/developers/publish.mdx
rename to docs/development/documentation/publish.mdx
index 3c4d2bca..4d7813df 100644
--- a/docs/developers/publish.mdx
+++ b/docs/development/documentation/publish.mdx
@@ -1,14 +1,12 @@
---
id: publish
-title: Publishing Meshtastic
-sidebar_label: Publishing Meshtastic
+title: Publishing Meshtastic.org
+sidebar_label: Publish
---
-This document is a WIP.
+## Publish Live
-If you’d like to do ‘real’ releases with your changes, the procedure is:
-
-## Device
+### Device
- Update protobufs
@@ -25,11 +23,11 @@ run bin/regen-protos.sh
- commit and push (or merge) to root of repo - this should cause GitHub to start a release build (see the CI actions)
- edit the draft release text and click publish
-### Update Protobufs
+#### Update Protobufs
-## Android
+### Android
-### Pre-requisites
+#### Pre-requisites
- Add repository secrets
- - KEYSTORE_FILENAME
@@ -43,31 +41,31 @@ run bin/regen-protos.sh
keyAlias=upload
storeFile=nononononono.jks
-### Instructions - Automated
+#### Instructions - Automated
- Update protobufs
- Go to Actions / Make Release / Run Workflow
- Pick the Releases branch
- Enter the version found in app/gradle.build
-## iOS
+### iOS
TBD
-## Meshtastic-flasher
+### Meshtastic-flasher
A `meshtastic-flasher` release consists of publishing the release to PyPi https://pypi.org/project/meshtastic-flasher/ as well as producing single-executable files that are downloadable from Github https://github.com/meshtastic/Meshtastic-gui-installer/releases.
-### Instructions - automated
+#### Instructions - automated
- Go to Actions / Make Release / Run Workflow https://github.com/meshtastic/Meshtastic-gui-installer/actions/workflows/release.yml
- Draft & Publish release https://github.com/meshtastic/Meshtastic-gui-installer/releases
-## Python
+### Python
A python release consists of publishing the release to PyPi https://pypi.org/project/meshtastic/ as well as producing single-executable files that are downloadable from Github https://github.com/meshtastic/Meshtastic-python/releases.
-### Pre-requisites
+#### Pre-requisites
No pre-requisites are needed locally to make a release. All builds are done via Github Actions currently.
@@ -78,7 +76,7 @@ pip3 install -r requirements.txt
pip install .
```
-### Instructions
+#### Instructions
- Update protobufs by running the "Update protobufs" workflow in Actions: https://github.com/meshtastic/Meshtastic-python/actions/workflows/update_protobufs.yml
@@ -102,9 +100,43 @@ pytest -m smoke1
You need permissions in the GitHub project to make a build
:::
-## Web
+### Web
Releases are automatically generated for every commit as per out [CI](https://github.com/meshtastic/web/blob/master/.github/workflows/main.yml). This performs two actions:
1. Generates a perpetually updated [GitHub release](https://github.com/meshtastic/web/releases/tag/latest) with an accompanying `build.tar` that a automatically get's pulled by the firmware CI at build time.
2. A hosted version is deployed to [client.meshtastic.org](https://client.meshtastic.org).
+
+
+## Publish to Vercel
+
+Setting up a Vercel account is an optional step that can help you view your changes to the documentation in a server environment just like the actual docs. This can be helpful to include when submitting a pull request so that developers can review your changes and visually check that things look correct.
+
+### Set up Vercel account
+
+- Go to [vercel.com](https://vercel.com)
+- Login with your GitHub account, click `Continue with GitHub`
+
+### Link your fork of the project
+
+- Click `New Project`
+- Under `Import Git Repository` select `+ Add GitHub Account`
+ You'll be redirected to GitHub to allow access to select repositories.
+- Select your fork of the project: `username/Meshtastic`
+
+### Configure project
+
+Configure project:
+
+- Set a name for the project
+- Select a framework preset: `Docusaurus 2`
+- Click `Deploy`
+
+That's it! You should now see your project with a green or orange status dot showing that your fork of the project has been compiled. There will be a commit-specific url that you can share to view your changes. There also will be a branch-specific url that you can view. If there are any errors it will show up red and include the logs for you to figure out what has gone wrong.
+
+:::tip
+There is a limited number of branch urls that you will be able to view. If you notice that option has disappeared, you can delete unused branches on your fork and that will enable that feature again.
+
+Branch urls are helpful in PRs because they will remain constant, and you won't need to resubmit a new url for review each new commit if changes are requested.
+:::
+
diff --git a/docs/developers/documentation/style-guides/_category_.yml b/docs/development/documentation/style-guides/_category_.yml
similarity index 81%
rename from docs/developers/documentation/style-guides/_category_.yml
rename to docs/development/documentation/style-guides/_category_.yml
index 0b871e94..fcda5668 100644
--- a/docs/developers/documentation/style-guides/_category_.yml
+++ b/docs/development/documentation/style-guides/_category_.yml
@@ -3,5 +3,6 @@ position: 1 # float position is supported
label: 'Style Guides'
collapsible: true # make the category collapsible
link:
+ slug: /development/docs/style-guide
type: generated-index
title: Style Guides
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/docs/developers/documentation/style-guides/markdown-features.mdx b/docs/development/documentation/style-guides/markdown-features.mdx
similarity index 96%
rename from docs/developers/documentation/style-guides/markdown-features.mdx
rename to docs/development/documentation/style-guides/markdown-features.mdx
index d367d7f0..c3ec3293 100644
--- a/docs/developers/documentation/style-guides/markdown-features.mdx
+++ b/docs/development/documentation/style-guides/markdown-features.mdx
@@ -1,6 +1,6 @@
---
-id: markdown-features
-title: Style Guide - Markdown Features
+id: markdown
+title: Markdown Features
sidebar_label: Markdown Features
---
diff --git a/docs/developers/documentation/style-guides/settings.mdx b/docs/development/documentation/style-guides/settings.mdx
similarity index 97%
rename from docs/developers/documentation/style-guides/settings.mdx
rename to docs/development/documentation/style-guides/settings.mdx
index ad7ec6c0..42f6fd19 100644
--- a/docs/developers/documentation/style-guides/settings.mdx
+++ b/docs/development/documentation/style-guides/settings.mdx
@@ -1,7 +1,7 @@
---
-id: style-guide-settings
-title: Style Guide - Settings Pages
-sidebar_label: Settings Pages
+id: config-pages
+title: Config Pages
+sidebar_label: Config Pages
---
## Overview
diff --git a/docs/development/firmware/_category_.yml b/docs/development/firmware/_category_.yml
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..9eb90696
--- /dev/null
+++ b/docs/development/firmware/_category_.yml
@@ -0,0 +1,7 @@
+label: Firmware
+collapsible: true
+position: 1
+link:
+ type: generated-index
+ title: Firmware
+ slug: /development/firmware
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/docs/developers/Firmware/build.mdx b/docs/development/firmware/build.mdx
similarity index 92%
rename from docs/developers/Firmware/build.mdx
rename to docs/development/firmware/build.mdx
index 7ef0a86e..3c32a3c2 100644
--- a/docs/developers/Firmware/build.mdx
+++ b/docs/development/firmware/build.mdx
@@ -1,12 +1,12 @@
---
id: build
-title: Creating a build environment
-sidebar_label: Building Meshtastic
+title: Building Meshtastic Firmware
+sidebar_label: Building Firmware
---
-Meshtastic uses the [PlatformIO](https://platformio.org) development environment, that enables easy multiplatform development and centralized tooling.
+Meshtastic uses [PlatformIO](https://platformio.org), a development environment that enables easy multi-platform development and centralized tooling.
-## Setup
+## Setup the build environment
1. Install PlatformIO, following the instructions available [here](https://platformio.org/platformio-ide).
diff --git a/docs/developers/Firmware/oled-l10n-guide.mdx b/docs/development/firmware/oled-guide.mdx
similarity index 94%
rename from docs/developers/Firmware/oled-l10n-guide.mdx
rename to docs/development/firmware/oled-guide.mdx
index ae54ff7e..7f567dba 100644
--- a/docs/developers/Firmware/oled-l10n-guide.mdx
+++ b/docs/development/firmware/oled-guide.mdx
@@ -1,7 +1,7 @@
---
-id: oled-l10n-guide
-title: OLED localization guide
-sidebar_label: OLED localization
+id: oled-guide
+title: OLED Localization Guide
+sidebar_label: OLED Localization
---
# OLED localization guide
diff --git a/docs/developers/Firmware/port-numbers.mdx b/docs/development/firmware/port-numbers.mdx
similarity index 96%
rename from docs/developers/Firmware/port-numbers.mdx
rename to docs/development/firmware/port-numbers.mdx
index 13f5d1eb..1a09574e 100644
--- a/docs/developers/Firmware/port-numbers.mdx
+++ b/docs/development/firmware/port-numbers.mdx
@@ -1,7 +1,7 @@
---
id: portnum
-title: Meshtastic port numbers
-sidebar_label: Port numbers
+title: Meshtastic Port Numbers
+sidebar_label: Port Numbers
---
For any new apps that run on the device or via sister apps on phones/PCs they should pick and use a unique 'portnum' for their application.
diff --git a/docs/developers/Firmware/stacktrace-decode.mdx b/docs/development/firmware/stacktraces.mdx
similarity index 65%
rename from docs/developers/Firmware/stacktrace-decode.mdx
rename to docs/development/firmware/stacktraces.mdx
index c3a0aefb..e1d933f9 100644
--- a/docs/developers/Firmware/stacktrace-decode.mdx
+++ b/docs/development/firmware/stacktraces.mdx
@@ -1,12 +1,14 @@
---
-id: stacktrace-decode
-title: Decoding Stacktraces
-sidebar_label: Decoding Stacktraces
+id: stacktraces
+title: Stacktraces
+sidebar_label: Stacktraces
---
+## Decoding Stacktraces
+
You may encounter a situation where your device crashes and are left with a stacktrace, below are two methods of decoding them.
-## Manual
+### Manual
:::info
This method uses the symbols of the `firmware.elf` file generated from your latest build, you may wish to rebuild to get up-to-date symbols.
@@ -24,9 +26,9 @@ Now run the exception decoder:
bin/exception_decoder.py backtrace.txt
```
-## Real Time
+### Real-Time
-In order to decode stack traces in real time, kep the following command (replacing `DEVICE_PORT` with your device's port) running in your terminal with the suspect device connected
+In order to decode stack traces in real time, keep the following command (replacing `DEVICE_PORT` with your device's port) running in your terminal with the suspect device connected
```shell
pio device monitor --port DEVICE_PORT -f esp32_exception_decoder
diff --git a/docs/software/js/connecting.mdx b/docs/development/js/connecting.mdx
similarity index 100%
rename from docs/software/js/connecting.mdx
rename to docs/development/js/connecting.mdx
diff --git a/docs/software/js/events.mdx b/docs/development/js/events.mdx
similarity index 100%
rename from docs/software/js/events.mdx
rename to docs/development/js/events.mdx
diff --git a/docs/software/js/http-api.mdx b/docs/development/js/http-api.mdx
similarity index 89%
rename from docs/software/js/http-api.mdx
rename to docs/development/js/http-api.mdx
index 5ba62d16..9fe2574a 100644
--- a/docs/software/js/http-api.mdx
+++ b/docs/development/js/http-api.mdx
@@ -5,7 +5,7 @@ sidebar_label: HTTP API
---
:::info
-Methods and types for using the device [HTTP API](http://example.com) are exported
+Methods and types for using the device [HTTP API](/docs/development/device/http-api) are exported
:::
```typescript
diff --git a/docs/software/js/getting-started.mdx b/docs/development/js/index.mdx
similarity index 83%
rename from docs/software/js/getting-started.mdx
rename to docs/development/js/index.mdx
index 3dc679c1..e8034f5b 100644
--- a/docs/software/js/getting-started.mdx
+++ b/docs/development/js/index.mdx
@@ -1,7 +1,9 @@
---
-id: getting-started
-title: Getting Started
-sidebar_label: Getting Started
+id: js
+title: Getting Started with Meshtastic.js
+slug: /development/js
+sidebar_position: 6
+sidebar_label: Javascript
---
:::tip
diff --git a/docs/software/python/cli/development.mdx b/docs/development/python/index.mdx
similarity index 83%
rename from docs/software/python/cli/development.mdx
rename to docs/development/python/index.mdx
index 1d7525e5..7aac3b58 100644
--- a/docs/software/python/cli/development.mdx
+++ b/docs/development/python/index.mdx
@@ -1,50 +1,49 @@
---
-id: development
+id: python
title: Meshtastic Python Development
-sidebar_label: Development
+sidebar_position: 5
+sidebar_label: Python
---
## A note to developers of this lib
We use the Visual Studio Code (VScode) default python formatting conventions (autopep8). So if you use that IDE you should be able to use "Format Document" and not generate unrelated diffs. If you use some other editor, please do not change formatting on lines you have not changed yourself.
-If you need to build a new release you will need:
-```
+### Building
+
+**To build a new release**
+
+```sh
apt install pandoc
sudo pip3 install markdown pdoc3 webencodings pyparsing twine autopep8 pylint pytest pytest-cov
```
-For development, you will probably want to run:
+**For development**
-```
+```sh
pip3 install -r requirements.txt
```
-To lint, run:
+### Linting
-```
+```sh
pylint meshtastic
```
+### Testing
-To test, first install this code locally, then run pytest:
+**Install and run pytest**
-```
+- For more verbosity, add `-v` or even `-vv`
+
+```sh
pip3 install .
-pytest
-```
-
-Possible options for testing:
-
-- For more verbosity, add "-v" or even "-vv" like this:
-
-```
pytest -vv
```
**Run just unit tests**
-```
+```sh
pytest
# or (more verbosely)
pytest -m unit
@@ -54,34 +53,36 @@ make
**Run just integration tests**
-```
+```sh
pytest -m int
```
**Run the smoke test with only one device connected serially (aka smoke1)**
-```
+```sh
pytest -m smoke1
```
-CAUTION: Running smoke1 will reset values on the device, including the region to 1 (US).
+:::caution
+Running `smoke1` will reset values on the device, including the region to 1 (US).
Be sure to hit the reset button on the device after the test is completed.
+:::
**Run the smoke test with only two device connected serially (aka smoke2)**
-```
+```sh
pytest -m smoke2
```
**Run the wifi smoke test**
-```
+```sh
pytest -m smokewifi
```
**Run a specific test**
-```
+```sh
pytest -msmoke1 meshtastic/tests/test_smoke1.py::test_smoke1_info
# or to run a specific smoke2 test
@@ -91,13 +92,13 @@ pytest -m smoke2 meshtastic/tests/test_smoke2.py::test_smoke2_info
pytest -m smokewifi meshtastic/tests/test_smoke_wifi.py::test_smokewifi_info
```
-**Add another classification of tests such as "unit" or "smoke1"**
+**Add another classification of tests such as `unit` or `smoke1`**
See [pytest.ini](https://github.com/meshtastic/Meshtastic-python/blob/master/pytest.ini).
**To see the unit test code coverage**
-```
+```sh
pytest --cov=meshtastic
# or if want html coverage report
pytest --cov-report html --cov=meshtastic
@@ -107,17 +108,17 @@ make cov
**To see slowest unit tests, you can run**
-```
+```sh
pytest --durations=0
# or
make slow
```
-**Generate the Python API documentation**
+### Generate the Python API documentation
Pre-generated: [API documentation](https://python.meshtastic.org)
-```
+```sh
bin/regen-docs.sh
```
diff --git a/docs/software/python/library.mdx b/docs/development/python/library.mdx
similarity index 99%
rename from docs/software/python/library.mdx
rename to docs/development/python/library.mdx
index f44a51ce..bbec7753 100644
--- a/docs/software/python/library.mdx
+++ b/docs/development/python/library.mdx
@@ -1,5 +1,5 @@
---
-id: python-library
+id: library
title: Using the Meshtastic Python Library
sidebar_label: Python Library
---
diff --git a/docs/development/reference/_category_.yml b/docs/development/reference/_category_.yml
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..2c209977
--- /dev/null
+++ b/docs/development/reference/_category_.yml
@@ -0,0 +1,6 @@
+label: Reference Material
+collapsible: true
+position: 20
+link:
+ type: generated-index
+ title: Reference Material
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/docs/developers/Organizational/readmes.mdx b/docs/development/reference/github.mdx
similarity index 79%
rename from docs/developers/Organizational/readmes.mdx
rename to docs/development/reference/github.mdx
index a650628a..76842df5 100644
--- a/docs/developers/Organizational/readmes.mdx
+++ b/docs/development/reference/github.mdx
@@ -1,16 +1,24 @@
---
-id: readmes
-title: README Structure
-sidebar_label: READMEs
+id: github
+title: GitHub
+sidebar_label: GitHub
---
-## Outline
+## Overview
+
+All of Meshtastic's code and documentation is hosted on GitHub. If you would like to contribute to the project, having a GitHub account is an important step to doing so.
+
+## Set up GitHub account
+
+- Go to [github.com](https://github.com)
+- Click `Sign Up`
+
+## README Template
All Meshtastic developers should follow this convention when writing a README for a repository.
