mirror of
https://github.com/meshtastic/meshtastic.git
synced 2025-03-05 21:00:08 -08:00
Merge branch 'master' into i18n
This commit is contained in:
commit
f14a781612
|
|
@ -1,4 +0,0 @@
|
|||
{
|
||||
"plugins": ["@docusaurus"],
|
||||
"extends": ["plugin:@docusaurus/recommended"]
|
||||
}
|
||||
3
.gitattributes
vendored
Normal file
3
.gitattributes
vendored
Normal file
|
|
@ -0,0 +1,3 @@
|
|||
* text=auto eol=lf
|
||||
*.{cmd,[cC][mM][dD]} text eol=crlf
|
||||
*.{bat,[bB][aA][tT]} text eol=crlf
|
||||
44
.github/workflows/ci.yml
vendored
44
.github/workflows/ci.yml
vendored
|
|
@ -1,38 +1,28 @@
|
|||
name: CI
|
||||
|
||||
on:
|
||||
push:
|
||||
branches:
|
||||
- 'master'
|
||||
workflow_run:
|
||||
workflows:
|
||||
- 'Update protobufs'
|
||||
pull_request:
|
||||
|
||||
jobs:
|
||||
deploy-website:
|
||||
environment: Production
|
||||
build:
|
||||
runs-on: ubuntu-latest
|
||||
|
||||
steps:
|
||||
- name: Checkout code
|
||||
- name: Checkout code & submodules
|
||||
uses: actions/checkout@v3
|
||||
with:
|
||||
submodules: true
|
||||
#- name: Install Go
|
||||
# uses: actions/setup-go@v3
|
||||
# with:
|
||||
# go-version: 1.19
|
||||
#- name: Install Protoc
|
||||
# uses: arduino/setup-protoc@v1
|
||||
# with:
|
||||
# version: '3.x'
|
||||
#- name: Install protoc-gen-doc
|
||||
# run: go install github.com/pseudomuto/protoc-gen-doc/cmd/protoc-gen-doc@latest
|
||||
#- name: Generate protobuf docs
|
||||
# run: protoc --doc_out="docs/developers/Protobufs" --doc_opt="./protobuf.tmpl,api.mdx" --proto_path="protobufs" protobufs/*.proto
|
||||
- uses: amondnet/vercel-action@v20
|
||||
|
||||
- name: Setup pnpm
|
||||
uses: pnpm/action-setup@v2.2.1
|
||||
with:
|
||||
vercel-token: ${{ secrets.VERCEL_TOKEN }}
|
||||
vercel-args: '--prod'
|
||||
vercel-org-id: ${{ secrets.ORG_ID}}
|
||||
vercel-project-id: ${{ secrets.PROJECT_ID}}
|
||||
scope: ${{ secrets.ORG_ID}}
|
||||
version: latest
|
||||
|
||||
- name: Install Dependencies
|
||||
run: pnpm install
|
||||
|
||||
- name: Trunk Check
|
||||
uses: trunk-io/trunk-action@v1
|
||||
|
||||
- name: Build Site
|
||||
run: pnpm build
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
27
.github/workflows/nightly.yml
vendored
Normal file
27
.github/workflows/nightly.yml
vendored
Normal file
|
|
@ -0,0 +1,27 @@
|
|||
name: Nightly
|
||||
on:
|
||||
schedule:
|
||||
- cron: 0 8 * * 1-5
|
||||
workflow_dispatch: {}
|
||||
|
||||
jobs:
|
||||
trunk_check:
|
||||
name: Trunk Check Upload
|
||||
runs-on: ubuntu-latest
|
||||
|
||||
steps:
|
||||
- name: Checkout
|
||||
uses: actions/checkout@v3
|
||||
|
||||
- name: Setup pnpm
|
||||
uses: pnpm/action-setup@v2.2.1
|
||||
with:
|
||||
version: latest
|
||||
|
||||
- name: Install Dependencies
|
||||
run: pnpm install
|
||||
|
||||
- name: Trunk Check
|
||||
uses: trunk-io/trunk-action@v1
|
||||
with:
|
||||
trunk-token: ${{ secrets.TRUNK_TOKEN }}
|
||||
31
.github/workflows/pr.yml
vendored
31
.github/workflows/pr.yml
vendored
|
|
@ -1,31 +0,0 @@
|
|||
name: Pull Request
|
||||
|
||||
on: pull_request
|
||||
|
||||
jobs:
|
||||
build:
|
||||
runs-on: ubuntu-latest
|
||||
steps:
|
||||
- name: Checkout code & submodules
|
||||
uses: actions/checkout@v3
|
||||
with:
|
||||
submodules: true
|
||||
|
||||
- name: Setup pnpm
|
||||
uses: pnpm/action-setup@v2.2.1
|
||||
with:
|
||||
version: latest
|
||||
|
||||
- name: Setup NodeJS
|
||||