Repobeats images can be generated at [repobeats.axiom.co](https://repobeats.axiom.co/)
-
```markdown
# Repo name
@@ -28,7 +36,6 @@ A description about the project
**[Documentation/API Reference](https://example.com)**
-
## Stats
diff --git a/docs/development/reference/lora-design.mdx b/docs/development/reference/lora-design.mdx
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..cd20d9e7
--- /dev/null
+++ b/docs/development/reference/lora-design.mdx
@@ -0,0 +1,8 @@
+---
+id: lora-design
+title: LoRa Design Guide
+sidebar_label: LoRa Datasheet
+sidebar_position: 1
+---
+
+- [LoRa Design Guide Datasheet](/documents/LoRa_Design_Guide.pdf)
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/docs/developers/protobufs/api.mdx b/docs/development/reference/protobuf-api.mdx
similarity index 98%
rename from docs/developers/protobufs/api.mdx
rename to docs/development/reference/protobuf-api.mdx
index 72375999..1f8b778e 100644
--- a/docs/developers/protobufs/api.mdx
+++ b/docs/development/reference/protobuf-api.mdx
@@ -1,9 +1,13 @@
---
-id: api
+id: protobuf-api
title: Protobuf API Reference
-sidebar_label: API
+slug: /developers/protobufs/api
+sidebar_label: Protobufs
+sidebar_position: 20
---
+
+
## admin.proto
@@ -301,6 +305,7 @@ Display Config
| compass_north_top | bool | If this is set, the displayed compass will always point north. if unset, the old behaviour (top of display is heading direction) is used. |
| flip_screen | bool | Flip screen vertically, for cases that mount the screen upside down |
| units | [`Config.DisplayConfig.DisplayUnits`](#configdisplayconfigdisplayunits) | Perferred display units |
+| oled | [`Config.DisplayConfig.OledType`](#configdisplayconfigoledtype) | Override auto-detect in screen |
@@ -477,6 +482,22 @@ How the GPS coordinates are displayed on the OLED screen.
+### Config.DisplayConfig.OledType
+
+:::note `enum` description
+Override OLED outo detect with this if it fails.
+:::
+
+
+| Name | Number | Description |
+| ---- | ------ | ----------- |
+| `OLED_AUTO` | `0` | Default / Auto |
+| `OLED_SSD1306` | `1` | Default / Auto |
+| `OLED_SH1106` | `2` | Default / Auto |
+
+
+
+
### Config.LoRaConfig.ModemPreset
:::note `enum` description
@@ -836,12 +857,12 @@ The other fields are either not sent at all, or sent in the special 16 byte LORA
| Field | Type | Description |
| ----- | ---- | ----------- |
-| from | fixed32 | The sending node number. Note: Our crypto implementation uses this field as well. See [crypto](/docs/developers/firmware/encryption) for details. FIXME - really should be fixed32 instead, this encoding only hurts the ble link though. |
+| from | fixed32 | The sending node number. Note: Our crypto implementation uses this field as well. See [crypto](/docs/about/overview/encryption) for details. FIXME - really should be fixed32 instead, this encoding only hurts the ble link though. |
| to | fixed32 | The (immediatSee Priority description for more details.y should be fixed32 instead, this encoding only hurts the ble link though. |
| channel | uint32 | (Usually) If set, this indicates the index in the secondary_channels table that this packet was sent/received on. If unset, packet was on the primary channel. A particular node might know only a subset of channels in use on the mesh. Therefore channel_index is inherently a local concept and meaningless to send between nodes. Very briefly, while sending and receiving deep inside the device Router code, this field instead contains the 'channel hash' instead of the index. This 'trick' is only used while the payload_variant is an 'encrypted'. |
| [**oneof**](https://developers.google.com/protocol-buffers/docs/proto3#oneof) payload_variant.decoded | [`Data`](#data) | TODO: REPLACE |
| [**oneof**](https://developers.google.com/protocol-buffers/docs/proto3#oneof) payload_variant.encrypted | bytes | TODO: REPLACE |
-| id | fixed32 | A unique ID for this packet. Always 0 for no-ack packets or non broadcast packets (and therefore take zero bytes of space). Otherwise a unique ID for this packet, useful for flooding algorithms. ID only needs to be unique on a _per sender_ basis, and it only needs to be unique for a few minutes (long enough to last for the length of any ACK or the completion of a mesh broadcast flood). Note: Our crypto implementation uses this id as well. See [crypto](/docs/developers/firmware/encryption) for details. FIXME - really should be fixed32 instead, this encoding only hurts the ble link though. |
+| id | fixed32 | A unique ID for this packet. Always 0 for no-ack packets or non broadcast packets (and therefore take zero bytes of space). Otherwise a unique ID for this packet, useful for flooding algorithms. ID only needs to be unique on a _per sender_ basis, and it only needs to be unique for a few minutes (long enough to last for the length of any ACK or the completion of a mesh broadcast flood). Note: Our crypto implementation uses this id as well. See [crypto](/docs/about/overview/encryption) for details. FIXME - really should be fixed32 instead, this encoding only hurts the ble link though. |
| rx_time | fixed32 | The time this message was received by the esp32 (secs since 1970). Note: this field is _never_ sent on the radio link itself (to save space) Times are typically not sent over the mesh, but they will be added to any Packet (chain of SubPacket) sent to the phone (so the phone can know exact time of reception) |
| rx_snr | float | Never* sent over the radio links. Set during reception to indicate the SNR of this packet. Used to collect statistics on current link quality. |
| hop_limit | uint32 | If unset treated as zero (no forwarding, send to adjacent nodes only) if 1, allow hopping through one node, etc... For our usecase real world topologies probably have a max of about 3. This field is normally placed into a few of bits in the header. |
@@ -1140,6 +1161,7 @@ To match the old style filenames, _ is converted to -, p is converted to .
| `LILYGO_TBEAM_S3_CORE` | `12` | New T-BEAM with ESP32-S3 CPU |
| `RAK11200` | `13` | RAK WisBlock ESP32 core: https://docs.rakwireless.com/Product-Categories/WisBlock/RAK11200/Overview/ |
| `NANO_G1` | `14` | B&Q Consulting Nano Edition G1: https://uniteng.com/wiki/doku.php?id=meshtastic:nano |
+| `TLORA_V2_1_1P8` | `15` | TODO: REPLACE |
| `STATION_G1` | `25` | B&Q Consulting Station Edition G1: https://uniteng.com/wiki/doku.php?id=meshtastic:station |
| `LORA_RELAY_V1` | `32` | Less common/prototype boards listed here (needs one more byte over the air) |
| `NRF52840DK` | `33` | TODO: REPLACE |
diff --git a/docs/software/web/development.mdx b/docs/development/web/index.mdx
similarity index 96%
rename from docs/software/web/development.mdx
rename to docs/development/web/index.mdx
index 410b0fcb..47a237ed 100644
--- a/docs/software/web/development.mdx
+++ b/docs/development/web/index.mdx
@@ -1,7 +1,8 @@
---
-id: web-development-software
-title: Information for developers of the web interface
-sidebar_label: Development
+id: web-interface
+title: Development Overview of the Web Interface
+sidebar_label: Web Interface
+sidebar_position: 4
---
## Considerations
diff --git a/docs/software/web/partitions.mdx b/docs/development/web/partitions.mdx
similarity index 93%
rename from docs/software/web/partitions.mdx
rename to docs/development/web/partitions.mdx
index 02b981c9..51d7f98a 100644
--- a/docs/software/web/partitions.mdx
+++ b/docs/development/web/partitions.mdx
@@ -1,5 +1,5 @@
---
-id: web-partitions-software
+id: esp32-partitions
title: Managing ESP32 partitions
sidebar_label: ESP32 partitions
---
@@ -53,7 +53,7 @@ Requires: [Python](https://www.python.org) and [esptool.py](https://github.com/e
### Visual Studio & PlatformIO
-There is also the method of using the Visual Studio IDE. This requires having Visual Studio and PlatformIO installed, along with having cloned the firmware code as per the [build instructions](/docs/developers/firmware/build). After loading the project in Visual Studio, select the PlatformIO alien icon, then find the appropriate device, and then click the Erase Flash command.
+There is also the method of using the Visual Studio IDE. This requires having Visual Studio and PlatformIO installed, along with having cloned the firmware code as per the [build instructions](/docs/development/firmware/build). After loading the project in Visual Studio, select the PlatformIO alien icon, then find the appropriate device, and then click the Erase Flash command.

diff --git a/docs/field-tests/_category_.yml b/docs/field-tests/_category_.yml
deleted file mode 100644
index 6aa00a04..00000000
--- a/docs/field-tests/_category_.yml
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,7 +0,0 @@
-position: 7 # float position is supported
-label: 'Field Tests'
-collapsible: true # make the category collapsible
-link:
- type: generated-index
- title: Field Tests
- slug: field-tests
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/docs/field-tests/antenna/index.mdx b/docs/field-tests/antenna/index.mdx
deleted file mode 100644
index c092855f..00000000
--- a/docs/field-tests/antenna/index.mdx
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,36 +0,0 @@
----
-title: Testing LoRa Antennas
-sidebar_label: LoRa Antennas
-sidebar_position: 1
----
-
-If you have sufficient range with your existing aerial, skip this section. If you don't, consider either getting more nodes and / or replace the stock aerial with one tuned (to your region transmitter's frequency):
-
-- A quarter wave _tuned_ stubby aerial (<10cm for fit-in-pocket) should have a real-world range of a couple of km without significant obstacles (buildings / hills).
-- Aerial criteria: 50 Ohm, appropriate connector (usually SMA male or U.FL), low VSWR (<2) (at tuning frequency - see its datasheet), gain > 0 dBi .
-- Caution, avoid suppliers who:
- - don't state the aerial's tuned frequency and its specific purpose (LoRa network)
- - claim huge gain figures on omni-directional aerials
- - don't provide boringly professional datasheets
-
-If you want more range, directionality, or specificity read on.
-
-## General guidance
-
-The Meshtastic system is designed to be simple and intuitive to use. However, its LoRa radios rely on point-to-point communications, unit-to-unit, aerial-to-aerial; quite different to the near ubiquitous radio coverage of today's cellphone & Wifi connections.
-
-Some understanding of the factors affecting radio communications will help achieve substantially better service and faster transmission over a greater range with your devices. Here, we'll attempt to provide a top-level set of guidance for use and aerial selection, how to test the aerials, a set of resources for further research, and plenty of opportunity for going deeper.
-
-The Meshtastic devices (of various flavors) lend themselves to experimentation, not only because you can replace their aerials, but also because of their mesh operation. All nodes will, without alteration, relay communications from any other members of the mesh around obstacles and over greater distances. The cost of aerial investment should be weighed against investment in additional low-cost nodes.
-
-:::caution
-While the LoRa devices we are using for Meshtastic are relatively low power radios, care should be taken _not_ to operate any radio transmission device without an aerial or with a poorly matched aerial. Un-transmitted radio signal reflected back to the transmitter can damage the device.
-:::
-
-The information collected here is by no means definitive, and necessarily abbreviated (it's a huge topic).
-
-## Discussion
-
-To comment on / join in antenna range [Meshtastic discourse](https://meshtastic.discourse.group/t/antenna-improved-range/227/35?u=sens8tion)
-
-There, you will also find reference to Meshtastic range achievements and aerial recommendations. (Note we've stopped short of making specific supplier aerial recommendations in this wiki.)
diff --git a/docs/getting-started/connect-device/_category_.yml b/docs/getting-started/connect-device/_category_.yml
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..4890fb02
--- /dev/null
+++ b/docs/getting-started/connect-device/_category_.yml
@@ -0,0 +1,7 @@
+label: Connect to Device
+collapsible: true
+position: 3
+link:
+ type: generated-index
+ title: Connect to Device
+ slug: /getting-started/connect-device
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/docs/getting-started/connect-device/bluetooth.mdx b/docs/getting-started/connect-device/bluetooth.mdx
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..b61d3f32
--- /dev/null
+++ b/docs/getting-started/connect-device/bluetooth.mdx
@@ -0,0 +1,10 @@
+---
+id: connect-ble
+title: Connecting using Bluetooth
+sidebar_label: Bluetooth
+#pagination_next: /docs/getting-started
+sidebar_position: 2
+---
+
+import Tabs from '@theme/Tabs';
+import TabItem from '@theme/TabItem';
diff --git a/docs/getting-started/connect-device/network.mdx b/docs/getting-started/connect-device/network.mdx
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..83b3f8d8
--- /dev/null
+++ b/docs/getting-started/connect-device/network.mdx
@@ -0,0 +1,15 @@
+---
+id: connect-network
+title: Connecting over TCP/IP Network (ESP32 Only)
+sidebar_label: Network (ESP32)
+#pagination_next: /docs/getting-started
+sidebar_position: 3
+---
+
+import Tabs from '@theme/Tabs';
+import TabItem from '@theme/TabItem';
+
+
+## WiFi
+
+## Ethernet
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/docs/getting-started/connect-device/serial.mdx b/docs/getting-started/connect-device/serial.mdx
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..6bc98873
--- /dev/null
+++ b/docs/getting-started/connect-device/serial.mdx
@@ -0,0 +1,10 @@
+---
+id: connect-serial
+title: Connecting using Serial
+sidebar_label: Serial
+#pagination_next: /docs/getting-started
+sidebar_position: 1
+---
+
+import Tabs from '@theme/Tabs';
+import TabItem from '@theme/TabItem';
diff --git a/docs/getting-started/flashing-firmware/esp32/cli-script.mdx b/docs/getting-started/flashing-firmware/esp32/cli-script.mdx
index fb6a8d41..5688e7c7 100644
--- a/docs/getting-started/flashing-firmware/esp32/cli-script.mdx
+++ b/docs/getting-started/flashing-firmware/esp32/cli-script.mdx
@@ -15,12 +15,12 @@ Make sure not to power the radio on without first attaching the antenna! You cou
For ESP32 devices if the device already has a version of Meshtastic installed using the OTA firmware upgrade tool in the Android app is the friendliest path for users. OTA firmware updates are not yet available on Apple platforms.
If your ESP32 device does not have Meshtastic pre-installed flashing
-Before you flash your device start by verifiying connectivity with the device being flashed. Outlined below are steps that can be taken to verify connectivity and, if necessary, to install the appropriate drivers. If you end up needing to install drivers be sure to reboot your computer afterwards to verify the installation is complete.
+Before you flash your device start by verifying connectivity with the device being flashed. Outlined below are steps that can be taken to verify connectivity and, if necessary, to install the appropriate drivers. If you end up needing to install drivers be sure to reboot your computer afterwards to verify the installation is complete.
:::note
-The [T-Beam 0.7](/docs/hardware/supported/tbeam#t-beam---v07) board is an earlier version of the T-Beam board, and due to changes in the design in subsequent iterations this board uses a specific firmware file different from the other T-Beam boards.
+The [T-Beam 0.7](/docs/hardware/devices/tbeam#t-beam---v07) board is an earlier version of the T-Beam board, and due to changes in the design in subsequent iterations this board uses a specific firmware file different from the other T-Beam boards.
-`firmware-tbeam0.7-1.x.x.bin` is the correct firmware. `firmware-tbeam-1.x.x.bin` is incompatible. For all other [T-Beam](/docs/hardware/supported/tbeam) boards `firmware-tbeam-1.x.x.bin` is the correct selection.
+`firmware-tbeam0.7-1.x.x.bin` is the correct firmware. `firmware-tbeam-1.x.x.bin` is incompatible. For all other [T-Beam](/docs/hardware/devices/tbeam) boards `firmware-tbeam-1.x.x.bin` is the correct selection.
:::
## Command Line Interface Instructions
diff --git a/docs/getting-started/flashing-firmware/esp32/external-serial-adapter.mdx b/docs/getting-started/flashing-firmware/esp32/external-serial-adapter.mdx
index 00fbff72..896192e8 100644
--- a/docs/getting-started/flashing-firmware/esp32/external-serial-adapter.mdx
+++ b/docs/getting-started/flashing-firmware/esp32/external-serial-adapter.mdx
@@ -21,7 +21,7 @@ Make sure not to power the radio on without first attaching the antenna! You cou
Situations that may require usage an external USB to Serial Adapter:
* Due to the chip shortage, recently purchased devices such as the TTGO T-Beam may come with legacy or non-standard USB to Serial adapter chips that are unreliable in some cases.
* Certain devices might have defective USB to Serial chip.
-* Certain devices, such as the [Hydra](https://github.com/Hydra-Designs/project-hydra-meshtastic-pcb) (Meshtastic-diy target).
+* Certain devices, such as the [Hydra](https://github.com/Hydra-Designs/project-hydra-meshtastic-pcb) (Meshtastic-DIY target).
### USB Serial Adapters
@@ -36,7 +36,7 @@ Plug the adapter into your computer without connecting it to any devices yet. En
### Connecting Adapter to the Device
:::info
-There are multiple ways to connect the pins of the adapter to the target device: pressing jumpers against contacts, using pogo pin jigs, etc. This tutorial features offset dupont headers soldered onto the operative gpio pins and connected via jumpers.
+There are multiple ways to connect the pins of the adapter to the target device: pressing jumpers against contacts, using pogo pin jigs, etc. This tutorial features offset dupont headers soldered onto the operative GPIO pins and connected via jumpers.
:::
Disconnect your USB to Serial Adapter from the computer before starting this process.
@@ -59,17 +59,17 @@ Example using the Meshtastic Flasher
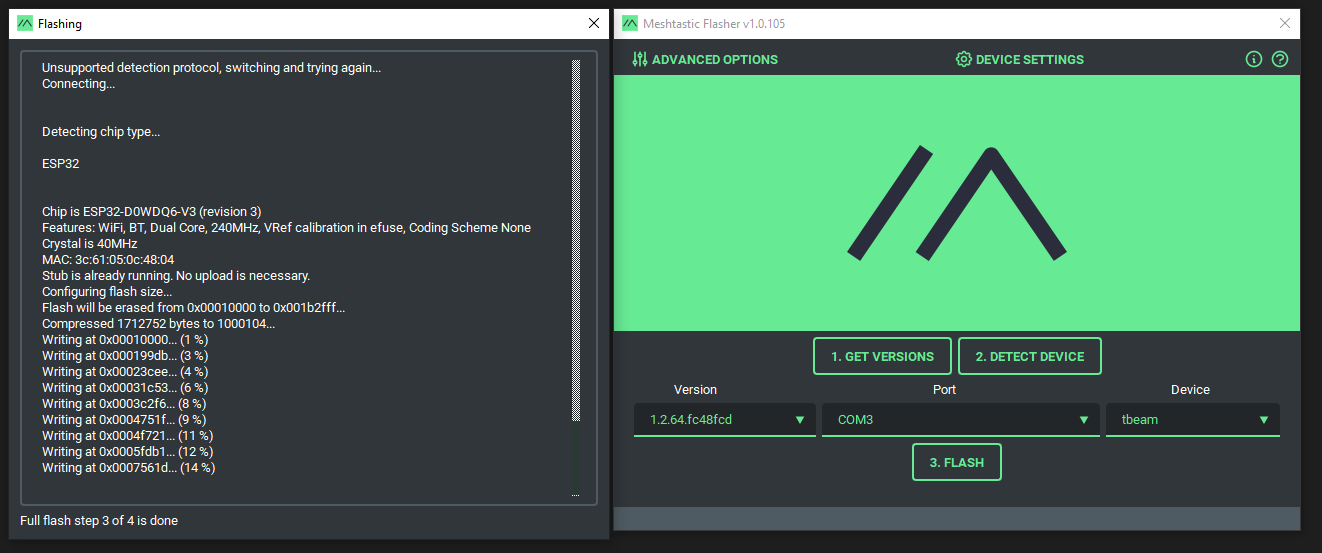
After flashing the device is complete, reset your device (via the RST button if available).
-If you have the meshastic python cli installed, you can run `meshatstic --noproto` to connect the device again over the adapter and view the serial output to confirm meshtastic installed correctly.
+If you have the Meshtastic Python CLI installed, you can run `meshtastic --noproto` to connect the device again over the adapter and view the serial output to confirm Meshtastic installed correctly.
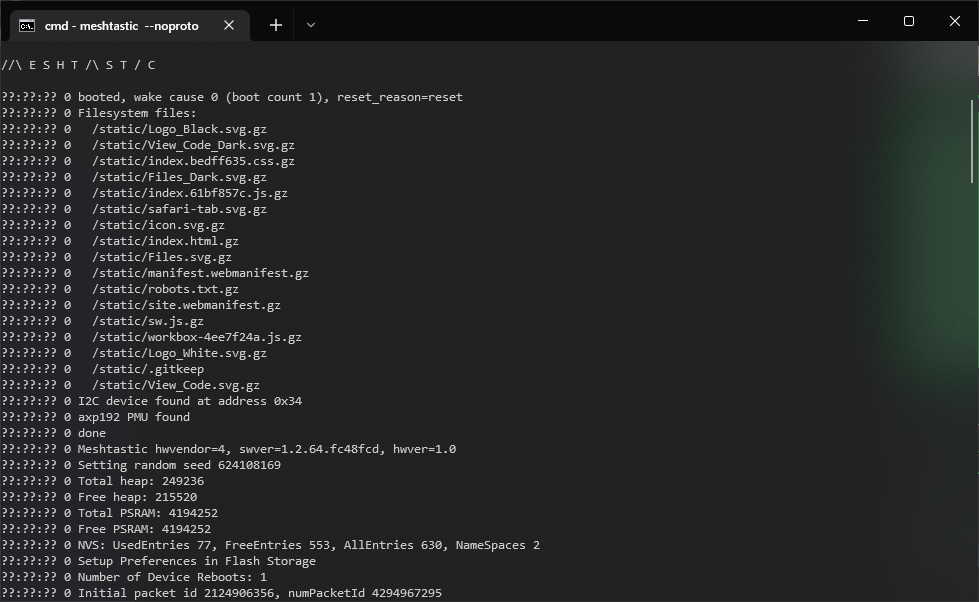
### Troubleshooting
-In the Mesthastic Flasher, device detection may not work when using the external USB to Serial adapter. You might need to manually select the correct device type from the dropdown.
+In the Meshtastic Flasher, device detection may not work when using the external USB to Serial adapter. You might need to manually select the correct device type from the drop-down.
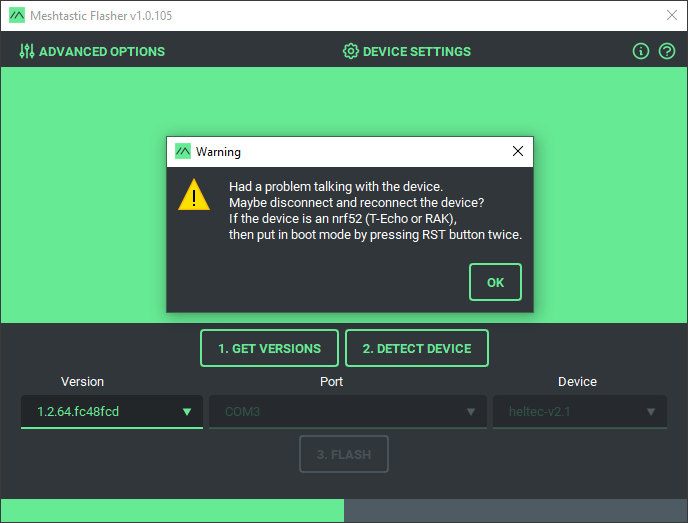
-Sometimes you might receive an error for COM port permission in the Mestastic Flasher or the manual device install scripts, this can be caused by a number of different issues.
+Sometimes you might receive an error for COM port permission in the Meshtastic Flasher or the manual device install scripts, this can be caused by a number of different issues.
You might need to run the process as an administrator, check to ensure software like Cura isn't monopolizing COM ports, or reboot.
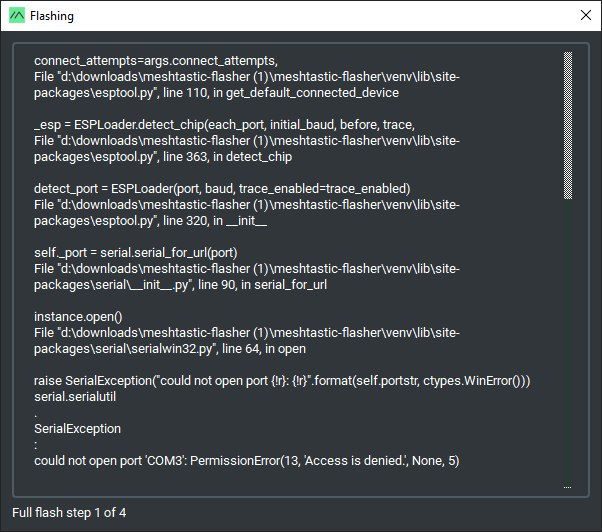
diff --git a/docs/getting-started/flashing-firmware/esp32/index.mdx b/docs/getting-started/flashing-firmware/esp32/index.mdx
index f3861a98..3af7e277 100644
--- a/docs/getting-started/flashing-firmware/esp32/index.mdx
+++ b/docs/getting-started/flashing-firmware/esp32/index.mdx
@@ -7,9 +7,7 @@ sidebar_position: 2
## Flashing Method for ESP32 Devices
-We recommend using the following methods for flashing ESP32 devices:
-
-1. The [Web-based installer](https://flasher.meshtastic.org) requires either Chrome or Edge broswers but is an excellent choice for quickly flashing devices.
+1. The [Web-based installer](https://flasher.meshtastic.org) requires either Chrome or Edge browsers but is an excellent choice for quickly flashing devices.
2. The [Python Flasher](/docs/software/python/flasher) does a lot under the hood to prevent you from needing to use the terminal. It also allows you to configure your device.
3. The [CLI Script](/docs/getting-started/flashing-firmware/esp32/cli-script) is considered the "manual process" for flashing firmware.
4. Flashing your device using an [external serial adapter](/docs/getting-started/flashing-firmware/esp32/external-serial-adapter) should only be attempted as a last resort if no other method has been successful.
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/docs/getting-started/flashing-firmware/esp32/python-flasher.mdx b/docs/getting-started/flashing-firmware/esp32/python-flasher.mdx
index fd42b885..e8b73f12 100644
--- a/docs/getting-started/flashing-firmware/esp32/python-flasher.mdx
+++ b/docs/getting-started/flashing-firmware/esp32/python-flasher.mdx
@@ -1,10 +1,10 @@
---
id: meshtastic-flasher-esp32
-title: Using Python Meshtastic Flasher
+title: Using Meshtastic Python Flasher
sidebar_label: Python Flasher
sidebar_position: 2
---
-import MFlasher from '../../../software/python/meshtastic-flasher.mdx'
+import MFlasher from '../../../software/python-flasher.mdx'
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/docs/getting-started/flashing-firmware/esp32/web-flasher.mdx b/docs/getting-started/flashing-firmware/esp32/web-flasher.mdx
index 6a84e362..f86fd86b 100644
--- a/docs/getting-started/flashing-firmware/esp32/web-flasher.mdx
+++ b/docs/getting-started/flashing-firmware/esp32/web-flasher.mdx
@@ -5,5 +5,8 @@ sidebar_label: Web Flasher (recommended)
sidebar_position: 1
---
+## Web Flasher
-The [Web-based Installer](https://flasher.meshtastic.org) requires Chrome or Edge browser.
\ No newline at end of file
+1. Plug in your device
+2. Visit [flasher.meshtastic.org](https://flasher.meshtastic.org) _\*requires Chrome or Edge browser_
+3. Follow the instructions
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/docs/getting-started/flashing-firmware/nrf52/drag-n-drop.mdx b/docs/getting-started/flashing-firmware/nrf52/drag-n-drop.mdx
index bbe414b8..57726749 100644
--- a/docs/getting-started/flashing-firmware/nrf52/drag-n-drop.mdx
+++ b/docs/getting-started/flashing-firmware/nrf52/drag-n-drop.mdx
@@ -9,27 +9,24 @@ import Tabs from '@theme/Tabs';
import TabItem from '@theme/TabItem';
:::info
-Before flashing confirm that you have [RAK4631](https://docs.rakwireless.com/Product-Categories/WisBlock/RAK4631/) and not a [RAK4631-R](https://docs.rakwireless.com/Product-Categories/WisBlock/RAK4631-R/) If this is not the case, fear not. The hardware is identical but requires changing the bootloader. Instructions on how to do this are located [here](/docs/getting-started/flashing-firmware/nrf52/#convert-rak4631-r-to-rak4631).
+Before flashing confirm that you have [RAK4631](https://docs.rakwireless.com/Product-Categories/WisBlock/RAK4631/) and not a [RAK4631-R](https://docs.rakwireless.com/Product-Categories/WisBlock/RAK4631-R/) If this is not the case, fear not. The hardware is identical but requires changing the bootloader. Instructions on how to do this are located [here](/docs/guides/convert-rak4631r).
:::
-The NRF52 based devices (LilyGO T-Echo, RAK Wisblock 4631) have the easiest firmware upgrade process. No driver or software install is required on any platform.
+## Upgrading from a previous version of Meshtastic
-Download and unzip the latest frimware from [Meshtastic Downloads](https://meshtastic.org/downloads).
+If you are upgrading your NRF52 device from a previous version of Meshtastic rather than starting from scratch, you may need to do a full factory reset of the internal flash memory. Stale data saved by previous versions of the Meshtastic firmware can cause devices to get stuck in a crash loop at startup.
-1. Connect your device to your computer with a data USB cable.
+Follow the guide to [factory erase your NRF52](/docs/guides/nrf52-erase) device before continuing to [flash firmware](#flash-firmware).
+
+
+## Flash Firmware
+
+Download and unzip the latest firmware from [Meshtastic Downloads](https://meshtastic.org/downloads).
+
+1. Connect your device to your computer with a USB data cable.
2. Double click the reset button on your device (this will put it into bootloader mode)
3. Notice a new drive will be mounted on your computer (Windows, Mac, or Linux)
4. Open this drive and you should see three files: `CURRENT.UF2`, `INDEX.HTM`, and `INFO_UF2.TXT`
-5. Drop the appropriate appropriate `firmware-DEVICE_NAME-vx.x.x-xxxxxxx.uf2` file from the release you want to install onto this drive
+5. Drop the appropriate firmware file (`firmware-DEVICE_NAME-vx.x.x-xxxxxxx.uf2`) from the release onto this drive.
-Once the file has finished copying onto the drive, the device will reboot and install the Meshtastic firmware.
-
-:::caution
-If you're upgrading your NRF52 device from a previous version of Meshtastic rather than starting from scratch, you may need to do a full factory reset of the internal flash memory. Stale data saved by previous versions of the Meshtastic firmware can cause devices to get stuck in a crash loop at startup.
-:::
-
-Meshtastic uses the [littlefs](https://github.com/littlefs-project/littlefs) library to store configuration, logs, and other data in the internal flash of NRF52 devices. Updating the firmware does _not_ erase this additional data, which can cause issues when the format and location of data changes between releases.
-
-To reset the flash storage on your NRF52 board, first follow steps 1-4 above. At step 5, copy the included file named `Meshtastic_nRF52_factory_erase.uf2` onto the virtual disk device instead of a `firmware-DEVICE_NAME...` binary. After the device resets, connect to it via serial console using the [Meshtastic CLI `--noproto`](/docs/software/python/cli/#--noproto) mode or a standalone serial client like `minicom`. When you connect to the serial console, press any key; you should see the message `Formating ... Done`.
-
-Once the flash is erased you can use steps 2-5 above to re-install the latest Meshtastic firmware on a clean storage filesystem.
+Once the file has finished copying onto the drive, the device will reboot and install the Meshtastic firmware.
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/docs/getting-started/flashing-firmware/nrf52/index.mdx b/docs/getting-started/flashing-firmware/nrf52/index.mdx
index e8116ef3..0b5e8473 100644
--- a/docs/getting-started/flashing-firmware/nrf52/index.mdx
+++ b/docs/getting-started/flashing-firmware/nrf52/index.mdx
@@ -7,35 +7,7 @@ sidebar_position: 2
## Flashing Methods for NRF52 Devices
-If you have RAK NRF based devices or a LilyGO T-Echo
+The NRF52 based devices have the easiest firmware upgrade process. No driver or software install is required on any platform.
1. The [drag and drop](/docs/getting-started/flashing-firmware/nrf52/drag-n-drop) firmware installation is considered the "manual process" and recommended as the easiest solution.
2. The [Python Flasher](/docs/software/python/flasher) application does a lot under the hood to prevent you from needing to use the terminal. It also allows you to configure your device.
-
-## Convert RAK4631-R to RAK4631
-
-The RAK4631-R is just the same as the RAK4631 in terms of hardware, the only difference is the bootloader it is shipped with.
-
-The RAK4631-R is shipped with the RUI3 bootloader, the RAK4631 with the Arduino bootloader.
-
-Running Meshtastic on RAK WisBlock NRF52-based boards relies on the Arduino bootloader.
-
-The process of converting the bootloader only needs to be performed once.
-
-This conversion requires the use of either a [DAPLink](https://daplink.io/) or [J-Link](https://www.segger.com/products/debug-probes/j-link/). The most reasonably priced and avaliable is the [RAKDAP1](https://store.rakwireless.com/products/daplink-tool).
-
-1. Install [Python](https://www.python.org/downloads/)
-2. Install [pyOCD](https://pyocd.io/)
- ```shell
- pip3 install pyocd
- ```
-3. Download the required bootloader: [WisCore_RAK4631_Board_Bootloader.hex](https://github.com/RAKWireless/WisBlock/releases/download/0.4.2/WisCore_RAK4631_Board_Bootloader.hex)
-4. Connect the RAKDAP as follows:
- [](/img/rak4631-rakdap1.png)
-5. Flash the bootloader
- ```shell
- pyocd flash -t nrf52840 .\WisCore_RAK4631_Board_Bootloader.hex
- ```
-6. Continue with the normal [flashing instructions](/docs/getting-started/flashing-firmware/nrf52/drag-n-drop)
-
-Alternate methods of flashing are outlined [here](https://github.com/RAKWireless/WisBlock/tree/master/bootloader/RAK4630).
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/docs/getting-started/flashing-firmware/nrf52/python-flasher.mdx b/docs/getting-started/flashing-firmware/nrf52/python-flasher.mdx
index 669150f2..751c2332 100644
--- a/docs/getting-started/flashing-firmware/nrf52/python-flasher.mdx
+++ b/docs/getting-started/flashing-firmware/nrf52/python-flasher.mdx
@@ -1,10 +1,10 @@
---
id: meshtastic-flasher-nrf52
-title: Using Python Meshtastic Flasher
+title: Using Meshtastic Python Flasher
sidebar_label: Python Flasher
sidebar_position: 2
---
-import MFlasher from '../../../software/python/meshtastic-flasher.mdx'
+import MFlasher from '../../../software/python-flasher.mdx'
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/docs/getting-started/index.mdx b/docs/getting-started/index.mdx
index 75b2aa5d..2f932b3d 100644
--- a/docs/getting-started/index.mdx
+++ b/docs/getting-started/index.mdx
@@ -1,5 +1,4 @@
---
-id: overview
title: Getting Started
sidebar_label: Getting Started
slug: /getting-started
@@ -10,13 +9,13 @@ import Link from '@docusaurus/Link';
import Tabs from '@theme/Tabs';
import TabItem from '@theme/TabItem';
-## Identify your Hardware
+## Identify Hardware
-The first order of business in getting started is determining what type of hardware you will be working with. Meshtastic currently supports devices with either of the two Microcontroller Units (MCU):
+The first order of business in getting started is determining what type of hardware you will be working with. Meshtastic currently supports devices with either of the two Micro-Controller Units (MCU):
### ESP32
-The ESP32 is older and consumes more power than the nrf52, but is equiped with both WiFi and Bluetooth. Supported ESP32 devices:
+The ESP32 is older and consumes more power than the nrf52, but is equipped with both WiFi and Bluetooth. Supported ESP32 devices:
- LILYGO® TTGO T-Beam
- LILYGO® TTGO Lora
@@ -25,33 +24,32 @@ The ESP32 is older and consumes more power than the nrf52, but is equiped with b
### NRF52
-The NRF52 is much more power effecient than the esp32 and easier to update, but is only equiped Bluetooth. Supported NRF52 devices:
+The NRF52 is much more power efficient than the esp32 and easier to update, but is only equipped with Bluetooth. Supported NRF52 devices:
- RAK WisBlock
- LILYGO® TTGO T-Echo
:::info
-If your device is not listed above, please review our [supported hardware](/docs/category/supported-hardware) devices to determine which MCU your device has or contact us in [Discord](https://discord.gg/ktMAKGBnBs) with any questions.
+If your device is not listed above, please review our [supported hardware](/docs/supported-hardware) devices to determine which MCU your device has or contact us in [Discord](https://discord.gg/ktMAKGBnBs) with any questions.
:::
-## Connect your device
+## Setup Working Environment
-:::danger
-Stop! Never power on the radio without attaching an antenna! (it could damage the radio chip)
+:::danger STOP! Put the power cable down!
+Never power on the radio without attaching an antenna! _it could damage the radio chip._
:::
Prior to connecting your Meshtastic device to the computer, you should perform the following basic checks.
### Verify data cable
-Some cables only provide _charging_, verify that your cable is also capable of _transfering data_ before proceeding.
+Some cables only provide _charging_, verify that your cable is also capable of _transferring data_ before proceeding.
There is no definitive way to determine the difference in cables if you aren't willing to pull it apart. Trying out a few cables will be the best way to verify.
Once you've located a working data cable, [install the correct serial driver](#install-serial-drivers) and [test for driver installation](#test-for-driver-installation).
-
-### Install Serial Drivers
+### Install serial drivers
-### Test for driver installation
+### Test driver installation
You can verify that you have a proper data cable (rather than a charge-only type cable) and that the appropriate drivers for your system are installed by performing the following test:
@@ -120,7 +118,7 @@ If you do not see your device:
2. You may need to [install the USB serial driver](/docs/getting-started/serial-drivers)).
:::
-## Flashing Firmware
+## Flash Firmware
### ESP32
@@ -135,7 +133,7 @@ If you do not see your device:
### NRF52
-For RAK4631 users, if you have a RAK4631-R (the RUI3 bootloader version of the RAK4631), please [convert to the Arduino bootloader](/docs/getting-started/flashing-firmware/nrf52/#convert-rak4631-r-to-rak4631)
+For RAK4631 users, if you have a RAK4631-R (the RUI3 bootloader version of the RAK4631), you must [convert it to use the Arduino bootloader](/docs/getting-started/flashing-firmware/nrf52/#convert-rak4631-r-to-rak4631)
+## Connect to Device
+
+Depending on your device, there are 3 ways to connect to your device:
+
+### Serial
+
+
+
+ Connect using Serial
+
+
+
+
+### Bluetooth
+
+
+
+ Connect using Bluetooth
+
+
+
+### Network
+
+Connecting over network is only supported on ESP32 devices.
+
+
+
+ Connect over Network
+
+
+
+
+## Configure Device
+
+The initial configuration of the device includes setting the regional settings...
+
+
+
+ Configure Device
+
+
+
## Use Meshtastic
-There are many ways to interact with and use Meshtastic, please visit the [Software](/docs/software) page for more information.
+### with Command Line Tools
+ - [Python CLI](/docs/software/python/cli)
### with mobile apps
- - [Android](/docs/software/android/)
- - [Apple](/docs/software/apple/)
+ - [Android](/docs/category/android-app)
+ - [Apple](/docs/category/apple-apps)
### with a browser
- https://client.meshtastic.org
- - [Meshtastic Web](/docs/software/web/)
+ - [Meshtastic Web](/docs/software/web-client)
### over the internet with MQTT
- [MQTT](/docs/software/mqtt/)
+There are many ways to interact with and use Meshtastic, please visit the [Software](/docs/software) page for more information.
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/docs/getting-started/init-config.mdx b/docs/getting-started/init-config.mdx
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..f4984870
--- /dev/null
+++ b/docs/getting-started/init-config.mdx
@@ -0,0 +1,103 @@
+---
+title: Initial Configuration
+sidebar_label: Initial Configuration
+slug: /getting-started/initial-config
+sidebar_position: 4
+---
+
+import Tabs from '@theme/Tabs';
+import TabItem from '@theme/TabItem';
+import LoRaRegions from '../blocks/_lora-regions.mdx';
+
+
+## Connection Supported Clients
+
+Depending on your connection, some configuration options are not fully supported. Find out which Client is best for your type of connection.
+
+
+
+
+- [Python CLI](/docs/software/python/cli/)
+- [Web Client](https://client.meshtastic.org)
+
+
+
+
+
+- [Web Client](https://client.meshtastic.org)
+
+
+
+
+
+- [Web Client](https://client.meshtastic.org)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+### Configure Regional Settings
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+:::info
+Region and Modem Preset can be configured on Android.
+:::
+
+
+
+
+:::info
+Configuration of Region, Modem Preset and Hop Limit is available on iOS, iPadOS and macOS at Settings > Radio Configuration > LoRa.
+:::
+
+
+
+
+```sh
+meshtastic --set lora.region
+```
+
+
+
+
+:::info
+No LoRa config options are available in the Flasher.
+:::
+
+
+
+
+:::info
+All LoRa config options are available in the Web UI.
+:::
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
diff --git a/docs/getting-started/serial-drivers/index.old b/docs/getting-started/serial-drivers/index.old
deleted file mode 100644
index 43d44365..00000000
--- a/docs/getting-started/serial-drivers/index.old
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,83 +0,0 @@
----
-id: serial-drivers
-title: Installing Serial Drivers
-sidebar_label: Install Serial Drivers
-sidebar_position: 1
----
-
-import Tabs from '@theme/Tabs';
-import TabItem from '@theme/TabItem';
-
-:::caution
-Make sure not to power the radio on without first attaching the antenna! You could damage the radio chip!
-:::
-
-Prior to connecting your Meshtastic device to the computer, you should perform the following basic checks.
-
-## Verify data cable
-
-Verify that you have a **data cable** and _not_ a **charging _only_ cable** before proceeding. There is no definitive way to determine the difference in cables if you aren't willing to pull it apart. Trying out a few cables will be the best way to verify.
-
-Once you've located a working data cable, [test for driver installation](/docs/getting-started/serial-drivers/#test-for-driver-installation) to see if you need to install a driver to communicate with your device.
-
-If you know you have installed the correct driver, the following step can be used to check if you have a proper data cable.
-
-## Test for driver installation
-
-You can verify that you have a proper data cable (rather than a charge-only type cable) and that the appropriate drivers for your system are installed by performing the following test:
-
-_select your operating system below_
-
-
-
-
-1. Connect your Meshtastic device to your USB port
-2. Open a **Terminal** and enter the following command:
-
- ```shell
- lsusb
- ```
-3. You should see something like:
-
- ```shell
- ID xxxx:xxxx Silicon Labs CP210x UART Bridge
- # or
- ID xxxx:xxxx QinHeng Electronics USB Single Serial
- # or
- FIXME (WISBLOCK OUTPUT)
- ```
-
-
-
-
-1. Navigate to `Apple Menu > About This Mac > System Report... > Hardware > USB`.
-2. You should see similar to one of the following entries:
- - `CP210X USB to UART Bridge Controller`
- - `CH9102 USB to UART Bridge Controller`
- - `WisCore RAK4631 Board`
-
-
-
-
-1. Navigate to `Device Manager > Ports (COM & LPT)`
-2. You should see similar to one of the following entries:
- - `Silicon Labs CP210X USB to UART Bridge (COM5)`
- - `Silicon Labs CH9102 USB to UART Bridge (COM5)`
- - `FIXME (WISBLOCK OUTPUT)`
-
-
-
-
-If you can see your device, you are ready to flash the firmware. Skip to the [Flashing Firmware](/docs/getting-started/flashing-firmware/) section.
-
-If you do not see your device after performing the check:
-
-1. You may be using a charging-only cable.
-2. You may need to install the USB serial driver corrosponding to your device ([ESP32](/docs/getting-started/serial-drivers/installing-esp32-serial-drivers) or [NRF52](/docs/getting-started/serial-drivers/installing-nrf52-serial-drivers)).
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/docs/getting-started/serial-drivers/serial-drivers-esp32.mdx b/docs/getting-started/serial-drivers/serial-drivers-esp32.mdx
index 064523ed..361be105 100644
--- a/docs/getting-started/serial-drivers/serial-drivers-esp32.mdx
+++ b/docs/getting-started/serial-drivers/serial-drivers-esp32.mdx
@@ -2,6 +2,7 @@
id: installing-esp32-serial-drivers
title: ESP32 Serial Drivers
sidebar_label: ESP32 Drivers
+#pagination_next: /docs/getting-started
sidebar_position: 1
---
diff --git a/docs/guides/_category_.yml b/docs/guides/_category_.yml
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..6a3e4cb3
--- /dev/null
+++ b/docs/guides/_category_.yml
@@ -0,0 +1,7 @@
+label: Guides
+collapsible: true
+position: 3
+link:
+ type: generated-index
+ title: Guides
+ slug: guides
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/docs/guides/convert-rak4631r.mdx b/docs/guides/convert-rak4631r.mdx
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..dacebba5
--- /dev/null
+++ b/docs/guides/convert-rak4631r.mdx
@@ -0,0 +1,28 @@
+---
+id: convert-rak4631r
+title: Convert RAK4631-R to RAK4631
+sidebar_label: Convert RAK4631-R
+sidebar_position: 4
+---
+
+The only difference between the _RAK4631-R_ (RUI3) and the _RAK4631_ (Arduino) is the bootloader it is shipped with - the hardware is the same.
+
+Meshtastic requires the Arduino bootloader on RAK WisBlock NRF52-based boards. The process of converting the bootloader only needs to be performed once.
+
+This conversion requires the use of either a [DAPLink](https://daplink.io/) or [J-Link](https://www.segger.com/products/debug-probes/j-link/). The most reasonably priced and available is the [RAKDAP1](https://store.rakwireless.com/products/daplink-tool).
+
+1. Install [Python](https://www.python.org/downloads/)
+2. Install [pyOCD](https://pyocd.io/)
+ ```shell
+ pip3 install pyocd
+ ```
+3. Download the required bootloader: [WisCore_RAK4631_Board_Bootloader.hex](https://github.com/RAKWireless/WisBlock/releases/download/0.4.2/WisCore_RAK4631_Board_Bootloader.hex)
+4. Connect the RAKDAP as follows:
+ [](/img/rak4631-rakdap1.png)
+5. Flash the bootloader
+ ```shell
+ pyocd flash -t nrf52840 .\WisCore_RAK4631_Board_Bootloader.hex
+ ```
+6. Continue with the normal [flashing instructions](/docs/getting-started/flashing-firmware/nrf52/drag-n-drop)
+
+Alternate methods of flashing are outlined [here](https://github.com/RAKWireless/WisBlock/tree/master/bootloader/RAK4630).
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/docs/guides/link-mqtt.mdx b/docs/guides/link-mqtt.mdx
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..8424cf2a
--- /dev/null
+++ b/docs/guides/link-mqtt.mdx
@@ -0,0 +1,10 @@
+---
+id: setup-mqtt
+title: Configuring MQTT
+sidebar_label: Setup MQTT
+sidebar_position: 1
+---
+
+import MQTT from '../software/mqtt/index.mdx'
+
+
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/docs/guides/link-remote-admin.mdx b/docs/guides/link-remote-admin.mdx
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..9db5a6bb
--- /dev/null
+++ b/docs/guides/link-remote-admin.mdx
@@ -0,0 +1,10 @@
+---
+id: remote-nodes
+title: Remote Node Administration
+sidebar_label: Administer Remote Nodes
+sidebar_position: 2
+---
+
+import RemoteAdmin from '../configuration/remote-admin.mdx'
+
+
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/docs/guides/nrf52-erase.mdx b/docs/guides/nrf52-erase.mdx
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..0591ddeb
--- /dev/null
+++ b/docs/guides/nrf52-erase.mdx
@@ -0,0 +1,22 @@
+---
+id: nrf52-erase
+title: Flash NRF52 Factory Erase
+sidebar_label: Factory Erase NRF52
+sidebar_position: 3
+---
+
+Meshtastic uses the [littlefs](https://github.com/littlefs-project/littlefs) library to store configuration, logs, and other data in the internal flash of NRF52 devices. Updating the firmware does _not_ erase this additional data, which can cause issues when the format and location of data changes between releases.
+
+To reset the flash storage on your NRF52 board:
+
+Download and unzip the latest firmware from [Meshtastic Downloads](https://meshtastic.org/downloads).
+
+1. Connect your device to your computer with a USB data cable.
+2. Double click the reset button on your device (this will put it into bootloader mode)
+3. Notice a new drive will be mounted on your computer (Windows, Mac, or Linux)
+4. Open this drive and you should see three files: `CURRENT.UF2`, `INDEX.HTM`, and `INFO_UF2.TXT`
+5. Copy the included file named `Meshtastic_nRF52_factory_erase.uf2` onto the virtual disk device. The device should reboot.
+6. Connect to the device via serial console using the [Meshtastic CLI `--noproto`](/docs/software/python/cli/#--noproto) mode or a standalone serial client like `minicom`.
+7. Press any key, you should see the message: `Formatting... Done`.
+
+Once the device has been erased, you can proceed to install the latest Meshtastic firmware on a clean storage filesystem by following the [flash firmware](/docs/getting-started/flashing-firmware/nrf52/drag-n-drop#flash-firmware) steps.
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/docs/hardware/_category_.yml b/docs/hardware/_category_.yml
index 45bce8b6..0c5e85d6 100644
--- a/docs/hardware/_category_.yml
+++ b/docs/hardware/_category_.yml
@@ -1,7 +1,7 @@
-position: 3 # float position is supported
-label: 'Hardware'
-collapsible: true # make the category collapsible
+label: Hardware
+collapsible: true
+position: 5
link:
type: generated-index
- title: Hardware
+ title: Supported Hardware
slug: hardware
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/docs/hardware/antennas.mdx b/docs/hardware/antennas.mdx
deleted file mode 100644
index 8399a30b..00000000
--- a/docs/hardware/antennas.mdx
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,53 +0,0 @@
----
-id: lora-antenna
-title: LoRa Antenna Selection
-sidebar_label: LoRa Antennas
-sidebar_position: 2
----
-
-The stock antennas provided with the T-Beam and other boards usually come from 'mixed bags'. They may not have been designed or tuned for your given frequency range, and they may not be of a quality design.
-
-Matching an antenna to the transceiver frequency is important, as is choosing an appropriate design.
-
-The antennas's design will affect:
-
-- Efficiency - The proportion of the signal which leaves the antenna
-- Direction in which the signal is transmitted
-- Interference by horizontal or vertical polarization
-- Amount of signal which is reflected back to the device itself
-
-:::caution
-While the LoRa devices we are using for Meshtastic are relatively low power radios, care should be taken _not_ to operate any radio transmission device without an aerial or with a poorly matched aerial. Un-transmitted radio signal reflected back to the transmitter can damage the device.
-:::
-
-## Important considerations
-
-### What transmission frequency are you using?
-- Devices on another frequency will not be able to interact with yours.
-- See this listing by [The Things Network](https://www.thethingsnetwork.org/docs/lorawan/frequencies-by-country.html) for frequencies licensed for specific countries.
-
-### How will you be carrying / transporting the radio?
-- A large directional aerial will transmit over significantly greater distance than an omni-directional aerial. However, it must be pointed at its target so isn't optimal for mobile use.
-- A tuned half-wave whip aerial may have more omni-directional range than the quarter wave stubby; but it will be conspicuous in your pocket.
-- Many antennas, especially quarter wave stubby antennas, require the use of ground planes to transmit at peak performance.
-
-### Do you want transmission in all directions?
-- While humans (mostly water) don't attenuate signal greatly (at LoRa frequencies), buildings & walls do.
-- If your aerial is permanently positioned against a building, signal transmitted towards the wall will be largely lost or attenuated.
-
-### Does my Meshtastic device have the right power range, impedance, and connector for the aerial?
-- For the LoRa devices, it should be 50 Ohm impedance with SMA connector. Many antennas will be recommended for LoRa use in their technical details.
-- By contrast, a close range, contactless Personal Area Network antenna, or a huge aerial at the end of length of coax designed for a 100W transmitter, are not going to be operable.
-
-
-### Cost, quality, and supply service?
-- The perfect aerial on paper, sourced from the other side of the world with mixed reviews, doesn't compare to a local supplier who has spent time carefully collating all of the aerial data-sheets for comparison _and_ holds stock immediately available. Personally, I prefer to pay significantly more for a time saving, quality service.
-
-### How close will the antenna be to my Meshtastic device?
-- Most cables will significantly degrade the signal strength over any significant distance. It is often more effective to place a node outside, than to have it indoors with the antenna outside. (The exception might be if there is extreme heat, cold, or humidity, and if the shortest possible low loss cable is used. Still, a proper enclosure should mitigate bad weather.)
-
-## Terminology / references
-
-You could do a lot worse than reading the [Wikipedia entry for Antenna](), along with the [Wikipedia entry for LoRa](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/LoRa).
-
-Instead of listing the terms, let us recommend this superb [tutorial](https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=J3PBL9oLPX8) by Andreas Spiess (the 'guy with the Swiss accent').
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/docs/hardware/devices/_category_.yml b/docs/hardware/devices/_category_.yml
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..6044c266
--- /dev/null
+++ b/docs/hardware/devices/_category_.yml
@@ -0,0 +1,7 @@
+label: Devices
+collapsible: true
+position: 1
+link:
+ type: generated-index
+ title: Supported Devices
+ slug: supported-hardware
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/docs/hardware/supported/lora.mdx b/docs/hardware/devices/lora.mdx
similarity index 96%
rename from docs/hardware/supported/lora.mdx
rename to docs/hardware/devices/lora.mdx
index fa8107e4..997f08fb 100644
--- a/docs/hardware/supported/lora.mdx
+++ b/docs/hardware/devices/lora.mdx
@@ -20,7 +20,7 @@ values={[
]}>
-- ESP32 - Wifi & Bluetooth
+- ESP32 - WiFi & Bluetooth
- SX1276 - LoRa Transceiver
- Frequency options:
- 868 MHz
@@ -30,17 +30,15 @@ values={[
- Reset and Program switches
- No GPS
-
- Firmware file: `firmware-tlora-v1-1.x.x.bin`
- [Purchase link](https://www.aliexpress.com/item/32840238513.html)
-
[](/img/hardware/lora-v1.png)
-- ESP32 - Wifi & Bluetooth
+- ESP32 - WiFi & Bluetooth
- SX127x - LoRa Transceiver
- Frequency options:
- 868 MHz
@@ -61,7 +59,7 @@ values={[
-- ESP32 - Wifi & Bluetooth
+- ESP32 - WiFi & Bluetooth
- SX127x - LoRa Transceiver
- Frequency options:
- 433 MHz
@@ -83,7 +81,7 @@ values={[
-- ESP32 - Wifi & Bluetooth
+- ESP32 - WiFi & Bluetooth
- SX127x - LoRa Transceiver
- Frequency options:
- 433 MHz
@@ -99,7 +97,6 @@ values={[
- Firmware file: `firmware-tlora-v2-1-1.6-1.x.x.bin`
- [Purchase link](https://www.aliexpress.com/item/32915894264.html)
-
:::warning
diff --git a/docs/hardware/supported/nano-g1.mdx b/docs/hardware/devices/nano-g1.mdx
similarity index 85%
rename from docs/hardware/supported/nano-g1.mdx
rename to docs/hardware/devices/nano-g1.mdx
index 35346bd5..8f552425 100644
--- a/docs/hardware/supported/nano-g1.mdx
+++ b/docs/hardware/devices/nano-g1.mdx
@@ -7,7 +7,7 @@ sidebar_position: 4
The Nano G1 is the first dedicated hardware to be designed from scratch purely for Meshtastic by Neil Hao. It has been designed to be small and compact with the inclusion of a high quality internal PCB antenna.
-Only the US 915 Mhz version is available currently. There should be an EU 868 Mhz version available in the future.
+Only the US 915 MHz version is available currently. There should be an EU 868 MHz version available in the future.
### Features
@@ -15,10 +15,10 @@ Only the US 915 Mhz version is available currently. There should be an EU 868 Mh
- ESP32 WROOM microprocessor - WiFi & Bluetooth
- Semtech SX1276 - LoRa Transceiver
- Frequency options:
- - 915 Mhz
+ - 915 MHz
- Additional ultra-low noise amplifier to improve LoRa receiver sensitivity
- ATGM336H-5N-71 Whole Constellation Positioning and Navigation Module (Supports GPS, BDS and GLONASS)
-- Built in 915Mhz Lora PCB Antenna (VSWR <=1.5 @ 915 Mhz)
+- Built in 915Mhz Lora PCB Antenna (VSWR <=1.5 @ 915 MHz)
- User button
- 1.3 inch OLED screen
- Buzzer
diff --git a/docs/hardware/supported/rak4631.mdx b/docs/hardware/devices/rak4631.mdx
similarity index 96%
rename from docs/hardware/supported/rak4631.mdx
rename to docs/hardware/devices/rak4631.mdx
index f14c471a..c603261b 100644
--- a/docs/hardware/supported/rak4631.mdx
+++ b/docs/hardware/devices/rak4631.mdx
@@ -38,7 +38,6 @@ values={[
- I2C, UART, GPIOs and analog input accessible with solder contacts
- Micro USB port for debugging and power
-
Further information on the RAK5005-O can be found on the [RAK Documentation Center](https://docs.rakwireless.com/Product-Categories/WisBlock/RAK5005-O/Overview/#product-description).
It may be possible to add a user button using the [13002 IO module](https://store.rakwireless.com/collections/wisblock-interface/products/adapter-module-rak13002).
@@ -46,7 +45,6 @@ It may be possible to add a user button using the [13002 IO module](https://stor
- [Update the bootloader](https://docs.rakwireless.com/Product-Categories/WisBlock/RAK4631/Quickstart/#updating-the-bootloader) on first use! This can be done easily with [Meshtastic-flasher](https://github.com/meshtastic/Meshtastic-gui-installer).
- Firmware for 5005 base board: [`firmware-rak4631-1.x.x.uf2`](/downloads)
-
-The [RAK1921 OLED display](https://store.rakwireless.com/products/rak1921-oled-display-panel) is a 0.96 inch monocrome display.
+The [RAK1921 OLED display](https://store.rakwireless.com/products/rak1921-oled-display-panel) is a 0.96 inch monochrome display.
- 0.96 inch OLED display
- Resolution 128 x 64 pixels
@@ -252,7 +250,7 @@ The [RAK1400 EPD module](https://store.rakwireless.com/products/wisblock-epd-mod
- Occupies the IO Port of a Wisblock Base
-- Firmware for 5005 with RAK14000 epaper: [`firmware-rak4631_eink-1.3.x.uf2`](/downloads)
+- Firmware for 5005 with RAK14000 e-paper: [`firmware-rak4631_eink-1.3.x.uf2`](/downloads)
2C on slot B for firmware versions 1.49 and above.
- uBlox Zoe-M8Q GNSS receiver
-- GPS, GLONASS, QZSS and BeiDou satelite support
+- GPS, GLONASS, QZSS and BeiDou satellite support
Further information on the RAK12500 can be found on the [RAK Documentation Center](https://docs.rakwireless.com/Product-Categories/WisBlock/RAK12500/Overview/#product-description).
@@ -305,7 +303,7 @@ Further information on the RAK18001 can be found on the [RAK Documentation Cente
-The [RAK13002 IO Module](https://store.rakwireless.com/collections/wisblock-interface/products/adapter-module-rak13002) can be used to, amongst other things, add a user button to the RAK base boards (excluding the RAK19003 Mini base board). It features a number of different interface options:
+The [RAK13002 IO Module](https://store.rakwireless.com/collections/wisblock-interface/products/adapter-module-rak13002) can be used to, among other things, add a user button to the RAK base boards (excluding the RAK19003 Mini base board). It features a number of different interface options:
- 2x I2C interfaces
- 2x UART interfaces
diff --git a/docs/hardware/supported/station-g1.mdx b/docs/hardware/devices/station-g1.mdx
similarity index 91%
rename from docs/hardware/supported/station-g1.mdx
rename to docs/hardware/devices/station-g1.mdx
index 49843154..c1a3c1ed 100644
--- a/docs/hardware/supported/station-g1.mdx
+++ b/docs/hardware/devices/station-g1.mdx
@@ -7,7 +7,7 @@ sidebar_position: 3
The Station G1 is the first dedicated hardware to be designed from scratch purely for Meshtastic Licensed (HAM) Operation by Neil Hao. It has been designed to be small and compact with the inclusion of 35dBm high power PA.
-Only the US 915 Mhz version is available currently. There should be an EU 433 Mhz version available in the future.
+Only the US 915 MHz version is available currently. There should be an EU 433 MHz version available in the future.
### Features
@@ -15,7 +15,7 @@ Only the US 915 Mhz version is available currently. There should be an EU 433 Mh
- ESP32 WROOM microprocessor - WiFi & Bluetooth
- Semtech SX1262 - LoRa Transceiver
- Frequency options:
- - 915 Mhz
+ - 915 MHz
- Additional 35dBm Lora Power Amplifier to boost the transmit power
- User button
- 1.3 inch OLED screen
diff --git a/docs/hardware/supported/tbeam.mdx b/docs/hardware/devices/tbeam.mdx
similarity index 96%
rename from docs/hardware/supported/tbeam.mdx
rename to docs/hardware/devices/tbeam.mdx
index 7ed0b940..cd9e8bfa 100644
--- a/docs/hardware/supported/tbeam.mdx
+++ b/docs/hardware/devices/tbeam.mdx
@@ -19,10 +19,11 @@ values={[
{label: 'T-Beam with M8N & SX1262', value: 'sx1262'},
{label: 'T-Beam v0.7', value:'0.7'}
]}>
+
-- Meshtastic pre-installed
-- ESP32 - Wifi & Bluetooth
+- Meshtastic preinstalled
+- ESP32 - WiFi & Bluetooth
- SX1276 - LoRa Transceiver
- Frequency options:
- 433 MHz
@@ -34,6 +35,7 @@ values={[
- Power, Program and Reset switches
- **Comes with 0.96 inch OLED display (some soldering required to assemble)**
+
- Firmware file: `firmware-tbeam-1.x.x.bin`
- [Purchase link](https://www.aliexpress.com/item/4001178678568.html)
@@ -42,9 +44,10 @@ values={[
[](/img/hardware/t-beam_v1.1_pinmap.webp)
+
-- ESP32 - Wifi & Bluetooth
+- ESP32 - WiFi & Bluetooth
- SX1276 - LoRa Transceiver
- Frequency options:
- 433 MHz
@@ -66,7 +69,7 @@ values={[
-- ESP32 - Wifi & Bluetooth
+- ESP32 - WiFi & Bluetooth
- **SX1262 - LoRa Transceiver - improved performance**
- Frequency options:
- 433 MHz
@@ -94,7 +97,7 @@ This is an earlier version of the T-Beam board, and due to changes in the design
`firmware-tbeam0.7-1.x.x.bin` is the correct firmware. `firmware-tbeam-1.x.x.bin` is incompatible. For all other T-Beam boards `firmware-tbeam-1.x.x.bin` is the correct selection.
:::
-- ESP32 - Wifi & Bluetooth
+- ESP32 - WiFi & Bluetooth
- SX1276 - LoRa Transceiver
- Frequency options:
- 433 MHz
diff --git a/docs/hardware/supported/techo.mdx b/docs/hardware/devices/techo.mdx
similarity index 95%
rename from docs/hardware/supported/techo.mdx
rename to docs/hardware/devices/techo.mdx
index b860b996..4f7a501b 100644
--- a/docs/hardware/supported/techo.mdx
+++ b/docs/hardware/devices/techo.mdx
@@ -5,7 +5,7 @@ sidebar_label: LILYGO® T-Echo
sidebar_position: 2
---
-The T-Echo is the latest device to be release by LILYGO® supporting a low power consumption microcontroller.
+The T-Echo is the latest device to be release by LILYGO® supporting a low power consumption micro-controller.
### Features
@@ -18,7 +18,6 @@ The T-Echo is the latest device to be release by LILYGO® supporting a low power
- Optional BME280 - Humidity and Pressure Sensor
- Comes with a case and battery
-### Resources
- Firmware file: `firmware-t-echo-2.x.x.uf2`
- [Purchase link](https://www.aliexpress.com/item/1005002842456390.html)
diff --git a/docs/hardware/enclosures/3dprinted.mdx b/docs/hardware/enclosures/3dprinted.mdx
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..ebab7f8f
--- /dev/null
+++ b/docs/hardware/enclosures/3dprinted.mdx
@@ -0,0 +1,8 @@
+---
+id: 3dprinted-enclosure
+title: 3D Printed Enclosures
+sidebar_label: 3D Printed
+sidebar_position: 1
+---
+
+... WIP
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/docs/hardware/enclosures/_category_.yml b/docs/hardware/enclosures/_category_.yml
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..1b93b495
--- /dev/null
+++ b/docs/hardware/enclosures/_category_.yml
@@ -0,0 +1,7 @@
+label: Enclosures
+collapsible: true
+position: 3
+link:
+ type: generated-index
+ title: Enclosures
+ slug: enclosures
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/docs/hardware/peripheral/antennas/_category_.yml b/docs/hardware/peripheral/antennas/_category_.yml
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..8f6e1482
--- /dev/null
+++ b/docs/hardware/peripheral/antennas/_category_.yml
@@ -0,0 +1,7 @@
+label: Antennas
+collapsible: true
+position: 1
+link:
+ type: generated-index
+ title: Antennas
+ slug: antenna
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/docs/field-tests/antenna/antenna-report.mdx b/docs/hardware/peripheral/antennas/antenna-report.mdx
similarity index 100%
rename from docs/field-tests/antenna/antenna-report.mdx
rename to docs/hardware/peripheral/antennas/antenna-report.mdx
diff --git a/docs/hardware/peripheral/antennas/lora-antennas.mdx b/docs/hardware/peripheral/antennas/lora-antennas.mdx
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..719c6c7c
--- /dev/null
+++ b/docs/hardware/peripheral/antennas/lora-antennas.mdx
@@ -0,0 +1,61 @@
+---
+id: lora-antenna
+title: LoRa Antenna Selection
+sidebar_label: LoRa Antennas
+sidebar_position: 2
+---
+
+The stock antennas provided with the T-Beam and other boards usually come from 'mixed bags'. They may not have been designed or tuned for your given frequency range, and they may not be of a quality design.
+
+Matching an antenna to the transceiver frequency is important, as is choosing an appropriate design.
+
+The antenna's design will affect:
+
+- Efficiency - The proportion of the signal which leaves the antenna
+- Direction in which the signal is transmitted
+- Interference by horizontal or vertical polarization
+- Amount of signal which is reflected back to the device itself
+
+:::caution
+While the LoRa devices we use for Meshtastic are relatively low power radios, care should be taken _not_ to operate any radio transmission device without an antenna or with a poorly matched antenna. Un-transmitted radio signal reflected back to the transmitter can damage the device.
+:::
+
+## Important considerations
+
+### What transmission frequency are you using?
+
+Devices on another frequency will not be able to interact with yours. See this listing by [The Things Network](https://www.thethingsnetwork.org/docs/lorawan/frequencies-by-country.html) for frequencies licensed for specific countries.
+
+### How will you be carrying / transporting the radio?
+
+A large directional antenna will transmit over significantly greater distance than an omni-directional antenna. However, it must be pointed at its target - so it is not optimal for mobile use.
+
+A tuned half-wave whip antenna may have more omni-directional range than the quarter wave stubby; but it will be conspicuous in your pocket.
+
+Many antennas, especially quarter wave stubby antennas, require the use of ground planes to transmit at peak performance.
+
+### Do you want transmission in all directions?
+
+While humans (mostly water) don't attenuate signal greatly (at LoRa frequencies), buildings & walls do. If your antenna is permanently positioned against a building, signal transmitted towards the wall will be largely lost or attenuated.
+
+### Does my Meshtastic device have the right power range, impedance, and connector for the antenna?
+
+For the LoRa devices, it should be 50 Ohm impedance with SMA connector. Many antennas will be recommended for LoRa use in their technical details.
+
+In contrast, a close range, contact-less Personal Area Network antenna, or a huge antenna at the end of length of coax designed for a 100W transmitter, are not going to be operable.
+
+### Cost, quality, and supply service?
+
+The perfect antenna on paper, sourced from the other side of the world with mixed reviews, doesn't compare to a local supplier who has spent time carefully collating all of the antenna data-sheets for comparison _and_ holds stock immediately available. Personally, I prefer to pay significantly more for a time saving, quality service.
+
+### How close will the antenna be to my Meshtastic device?
+
+Most cables will significantly degrade the signal strength over any significant distance. It is often more effective to place a node outside than to have it indoors with the antenna outside. The exception might be if there is extreme heat, cold, or humidity, and if the shortest possible low loss cable is used.
+
+Still, a proper enclosure should mitigate bad weather.
+
+## Terminology / references
+
+You could do a lot worse than reading the [Wikipedia entry for Antenna](), along with the [Wikipedia entry for LoRa](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/LoRa).
+
+Instead of listing the terms, let us recommend this superb [tutorial](https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=J3PBL9oLPX8) by Andreas Spiess (the 'guy with the Swiss accent').
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/docs/field-tests/antenna/resources.mdx b/docs/hardware/peripheral/antennas/resources.mdx
similarity index 100%
rename from docs/field-tests/antenna/resources.mdx
rename to docs/hardware/peripheral/antennas/resources.mdx
diff --git a/docs/field-tests/antenna/testing.mdx b/docs/hardware/peripheral/antennas/testing.mdx
similarity index 69%
rename from docs/field-tests/antenna/testing.mdx
rename to docs/hardware/peripheral/antennas/testing.mdx
index e46aff6a..8a403769 100644
--- a/docs/field-tests/antenna/testing.mdx
+++ b/docs/hardware/peripheral/antennas/testing.mdx
@@ -7,6 +7,32 @@ sidebar_position: 1
Testing of antennas can be both simple and complex. At its simplest, testing involves sending messages from different locations and seeing which ones are received, and then comparing the results against other antennas. At the complex end, this can be using expensive test chambers and equipment to measure the signal strength, gain, and radiation patterns. However, it seems that a reasonable job can be done with cheaper methods.
+If you have sufficient range with your existing aerial, skip this section. If you don't, consider either getting more nodes and / or replace the stock aerial with one tuned (to your region transmitter's frequency):
+
+- A quarter wave _tuned_ stubby aerial (<10cm for fit-in-pocket) should have a real-world range of a couple of km without significant obstacles (buildings / hills).
+- Aerial criteria: 50 Ohm, appropriate connector (usually SMA male or U.FL), low VSWR (<2) (at tuning frequency - see its datasheet), gain > 0 dBi .
+- Caution, avoid suppliers who:
+ - don't state the aerial's tuned frequency and its specific purpose (LoRa network)
+ - claim huge gain figures on omni-directional aerials
+ - don't provide boringly professional datasheets
+
+If you want more range, directionality, or specificity read on.
+
+## General guidance
+
+The Meshtastic system is designed to be simple and intuitive to use. However, its LoRa radios rely on point-to-point communications, unit-to-unit, aerial-to-aerial; quite different to the near ubiquitous radio coverage of today's cellphone & Wifi connections.
+
+Some understanding of the factors affecting radio communications will help achieve substantially better service and faster transmission over a greater range with your devices. Here, we'll attempt to provide a top-level set of guidance for use and aerial selection, how to test the aerials, a set of resources for further research, and plenty of opportunity for going deeper.
+
+The Meshtastic devices (of various flavors) lend themselves to experimentation, not only because you can replace their aerials, but also because of their mesh operation. All nodes will, without alteration, relay communications from any other members of the mesh around obstacles and over greater distances. The cost of aerial investment should be weighed against investment in additional low-cost nodes.
+
+:::caution
+While the LoRa devices we are using for Meshtastic are relatively low power radios, care should be taken _not_ to operate any radio transmission device without an aerial or with a poorly matched aerial. Un-transmitted radio signal reflected back to the transmitter can damage the device.
+:::
+
+The information collected here is by no means definitive, and necessarily abbreviated (it's a huge topic).
+
+
## Range Testing
As mentioned, while stating the obvious, the simplest way of performing a test is:
@@ -61,3 +87,11 @@ For a bit of light reading on environmental research:
In summary - wavelengths in Europe fair well in plain sight, curve over not-so-tall obstacles (including trees), and they reflect off surfaces at low angles of incidence. They go through humans without much attenuation; but not brick, stone, or anything with more attenuation than glass / Kevlar. Oh, and don’t sit under an LTE tower and expect it to be plain sailing. RF emissions at adjacent frequencies can interfere at a high enough power.
+
+## Discussion
+
+To comment on / join in antenna range [Meshtastic discourse](https://meshtastic.discourse.group/t/antenna-improved-range/227/35?u=sens8tion)
+
+There, you will also find reference to Meshtastic range achievements and aerial recommendations. (Note we've stopped short of making specific supplier aerial recommendations in this wiki.)
+
+
diff --git a/docs/hardware/peripheral/buttons/index.mdx b/docs/hardware/peripheral/buttons/index.mdx
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..993aa195
--- /dev/null
+++ b/docs/hardware/peripheral/buttons/index.mdx
@@ -0,0 +1,16 @@
+---
+id: buttons
+title: Buttons
+sidebar_label: Buttons
+sidebar_position: 3
+---
+
+A number of devices have buttons that can be used to interact with the firmware. These buttons have a number of different functions:
+
+- Reset button - This is present on most devices.
+- Power button - This is present on some devices. A long press powers the device off or turns it back on again.
+- Program button - This is present of some devices and has a number of functions:
+ - Single press - This changes the page of information displayed on the screen.
+ - Double press - This sets the Bluetooth pairing code to `123456` (useful if you do not have a screen on the device).
+ - Long press - This adjusts the contrast of the screen.
+ - Long press during reboot - This turns on the software WiFi access point on devices that support WiFi.
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/docs/software/device/remote-hardware-service.mdx b/docs/hardware/peripheral/index.mdx
similarity index 76%
rename from docs/software/device/remote-hardware-service.mdx
rename to docs/hardware/peripheral/index.mdx
index 5578696d..a97bb52e 100644
--- a/docs/software/device/remote-hardware-service.mdx
+++ b/docs/hardware/peripheral/index.mdx
@@ -1,9 +1,26 @@
---
-id: remote-hardware-service
-title: Remote Hardware Service
-sidebar_label: Remote Hardware
+id: peripherals
+title: A Note on Peripherals
+sidebar_label: Peripherals
+sidebar_position: 2
---
+## Firmware Versions
+
+The device firmware runs on the nodes to build the mesh for communication. Each different make and model of device requires a different build of the Meshtastic firmware in order to run properly. Thankfully, due to the design of Meshtastic, it is possible to port the firmware to new devices as they become available. The firmware currently runs on a range of ESP32 based devices, but there is also increasing support for the nRF52 microprocessor with some more recent devices coming to market.
+
+The current firmware has support for a screen to display received messages, along with information about nodes on the mesh, and more detailed information about the device on which it is running.
+
+The latest firmware can be downloaded from the [Downloads](/downloads) page. If you wish to view the code or contribute to development of the firmware, please visit the device code GitHub page.
+
+:::info
+Please be aware that there are significant changes between version branches 1.2.x and 1.3.x which mean that devices need to be running the same branch of firmware to be able to talk to each other. Python, Android, and other software applications will also need to be running the same branch to be able to talk to the device.
+:::
+
+
+## Remote Hardware
+
+
:::warning
GPIO access is fundamentally dangerous because invalid options can physically damage or destroy your hardware. Ensure that you fully understand the schematic for your particular device before trying this as we do not offer a warranty. Use at your own risk.
:::
@@ -14,13 +31,13 @@ This feature uses a preinstalled module in the device code and associated comman
You can get the latest python tool/library with `pip3 install --upgrade meshtastic` on Windows/Linux/OS-X. See the [python section](/docs/software/python/cli/installation) for more details.
-## Supported operations in the initial release
+### Supported operations in the initial release
- Set any GPIO
- Read any GPIO
- Receive notification of changes in any GPIO
-## Setup
+### Setup
To prevent access from untrusted users, you must first make a `gpio` channel that is used for authenticated access to this feature. You'll need to install this channel on both the local and remote node.
@@ -43,7 +60,7 @@ If doing local testing, may want to change the speed of the channel at this time
meshtastic --info
```
-4. Connect the remote device via USB (or use the [remote admin](device-remote-admin) feature to reach it through the mesh)
+4. Connect the remote device via USB (or use the [remote admin](/docs/configuration/remote-admin) feature to reach it through the mesh)
5. Set it to join the gpio channel you created
```shell
@@ -52,7 +69,7 @@ If doing local testing, may want to change the speed of the channel at this time
Now both devices should be able to talk over the `gpio` channel. Send a text message from one the other other verify. Also run "--nodes" to verify the second node shows up.
-## A little bit of information about masks
+### A little bit of information about masks
To determine the appropriate mask for the pin(s) that you want to know. The python program (and output) below might help:
@@ -106,7 +123,7 @@ GPIO:43 mask:0x80000000000
GPIO:44 mask:0x100000000000
```
-## How to easily test GPIO operations?
+### How to easily test GPIO operations?
You can add a simple LED and resistor to validate that the GPIO operations work as expected. Used the tutorial at https://www.instructables.com/Slide-Switch-With-Arduino-Uno-R3/ as a guide.
@@ -131,11 +148,11 @@ By default, the pin may be "off" or "on". (It will most likely "off".) See the s
[](/img/LED_on_TLoraV1.jpg)
-## Doing GPIO operations
+### Doing GPIO operations
You can programmatically do operations from your own python code by using the Meshtastic `RemoteHardwareClient` class. See the [python API](/docs/software/python/cli/installation) documentation for more details.
-## Using GPIOs from the python CLI
+### Using GPIOs from the python CLI
Writing a GPIO (ex: turn "on" GPIO4):
diff --git a/docs/hardware/peripheral/screens/index.mdx b/docs/hardware/peripheral/screens/index.mdx
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..44c4b668
--- /dev/null
+++ b/docs/hardware/peripheral/screens/index.mdx
@@ -0,0 +1,32 @@
+---
+id: screens
+title: Screens
+sidebar_label: Screens
+sidebar_position: 2
+---
+
+A number of devices have screens capable of displaying the messages received, information about the mesh, and other details. On powering the device it will display the Meshtastic splash screen with the version number for a couple of seconds:
+
+
+
+The screen is split up into pages, through which you can navigate using the program button as described above. The first page to be displayed will be the message screen where received messages are displayed along with the name of the node it came from. The devices will automatically switch to this page when a new message is received.
+
+
+
+The next pages display information about the nodes that are currently on the mesh. This includes the distance and direction to that node, the signal strength, and the time last seen.
+
+ 
+
+The next page shows information about the device, battery power, current / total nodes, number of GPS satellites seen, channel name, last digits of the MAC address, and a brief log including the names of the last nodes to join the mesh.
+
+
+
+The final page shows current battery voltage and percent charge, as well as noting how long the device has been online and the current GPS time, and GPS location.
+
+
+
+If the device WiFi has been enabled (only possible on ESP32 devices), another page appears displaying information about the WiFi settings, IP address, and number of devices connected to the WiFi.
+
+
+
+With a further press of the program button, the screen will cycle round to the message page.
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/docs/hardware/supported/_category_.yml b/docs/hardware/supported/_category_.yml
deleted file mode 100644
index 8cb5bb99..00000000
--- a/docs/hardware/supported/_category_.yml
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,7 +0,0 @@
-
-position: 1 # float position is supported
-label: 'Supported Hardware'
-collapsible: true # make the category collapsible
-link:
- type: generated-index
- title: Supported Hardware
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/docs/legal/index.mdx b/docs/legal/index.mdx
index 73c98e52..0ff7024d 100644
--- a/docs/legal/index.mdx
+++ b/docs/legal/index.mdx
@@ -10,7 +10,7 @@ sidebar_position: 9
This project is still pretty young but moving at a pretty good pace. Not all features are fully implemented in the current alpha builds.
- We don't make these devices and they haven't been tested by UL or the FCC. If you use them, you are experimenting and we can't promise they won't burn your house down ;-)
-- The encryption implementation is good but see this list of [caveats](/docs/developers/firmware/encryption#summary-of-strengthsweaknesses-of-our-current-implementation) to determine risks you might face.
+- The encryption implementation is good but see this list of [caveats](/docs/about/overview/encryption#summary-of-strengthsweaknesses-of-our-current-implementation) to determine risks you might face.
## Legal FAQ
diff --git a/docs/settings/config/index.mdx b/docs/settings/config/index.mdx
deleted file mode 100644
index 07a176f7..00000000
--- a/docs/settings/config/index.mdx
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,20 +0,0 @@
----
-id: config
-title: Configuration Sections
-sidebar_label: Config Sections
-sidebar_position: 1
----
-
-There are several config sections in the Meshtastic firmware, these are broken out so they can be sent as small admin messages over the mesh.
-
-| Name | Description |
-|:----:|:-----------:|
-| [Bluetooth](bluetooth) | Bluetooth config options are: Enabled, Pairing Mode and Fixed PIN. |
-| [Channels](channels) | Channels config options are: Index, Role and Settings. |
-| [Device](device) | Device config options are: Device Role, Serial Output, Debug Log and Factory Reset. |
-| [Display](display) | Display config options are: Screen On Duration, Auto Carousel Interval, Always Point North, and GPS Format. |
-| [LoRa](lora) | The LoRa config options are: Region, Modem Preset, Max Hops, Transmit Power, Bandwidth, Spread Factor, Coding Rate, Frequency Offset, Transmit Disabled and Ignore Incoming Array. |
-| [Network](network) | Network config options are: WiFi Enabled, WiFi SSID, WiFi PSK, WiFi Mode and NTP Server. |
-| [Position](position) | Position config options are: GPS Enabled, GPS Update Interval, GPS Attempt Time, Fixed Position, Smart Broadcast, Broadcast Interval and Position Packet Flags. |
-| [Power](power) | Power config options are: Charge Current, Power Saving, Shutdown after losing power, ADC Multiplier Override Wait Bluetooth Interval, Mesh Super Deep Sleep Timeout, Super Deep Sleep Interval, Light Sleep Interval and Minimum Wake Interval. |
-| [User](user) | The user config options are: Long Name, Short Name, and Is Licensed |
diff --git a/docs/settings/index.mdx b/docs/settings/index.mdx
deleted file mode 100644
index db96189b..00000000
--- a/docs/settings/index.mdx
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,37 +0,0 @@
----
-title: Device Settings
-sidebar_label: Device Settings
-slug: /settings
-sidebar_position: 5
----
-
-import Tabs from '@theme/Tabs';
-import TabItem from '@theme/TabItem';
-
-Configuration for Meshtastic devices has been completely overhauled in version 1.3.
-
-In order to facilitate a more stable admin channel for remote management of nodes we have broken our large monolithic config structure into six sections that can be saved individually, protecting our precious mesh bandwidth.
-
-Default settings values are prefered whenever possible as they consume no bandwidth when sent over the mesh.
-
-## [Config Sections](settings/config)
-
-Meshtastic config is broken into several sections:
-[Bluetooth](settings/config/bluetooth),
-[Device](settings/config/device),
-[Display](settings/config/display),
-[LoRa](settings/config/lora),
-[Network](settings/config/network),
-[Position](settings/config/position),
-[Power](settings/config/power) and
-[User](settings/config/user).
-
-## [Module Config](settings/moduleconfig)
-
-Meshtastic includes the following modules:
-[Canned Messages](settings/moduleconfig/canned-message),
-[External Notification](settings/moduleconfig/external-notification),
-[MQTT](settings/moduleconfig/mqtt),
-[Range Test](settings/moduleconfig/range-test),
-[Serial](settings/moduleconfig/serial), and
-[Telemetry (sensors)](settings/moduleconfig/telemetry).
diff --git a/docs/settings/moduleconfig/index.mdx b/docs/settings/moduleconfig/index.mdx
deleted file mode 100644
index 0ea568a6..00000000
--- a/docs/settings/moduleconfig/index.mdx
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,17 +0,0 @@
----
-id: module-config
-title: Module Configuration
-sidebar_label: Module Config
-sidebar_position: 2
----
-
-Modules are included in the firmware and allow users to extend the functionality of their mesh or device.
-
-| Name | Description |
-|:----:|:-----------:|
-| [Canned Message](canned-message) | Set a number of predefined messages to send out directly from the device with the use of an input device like a rotary encoder. |
-| [External Notification](external-notification) | Incoming messages are able to alert you using circuits you attach to the device (LEDs, Buzzers, etc) |
-| [MQTT](mqtt) | Forward packets along to an MQTT server. This allows users on the local mesh to communicate with users on another mesh over the internet. |
-| [Range Test](range-test) | Send messages with GPS location at an interval to test the distance your devices can communicate. Requires (at least) one device set up as a sender and one as a receiver. The receiver(s) will log all incoming messages to a CSV. |
-| [Serial Module](serial) | Send messages across the mesh by sending strings over a serial port. |
-| [Telemetry](telemetry) | Attach sensors to the device and transmit readings on a regular interval to the mesh. |
diff --git a/docs/software/_category_.yml b/docs/software/_category_.yml
index 507913f7..d78fe92d 100644
--- a/docs/software/_category_.yml
+++ b/docs/software/_category_.yml
@@ -1,7 +1,6 @@
-
-position: 4 # float position is supported
label: Software
-collapsible: true # make the category collapsible
+collapsible: true
+position: 6
link:
type: generated-index
title: Software
diff --git a/docs/software/android/_category_.yml b/docs/software/android/_category_.yml
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..50b7807a
--- /dev/null
+++ b/docs/software/android/_category_.yml
@@ -0,0 +1,6 @@
+label: Android App
+collapsible: true
+position: 1
+link:
+ type: generated-index
+ title: Android App
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/docs/software/android/index.mdx b/docs/software/android/installation.mdx
similarity index 98%
rename from docs/software/android/index.mdx
rename to docs/software/android/installation.mdx
index 7d75d7aa..f257418a 100644
--- a/docs/software/android/index.mdx
+++ b/docs/software/android/installation.mdx
@@ -1,7 +1,7 @@
---
id: android-installation
title: Android Application Installation
-sidebar_label: Android App
+sidebar_label: Installation
sidebar_position: 1
---
diff --git a/docs/software/android/usage.mdx b/docs/software/android/usage.mdx
index a16882f0..eb9ed336 100644
--- a/docs/software/android/usage.mdx
+++ b/docs/software/android/usage.mdx
@@ -1,7 +1,8 @@
---
id: android-usage
-title: Android application usage
+title: Android Application Usage
sidebar_label: Usage
+sidebar_position: 2
---
## Introduction
diff --git a/docs/software/apple/_category_.yml b/docs/software/apple/_category_.yml
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..9a6fa6dd
--- /dev/null
+++ b/docs/software/apple/_category_.yml
@@ -0,0 +1,6 @@
+label: Apple Apps
+collapsible: true
+position: 2
+link:
+ type: generated-index
+ title: Apple Applications
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/docs/software/apple/index.mdx b/docs/software/apple/index.mdx
deleted file mode 100644
index 5cda9ca1..00000000
--- a/docs/software/apple/index.mdx
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,14 +0,0 @@
----
-id: ios-development
-title: Apple Applications
-sidebar_label: Apple Apps
-sidebar_position: 2
----
-
-The Meshtastic Apple Apps are currently available in TestFlight as public betas with a projected App Store release November of 2022.
-
-There are lesss than 1000 remaining beta spaces available and there are no codes.
-
-iOS 16 is required and you can sign up by opening the following link on any iOS, iPadOS device with TestFlight installed.
-
-https://testflight.apple.com/join/c8nNl8q1
diff --git a/docs/software/apple/installation.mdx b/docs/software/apple/installation.mdx
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..727dad97
--- /dev/null
+++ b/docs/software/apple/installation.mdx
@@ -0,0 +1,30 @@
+---
+id: installation
+title: Apple Application Installation
+sidebar_label: Installation
+---
+
+The Meshtastic Apple Apps are currently available in TestFlight as public betas with a projected App Store release November of 2022.
+
+There are less than 1000 remaining beta spaces available and there are no codes.
+
+iOS 16 is required and you can sign up by opening the following link on any iOS, iPadOS device with TestFlight installed.
+
+https://testflight.apple.com/join/c8nNl8q1
+
+
+## iOS and iPadOS
+
+### TestFlight
+
+A beta iOS and iPadOS application is available in the TestFlight app using the following link:
+
+https://testflight.apple.com/join/c8nNl8q1
+
+## macOS
+
+### TestFlight
+
+A beta macOS application will be available in the TestFlight app for macOS using the following link once macOS Ventura is released:
+
+https://testflight.apple.com/join/c8nNl8q1
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/docs/software/apple/ios.mdx b/docs/software/apple/ios.mdx
deleted file mode 100644
index 2082623d..00000000
--- a/docs/software/apple/ios.mdx
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,11 +0,0 @@
----
-id: ios
-title: iOS & iPadOS
-sidebar_label: iOS & iPadOS
----
-
-## iOS and iPadOS TestFlight
-
-A beta iOS and iPadOS application is available in the TestFlight app using the following link:
-
-https://testflight.apple.com/join/c8nNl8q1
diff --git a/docs/software/apple/macos.mdx b/docs/software/apple/macos.mdx
deleted file mode 100644
index 86c2b87f..00000000
--- a/docs/software/apple/macos.mdx
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,12 +0,0 @@
----
-id: macos
-title: macOS
-sidebar_label: macOS
----
-
-
-## macOS TestFlight
-
-A beta macOS application will be available in the TestFlight app for macOS using the following link once macOS Ventura is released:
-
-https://testflight.apple.com/join/c8nNl8q1
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/docs/software/apple/maps.mdx b/docs/software/apple/usage.mdx
similarity index 92%
rename from docs/software/apple/maps.mdx
rename to docs/software/apple/usage.mdx
index 69f4d4a5..0488f99b 100644
--- a/docs/software/apple/maps.mdx
+++ b/docs/software/apple/usage.mdx
@@ -1,9 +1,11 @@
---
-id: offline-maps
-title: Offline Maps
-sidebar_label: Offline Maps
+id: apple-apps-usage
+title: Apple Application Usage
+sidebar_label: Usage
---
+## Offline Maps
+
The Meshtastic app for iOS, iPadOS and macOS supports the sharing of a .mbtiles file with the app for offline map support.
There is an open source cross platform mapping program call [QGIS](https://www.qgis.org/en/site/)
diff --git a/docs/software/device/Index.mdx b/docs/software/device/Index.mdx
deleted file mode 100644
index 4ece5f6f..00000000
--- a/docs/software/device/Index.mdx
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,56 +0,0 @@
----
-id: device-firmware
-title: Device firmware
-sidebar_label: Device firmware
-sidebar_position: 3
----
-
-The device firmware runs on the nodes to build the mesh for communication. Each different make and model of device requires a different build of the Meshtastic firmware in order to run properly. Thankfully, due to the design of Meshtastic, it is possible to port the firmware to new devices as they become available. The firmware currently runs on a range of ESP32 based devices, but there is also increasing support for the nRF52 microprocessor with some more recent devices coming to market.
-
-The current firmware has support for a screen to display received messages, along with information about nodes on the mesh, and more detailed information about the device on which it is running.
-
-The latest firmware can be downloaded from the [Downloads](/downloads) page. If you wish to view the code or contribute to development of the firmware, please visit the device code GitHub page.
-
-:::info
-Please be aware that there are significant changes between version branches 1.2.x and 1.3.x which mean that devices need to be running the same branch of firmware to be able to talk to each other. Python, Android, and other software applications will also need to be running the same branch to be able to talk to the device.
-:::
-
-### Buttons
-
-A number of devices have buttons that can be used to interact with the firmware. These buttons have a number of different functions:
-
-- Reset button - This is present on most devices.
-- Power button - This is present on some devices. A long press powers the device off or turns it back on again.
-- Program button - This is present of some devices and has a number of functions:
- - Single press - This changes the page of information displayed on the screen.
- - Double press - This sets the Bluetooth pairing code to `123456` (useful if you do not have a screen on the device).
- - Long press - This adjusts the contrast of the screen.
- - Long press during reboot - This turns on the software Wifi access point on devices that support Wifi.
-
-### Screens
-
-A number of devices have screens capable of displaying the messages received, information about the mesh, and other details. On powering the device it will display the Meshtastic splash screen with the version number for a couple of seconds:
-
-
-
-The screen is split up into pages, through which you can navigate using the program button as described above. The first page to be displayed will be the message screen where received messages are displayed along with the name of the node it came from. The devices will automatically switch to this page when a new message is received.
-
-
-
-The next pages display information about the nodes that are currently on the mesh. This includes the distance and direction to that node, the signal strength, and the time last seen.
-
- 
-
-The next page shows information about the device, battery power, current / total nodes, number of GPS satellites seen, channel name, last digits of the MAC address, and a brief log including the names of the last nodes to join the mesh.
-
-
-
-The final page shows current battery voltage and percent charge, as well as noting how long the device has been online and the current GPS time, and GPS location.
-
-
-
-If the device Wifi has been enabled (only possible on ESP32 devices), another page appears displaying information about the WiFi settings, IP address, and number of devices connected to the WiFi.
-
-
-
-With a further press of the program button, the screen will cycle round to the message page.
diff --git a/docs/software/go/_category_.yml b/docs/software/go/_category_.yml
deleted file mode 100644
index bee7e630..00000000
--- a/docs/software/go/_category_.yml
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,7 +0,0 @@
-label: Golang
-collapsible: true # make the category collapsible
-position: 7
-link:
- type: generated-index
- title: Golang
- slug: /software/go
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/docs/software/go/cli.mdx b/docs/software/go/cli.mdx
deleted file mode 100644
index f5662352..00000000
--- a/docs/software/go/cli.mdx
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,9 +0,0 @@
----
-id: golang-cli
-title: Meshtastic Go CLI
-sidebar_label: CLI
----
-
-:::info
-This project is currently in progress
-:::
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/docs/software/go/desktop.mdx b/docs/software/go/desktop.mdx
deleted file mode 100644
index e1c24992..00000000
--- a/docs/software/go/desktop.mdx
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,9 +0,0 @@
----
-id: golang-desktop
-title: Meshtastic Desktop
-sidebar_label: Desktop
----
-
-:::info
-This project is currently in progress
-:::
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/docs/software/go/library.mdx b/docs/software/go/library.mdx
deleted file mode 100644
index 4a58d1f0..00000000
--- a/docs/software/go/library.mdx
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,9 +0,0 @@
----
-id: golang-library
-title: Meshtastic Go Library
-sidebar_label: Go Library
----
-
-:::info
-This project is currently in progress
-:::s
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/docs/software/js/_category_.yml b/docs/software/js/_category_.yml
deleted file mode 100644
index b9c3cd23..00000000
--- a/docs/software/js/_category_.yml
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,7 +0,0 @@
-position: 6 # float position is supported
-label: 'Javascript'
-collapsible: true # make the category collapsible
-link:
- type: generated-index
- title: Javascript
- slug: /software/js
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/docs/software/other/linux-native-application.mdx b/docs/software/linux-native.mdx
similarity index 96%
rename from docs/software/other/linux-native-application.mdx
rename to docs/software/linux-native.mdx
index 1a9d0f0e..0c057dd3 100644
--- a/docs/software/other/linux-native-application.mdx
+++ b/docs/software/linux-native.mdx
@@ -1,7 +1,8 @@
---
-id: linux-native-application
-title: Linux native application
-sidebar_label: Linux native application
+id: linux-native
+title: Linux Native Application
+sidebar_label: Linux Native
+sidebar_position: 9
---
The device software can also run on a native Linux machine thanks to the [Portduino framework](https://github.com/geeksville/framework-portduino).
@@ -15,7 +16,7 @@ For instructions on how to use it, see the [interactive simulator](https://githu
## Usage with a Linux machine {#usage-with-a-linux-machine}
The easiest way of building the native application is using Visual Studio Code with the PlatformIO extension.
-See the instructions for creating such a building environment [here](/docs/developers/Firmware/build).
+See the instructions for creating such a building environment [here](/docs/development/firmware/build).
Then after opening the firmware repository in Visual Studio Code, simply click on the PlatformIO extension in the left bar, select native and click on 'Build'.
This will generate the binary file 'program' which you can find in `.pio/build/native/`.
diff --git a/docs/software/mqtt/index.mdx b/docs/software/mqtt/index.mdx
index f9a5c39d..fb8c26c5 100644
--- a/docs/software/mqtt/index.mdx
+++ b/docs/software/mqtt/index.mdx
@@ -2,16 +2,16 @@
id: mqtt
title: MQTT
sidebar_label: MQTT
-sidebar_position: 4
+sidebar_position: 6
---
## Bridging networks
-Meshtastic networks in different locations beyond the reach of LoRa can be easily bridged together using MQTT. The simplest option is to connect your mesh to the official Meshtastic MQTT broker. This makes your devices appear on the world map, and provides a copy of your mesh traffic, translated into JSON. All you have to do to join the public MQTT server is to Enable MQTT and set uplink and downlink on the channels that you want to share over MQTT. The default device configuration using the public MQTT Server is encrypted.
+Meshtastic networks in different locations beyond the reach of LoRa can be easily bridged together using MQTT. The simplest option is to connect your mesh to the official Meshtastic MQTT broker. This makes your devices appear on the world map, and provides a copy of your mesh traffic, translated into JSON. All you have to do to join the public MQTT server is to Enable MQTT and set Uplink and Downlink on the channels that you want to share over MQTT. The default device configuration using the public MQTT Server is encrypted.
You can also share channel settings with a remote network. If you use the default meshtastic MQTT server, packets are always encrypted. If you use a custom MQTT broker (ie set `mqtt.address`), the `mqtt.encryption_enabled` setting applies, which by default is false. You can also specify your own private MQTT broker and specify authentication for that broker to bridge several mesh networks together, via the internet (or just a local IP network).
-You can find the settings available for MQTT [here](https://meshtastic.org/docs/settings/moduleconfig/mqtt).
+You can find the settings available for MQTT [here](/docs/settings/moduleconfig/mqtt).
## Software Integrations
@@ -40,7 +40,7 @@ The payload is a raw protobuf. Looking at the MQTT traffic with a program like `
ShortFast !937bed1c
```
-Packets from the following [port numbers](/docs/developers/Firmware/portnum) are serialized to JSON and then forwarded to the `msh/2/json/CHANNELID/DEVICEID` topic: `TEXT_MESSAGE_APP`, `ENVIRONMENTAL_MEASUREMENT_APP`, `NODEINFO_APP` and `POSITION_APP`.
+Packets from the following [port numbers](/docs/development/firmware/portnum) are serialized to JSON and then forwarded to the `msh/2/json/CHANNELID/DEVICEID` topic: `TEXT_MESSAGE_APP`, `ENVIRONMENTAL_MEASUREMENT_APP`, `NODEINFO_APP` and `POSITION_APP`.
An example of a received `NODEINFO_APP` message:
@@ -112,7 +112,7 @@ The unique ID for a node. A hex string that starts with an ! symbol.
#### USERID
-A user ID string. This string is either a user ID if known or a nodeid to simply deliver the message to whoever the local user is of a particular device (i.e. person who might see the screen). FIXME, see what riot.im uses and perhaps use that convention? Or use the signal +phone number convention? Or the email addr?
+A user ID string. This string is either a user ID if known or a nodeid to simply deliver the message to whoever the local user is of a particular device (i.e. person who might see the screen). FIXME, see what riot.im uses and perhaps use that convention? Or use the signal +phone number convention? Or the email address?
#### CHANNELID
@@ -120,7 +120,7 @@ FIXME, figure out how channelids work
### Gateway nodes
-Any meshtastic node that has a direct connection to the internet (either via a helper app or installed Wifi/4G/satellite hardware) can function as a "Gateway node".
+Any meshtastic node that has a direct connection to the internet (either via a helper app or installed WiFi/4G/satellite hardware) can function as a "Gateway node".
Gateway nodes (via code running in the phone) will contain two tables to whitelist particular traffic to either be delivered toward the internet, or down toward the mesh. Users that are developing custom apps will be able to customize these filters/subscriptions.
@@ -139,13 +139,13 @@ An existing public [MQTT broker](https://mosquitto.org) will be the default for
1. install mqtt server
-```
+```sh
brew install mosquitto
```
2. start the mqtt server
-```
+```sh
brew services restart mosquitto
```
@@ -153,13 +153,13 @@ brew services restart mosquitto
Note: this will wait until you press control-c (publish a message, see below)
-```
+```sh
mosquitto_sub -t test/hello
```
4. In another window, publish a message to that topic:
-```
+```sh
mosquitto_pub -h localhost -q 0 -t test/hello -m 'yo!'
```
@@ -173,7 +173,7 @@ allow_anonymous true
6. Restart the service:
-```
+```sh
brew services restart mosquitto
```
@@ -183,7 +183,7 @@ brew services restart mosquitto
Here is an example publish message in python:
-```
+```python
#!/usr/bin/env python3
import paho.mqtt.client as mqtt
from random import randrange, uniform
@@ -201,7 +201,7 @@ while True:
Here is example subscribe in python:
-```
+```python
#!/usr/bin/env python3
import paho.mqtt.client as paho
@@ -228,8 +228,9 @@ if __name__ == '__main__':
### Using MQTT with Node-RED
-Below is a valid json envelope for information sent by MQTT to a device for broadcast onto the mesh.
- ```
+Below is a valid JSON envelope for information sent by MQTT to a device for broadcast onto the mesh.
+
+ ```json
{
"sender":"whatever you want to be the SENDER",
"type":"sendtext",
@@ -240,17 +241,17 @@ Below is a valid json envelope for information sent by MQTT to a device for broa
Node-RED is a free cross-platform programming tool for wiring together hardware, APIs, and online services developed originally by IBM for IOT. It is widely used for home automation by many non-professional programmers and runs well on Pi's. Node-red has many plug-in modules written by the community. I will use this platform as a practical example on how to interface with the MQTT features of Meshtastic. Everything can be done from GUI's without using command line.
Step one: use http://client.meshtastic.org/ one of the Apple apps or the CLI to connect to your device and adjust these settings.
-Enable and enter network ssid/psk. Settings--> Device Config--> Network; Save.
+Enable and enter network SSID/PSK. Settings--> Device Config--> Network; Save.
Set MQTT server address. Settings--> Module Config--> MQTT config; Verify Encryption Enabled is OFF. Turn JSON Output Enabled ON. Save.
-Go to Channel Editor and set uplink and downling enabled to True. Save.
+Go to Channel Editor and set Uplink and Downlink enabled to True. Save.
-Step two: if you don't want to depend on JSON decoding on the device, you can decode the proto messages off-device. To do that you will need to get the .proto files from https://github.com/meshtastic/protobufs. They function as a schema and are required for decoding in Node-RED. Save the files where the node-RED application can access them and note the file path of the "mqtt.proto" file.
+Step two: if you don't want to depend on JSON decoding on the device, you can decode the protobuf messages off-device. To do that you will need to get the .proto files from https://github.com/meshtastic/protobufs. They function as a schema and are required for decoding in Node-RED. Save the files where the node-RED application can access them and note the file path of the "mqtt.proto" file.
-Step three: install Node-RED plug-ins to your node-RED application for an embedded mqqt server and a protobuf decoder.
+Step three: install Node-RED plug-ins to your node-RED application for an embedded MQQT server and a protobuf decoder.
https://flows.nodered.org/node/node-red-contrib-aedes
https://flows.nodered.org/node/node-red-contrib-protobuf
-Drag, drop, and wire the nodes like this. For this example, I ran node-RED on a Windows machine. Note that file paths might be specified differently on different platforms. MQTT server wild cards are usually the same. A "+" is a single level wildcard for a specific topic level. A "#" is a multiple level wildcard that can be used at the end of a topic filter. The debug messages shown are what happens when the inject button sends a json message with a topic designed to be picked up by the specified Meshtastic device and then having it rebroadcast the message.
+Drag, drop, and wire the nodes like this. For this example, I ran node-RED on a Windows machine. Note that file paths might be specified differently on different platforms. MQTT server wild cards are usually the same. A "+" is a single level wildcard for a specific topic level. A "#" is a multiple level wildcard that can be used at the end of a topic filter. The debug messages shown are what happens when the inject button sends a JSON message with a topic designed to be picked up by the specified Meshtastic device and then having it rebroadcast the message.
[](/documents/mqtt/NodeRedTwo.jpg)
[](/documents/mqtt/NodeRedThree.jpg)
@@ -260,7 +261,7 @@ The aedes broker must be set up on the same flow as the other nodes. By activati
[](/documents/mqtt/Broker1.jpg)
Receiving a json mqqt message is very simple.
[](/documents/mqtt/Consume.jpg)
-Injecting a json message to be sent by a device is also very simple. You do need the correct enevelope.
+Injecting a json message to be sent by a device is also very simple. You do need the correct envelope.
[](/documents/mqtt/Inject.jpg)
Forwarding a text message from one device, through a broker, to another broker/device/channel would look like this.
[](/documents/mqtt/Forward.jpg)
diff --git a/docs/software/other/_category_.yml b/docs/software/other/_category_.yml
deleted file mode 100644
index ac11fb4e..00000000
--- a/docs/software/other/_category_.yml
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,8 +0,0 @@
-
-position: 9 # float position is supported
-label: Other
-collapsible: true # make the category collapsible
-link:
- type: generated-index
- title: Other
- slug: /software/other
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/docs/software/python/cli/cli.mdx b/docs/software/python-cli/index.mdx
similarity index 98%
rename from docs/software/python/cli/cli.mdx
rename to docs/software/python-cli/index.mdx
index 0ed94282..d4806a29 100644
--- a/docs/software/python/cli/cli.mdx
+++ b/docs/software/python-cli/index.mdx
@@ -1,7 +1,9 @@
---
id: python-cli
title: Meshtastic Command Line Interface
+slug: /software/python/cli
sidebar_label: Python CLI
+sidebar_position: 4
---
# Meshtastic Python CLI Guide
@@ -95,7 +97,7 @@ meshtastic --get lora.region
Sets a preferences field.
-Configuration values are described in this section: [Configuration Sections](https://meshtastic.org/docs/settings/config/)
+Configuration values are described in this section: [Configuration Sections](https://meshtastic.org/docs/mesh/device/config/)
**Usage**
diff --git a/docs/software/python/cli/installation.mdx b/docs/software/python-cli/installation.mdx
similarity index 78%
rename from docs/software/python/cli/installation.mdx
rename to docs/software/python-cli/installation.mdx
index bd9fe585..6a47a018 100644
--- a/docs/software/python/cli/installation.mdx
+++ b/docs/software/python-cli/installation.mdx
@@ -1,7 +1,8 @@
---
id: installation
-title: Meshtastic-python installation
+title: Meshtastic Python CLI installation
sidebar_label: Installation
+slug: /software/python/cli/installation
sidebar_position: 1
---
@@ -14,7 +15,7 @@ The [Meshtastic-python repo](https://github.com/meshtastic/Meshtastic-python) an
If you wish to view the code or contribute to development of the python library or the command line interface, please visit the Meshtastic python [GitHub page](https://github.com/meshtastic/Meshtastic-python).
-There are standalone executables for Mac, Windows and Ubuntu if you do not want to install python and/or the python libraries required to run the mestastic CLI tool. See [Standalone](/docs/software/python/python-standalone) for more information.
+There are standalone executables for Mac, Windows and Ubuntu if you do not want to install python and/or the python libraries required to run the mestastic CLI tool. See [Standalone](#standalone) for more information.
Installation can also be easily done through the [Python package installer pip](https://pypi.org/project/meshtastic):
:::note
@@ -202,3 +203,102 @@ Be aware that the Meshtastic CLI is not able to control the nodes over USB throu
:::info
You may need to close and re-open the CLI. The path variables may or may not update for the current session when installing.
:::
+
+
+## Standalone
+
+
+There are standalone executable files for Mac, Windows and Ubuntu. A single file is all you need to run the command line interface (CLI) Meshtastic tool. There is a zip file per operating system. To use, see the operating system specific notes below:
+
+They can be found on the [Releases](https://github.com/meshtastic/Meshtastic-python/releases) page.
+
+
+
+
+- Download meshtastic_ubuntu
+
+- Run the following command to make the file executable and rename it 'meshtastic':
+
+```
+chmod +x meshtastic_ubuntu && mv meshtastic_ubuntu meshtastic
+```
+
+- To run the cli:
+
+```
+./meshtastic
+```
+
+:::tip
+Copy (or move) this binary somewhere in your path.
+:::
+
+
+
+
+- Download meshtastic_mac
+
+- Run the following command to make the file executable and to rename it 'meshtastic':
+
+```
+chmod +x meshtastic_mac && mv meshtastic_mac meshtastic
+```
+
+- Try to run it:
+
+```
+./meshtastic
+```
+
+:::note
+You may get a dialog that says:
+"meshtastic" can't be opened because Apple cannot check it for malicious software.
+:::
+
+- To fix, go into "System Preferences", "Security & Privacy", "General" tab, and click on the "Allow Anyway" button.
+
+- Try to run it again:
+
+```
+./meshtastic
+```
+
+:::note
+You may get a dialog that says:
+"meshtastic" can't be opened because Apple cannot check it for malicious software.
+Click "Open".
+:::
+
+- Now when you want to run it, you can simply run:
+
+```
+./meshtastic
+```
+
+:::tip
+Copy (or move) this binary somewhere in your path.
+:::
+
+
+
+
+- Download meshtastic_windows
+
+- Rename to meshtastic.exe
+
+- To run, open a windows command prompt, navigate to the location of the executable and run:
+
+```
+meshtastic.exe
+```
+
+
+
+
diff --git a/docs/software/python/cli/uses.mdx b/docs/software/python-cli/usage.mdx
similarity index 99%
rename from docs/software/python/cli/uses.mdx
rename to docs/software/python-cli/usage.mdx
index 6eddb973..56eff6bf 100644
--- a/docs/software/python/cli/uses.mdx
+++ b/docs/software/python-cli/usage.mdx
@@ -2,6 +2,7 @@
id: usage
title: Using the Meshtastic CLI
sidebar_label: Usage
+slug: /software/python/cli/usage
sidebar_position: 2
---
diff --git a/docs/software/python/meshtastic-flasher.mdx b/docs/software/python-flasher.mdx
similarity index 97%
rename from docs/software/python/meshtastic-flasher.mdx
rename to docs/software/python-flasher.mdx
index b5b0350d..b47d51ca 100644
--- a/docs/software/python/meshtastic-flasher.mdx
+++ b/docs/software/python-flasher.mdx
@@ -1,8 +1,9 @@
---
id: flasher
-title: Using Meshtastic Flasher
-sidebar_label: Meshtastic Flasher
-sidebar_position: 1
+title: Using Meshtastic Python Flasher
+sidebar_label: Python Flasher
+slug: /software/python/flasher
+sidebar_position: 5
---
import Tabs from '@theme/Tabs';
diff --git a/docs/software/python/_category_.yml b/docs/software/python/_category_.yml
deleted file mode 100644
index 4dbc557b..00000000
--- a/docs/software/python/_category_.yml
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,7 +0,0 @@
-label: Python
-collapsible: true # make the category collapsible
-position: 5 # float position is supported
-link:
- type: generated-index
- title: Python
- slug: /software/python-cli
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/docs/software/python/standalone.mdx b/docs/software/python/standalone.mdx
deleted file mode 100644
index c3fa8031..00000000
--- a/docs/software/python/standalone.mdx
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,102 +0,0 @@
----
-id: python-standalone
-title: Meshtastic-python standalone executable
-sidebar_label: Standalone
----
-
-import Tabs from '@theme/Tabs';
-import TabItem from '@theme/TabItem';
-
-There are standalone executable files for Mac, Windows and Ubuntu. A single file is all you need to run the command line interface (CLI) Meshtastic tool. There is a zip file per operating system. To use, see the operating system specific notes below:
-
-They can be found on the [Releases](https://github.com/meshtastic/Meshtastic-python/releases) page.
-
-
-
-
-- Download meshtastic_ubuntu
-
-- Run the following command to make the file executable and rename it 'meshtastic':
-
-```
-chmod +x meshtastic_ubuntu && mv meshtastic_ubuntu meshtastic
-```
-
-- To run the cli:
-
-```
-./meshtastic
-```
-
-:::tip
-Copy (or move) this binary somewhere in your path.
-:::
-
-
-
-
-- Download meshtastic_mac
-
-- Run the following command to make the file executable and to rename it 'meshtastic':
-
-```
-chmod +x meshtastic_mac && mv meshtastic_mac meshtastic
-```
-
-- Try to run it:
-
-```
-./meshtastic
-```
-
-:::note
-You may get a dialog that says:
-"meshtastic" can't be opened because Apple cannot check it for malicious software.
-:::
-
-- To fix, go into "System Preferences", "Security & Privacy", "General" tab, and click on the "Allow Anyway" button.
-
-- Try to run it again:
-
-```
-./meshtastic
-```
-
-:::note
-You may get a dialog that says:
-"meshtastic" can't be opened because Apple cannot check it for malicious software.
-Click "Open".
-:::
-
-- Now when you want to run it, you can simply run:
-
-```
-./meshtastic
-```
-
-:::tip
-Copy (or move) this binary somewhere in your path.
-:::
-
-
-
-
-- Download meshtastic_windows
-
-- Rename to meshtastic.exe
-
-- To run, open a windows command prompt, navigate to the location of the executable and run:
-
-```
-meshtastic.exe
-```
-
-
-
diff --git a/docs/software/web/index.mdx b/docs/software/web-client.mdx
similarity index 93%
rename from docs/software/web/index.mdx
rename to docs/software/web-client.mdx
index f0c4d87e..48b7caca 100644
--- a/docs/software/web/index.mdx
+++ b/docs/software/web-client.mdx
@@ -1,8 +1,8 @@
---
-id: web-app-software
-title: Web interface overview
-sidebar_label: Web Interface
-sidebar_position: 8
+id: web-client
+title: Web Client Overview
+sidebar_label: Web Client
+sidebar_position: 3
---
@@ -37,13 +37,13 @@ You can accessing your device over HTTP after you set up and enabled the [Client
Bluetooth support is governed by the availability of the [Web Bluetooth API](https://web.dev/bluetooth) as illustrated blow, support is primarily available in Chromium browsers
-
+
### Serial (USB)
The method with the least platform support, uses the [Web Serial API](https://web.dev/serial) allows us to connect directly to a Meshtastic node over USB, accessing it directly within your browser.
-
+
## Updating
@@ -85,4 +85,4 @@ Option 3) Flash the device with the SPIFFS instructions in platform.io.
This issue is likely found on old versions of the web interface. Device firmware now includes the web interface and the file system has been changed. Flashing the device with [Meshtastic-flasher](/docs/software/python/flasher) will update you to the current web interface. Access to the files in the filesystem is actively being developed, but is not currently available.
:::
-Cause: Typically a small partition has been set aside from previous firmware installed on the module. Instructions for how to fix this can be found on the [ESP32-Partitions](/docs/software/web/web-partitions-software) page.
+Cause: Typically a small partition has been set aside from previous firmware installed on the module. Instructions for how to fix this can be found on the [ESP32-Partitions](/docs/development/web/esp32-partitions) page.
diff --git a/docusaurus.config.js b/docusaurus.config.js
index 1c4ca954..857ab24d 100644
--- a/docusaurus.config.js
+++ b/docusaurus.config.js
@@ -20,9 +20,6 @@ const config = {
content:
'🎉 Meshtastic 2.0 Has Now Launched! Check it Out Here 🎉',
},
- colorMode: {
- respectPrefersColorScheme: true,
- },
docs: {
sidebar: {
autoCollapseCategories: true,
@@ -39,32 +36,43 @@ const config = {
items: [
{
label: 'Docs',
+ to: 'docs/introduction',
+ },
+ {
+ label: 'Downloads',
+ to: 'downloads',
+ },
+ {
+ label: 'About',
+ position: 'right',
items: [
+ {
+ label: 'Introduction',
+ to: 'docs/introduction',
+ },
{
label: 'Getting Started',
to: 'docs/getting-started',
},
{
- label: 'Configuration',
- to: 'docs/settings',
+ label: 'Contributing',
+ to: 'docs/contributing',
},
{
- label: 'Hardware',
- to: 'docs/hardware',
+ label: 'Legal',
+ to: 'docs/legal',
},
{
- label: 'Software',
- to: 'docs/software',
- },
- {
- label: 'Developers',
- to: 'docs/developers',
+ label: 'FAQs',
+ to: 'docs/faq',
},
],
},
{
- label: 'Downloads',
- to: 'downloads',
+ href: 'https://github.com/meshtastic',
+ position: 'right',
+ className: 'header-github-link',
+ 'aria-label': 'GitHub repository',
},
],
},
@@ -78,6 +86,9 @@ const config = {
contextualSearch: false,
searchPagePath: 'search',
},
+ colorMode: {
+ respectPrefersColorScheme: true,
+ },
},
plugins: [
() => {
diff --git a/protobuf.tmpl b/protobuf.tmpl
index d178846f..bda17827 100644
--- a/protobuf.tmpl
+++ b/protobuf.tmpl
@@ -1,9 +1,13 @@
---
-id: api
+id: protobuf-api
title: Protobuf API Reference
-sidebar_label: API
+slug: /developers/protobufs/api
+sidebar_label: Protobufs
+sidebar_position: 20
---
+
+
{{range .Files}}
## {{.Name}}
{{if .Messages}}
diff --git a/protobufs b/protobufs
index ed9f2499..a0fe9ec8 160000
--- a/protobufs
+++ b/protobufs
@@ -1 +1 @@
-Subproject commit ed9f2499d692925461facd64c6af2d2a7672245a
+Subproject commit a0fe9ec8614cd27af7691869ccbd20c39e48a086
diff --git a/scripts/gen-proto-docs.sh b/scripts/gen-proto-docs.sh
index 3d8c387c..f3bed9e6 100755
--- a/scripts/gen-proto-docs.sh
+++ b/scripts/gen-proto-docs.sh
@@ -10,7 +10,7 @@ cd "${PROJECT_BASE}"/protobufs || exit
git checkout master
if git submodule status | grep -q '^[-]|^[+]' ; then \
- echo "INFO: Reinitializing git submodules..."; \
+ echo "INFO: Re-initializing git submodules..."; \
git submodule update --init --recursive; \
else \
echo "INFO: Updating git submodules..."; \
@@ -19,6 +19,6 @@ else \
fi
# remove old generated protos
-rm -rf "${PROJECT_BASE}/docs/developers/Protobufs/*"
+rm -rf "${PROJECT_BASE}/docs/development/reference/protobuf-api.mdx"
-protoc --doc_opt="${PROJECT_BASE}/protobuf.tmpl,api.mdx" --doc_out="${PROJECT_BASE}/docs/developers/Protobufs/" --proto_path="${PROJECT_BASE}/protobufs" *.proto
\ No newline at end of file
+protoc --doc_opt="${PROJECT_BASE}/protobuf.tmpl,protobuf-api.mdx" --doc_out="${PROJECT_BASE}/docs/development/reference/" --proto_path="${PROJECT_BASE}/protobufs" *.proto
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/src/pages/downloads/index.tsx b/src/pages/downloads/index.tsx
index 5dbac4cf..e8e564e1 100644
--- a/src/pages/downloads/index.tsx
+++ b/src/pages/downloads/index.tsx
@@ -135,7 +135,7 @@ const Firmware = (): JSX.Element => {
className="m-auto flex rounded-lg border-4 border-transparent bg-accent p-1 font-semibold text-black shadow-md hover:text-black hover:brightness-110 active:border-green-200"
target="_blank"
rel="noopener noreferrer"
- href="https://meshtastic.org/docs/software/android/#f-droid"
+ href="https://meshtastic.org/docs/software/android/android-installation"
>
F-Droid