uses: actions/setup-node@v3
|
||||
with:
|
||||
node-version: 17
|
||||
|
||||
- name: Install Dependencies
|
||||
run: pnpm install
|
||||
|
||||
- name: Lint & Format
|
||||
run: pnpm format
|
||||
|
||||
- name: Build Site
|
||||
run: pnpm build
|
||||
26
.github/workflows/update_protobufs.yml
vendored
26
.github/workflows/update_protobufs.yml
vendored
|
|
@ -1,26 +0,0 @@
|
|||
name: "Update protobufs"
|
||||
on: workflow_dispatch
|
||||
|
||||
jobs:
|
||||
update-protobufs:
|
||||
environment: Production
|
||||
runs-on: ubuntu-latest
|
||||
|
||||
steps:
|
||||
- name: Checkout code
|
||||
uses: actions/checkout@v3
|
||||
with:
|
||||
submodules: true
|
||||
|
||||
- name: Update Submodule
|
||||
run: |
|
||||
git pull --recurse-submodules
|
||||
git submodule update --remote --recursive
|
||||
|
||||
- name: Commit update
|
||||
run: |
|
||||
git config --global user.name 'github-actions'
|
||||
git config --global user.email 'bot@noreply.github.com'
|
||||
git remote set-url origin https://x-access-token:${{ secrets.GITHUB_TOKEN }}@github.com/${{ github.repository }}
|
||||
git add protobufs
|
||||
git commit -m "Update protobuf submodule" && git push || echo "No changes to commit"
|
||||
3
.gitmodules
vendored
3
.gitmodules
vendored
|
|
@ -1,6 +1,3 @@
|
|||
[submodule "protobufs"]
|
||||
path = protobufs
|
||||
url = https://github.com/meshtastic/protobufs/
|
||||
[submodule "static/design"]
|
||||
path = static/design
|
||||
url = https://github.com/meshtastic/design/
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -1 +0,0 @@
|
|||
"@meshtastic/eslint-config/prettier"
|
||||
7
.trunk/.gitignore
vendored
Normal file
7
.trunk/.gitignore
vendored
Normal file
|
|
@ -0,0 +1,7 @@
|
|||
*out
|
||||
*logs
|
||||
*actions
|
||||
*notifications
|
||||
plugins
|
||||
user_trunk.yaml
|
||||
user.yaml
|
||||
9
.trunk/configs/.eslintrc
Normal file
9
.trunk/configs/.eslintrc
Normal file
|
|
@ -0,0 +1,9 @@
|
|||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
{
|
||||
"extends": ["eslint:recommended", "plugin:@typescript-eslint/recommended", "plugin:@docusaurus/recommended"],
|
||||
"parser": "@typescript-eslint/parser",
|
||||
"plugins": ["@docusaurus", "@typescript-eslint"],
|
||||
"root": true
|
||||
}
|
||||
10
.trunk/configs/.markdownlint.yaml
Normal file
10
.trunk/configs/.markdownlint.yaml
Normal file
|
|
@ -0,0 +1,10 @@
|
|||
# Autoformatter friendly markdownlint config (all formatting rules disabled)
|
||||
default: true
|
||||
blank_lines: false
|
||||
bullet: false
|
||||
html: false
|
||||
indentation: false
|
||||
line_length: false
|
||||
spaces: false
|
||||
url: false
|
||||
whitespace: false
|
||||
3
.trunk/configs/.prettierrc
Normal file
3
.trunk/configs/.prettierrc
Normal file
|
|
@ -0,0 +1,3 @@
|
|||
{
|
||||
"trailingComma": "none"
|
||||
}
|
||||
7
.trunk/configs/.shellcheckrc
Normal file
7
.trunk/configs/.shellcheckrc
Normal file
|
|
@ -0,0 +1,7 @@
|
|||
enable=all
|
||||
source-path=SCRIPTDIR
|
||||
disable=SC2154
|
||||
|
||||
# If you're having issues with shellcheck following source, disable the errors via:
|
||||
# disable=SC1090
|
||||
# disable=SC1091
|
||||
14
.trunk/configs/svgo.config.js
Normal file
14
.trunk/configs/svgo.config.js
Normal file
|
|
@ -0,0 +1,14 @@
|
|||
module.exports = {
|
||||
plugins: [
|
||||
{
|
||||
name: "preset-default",
|
||||
params: {
|
||||
overrides: {
|
||||
removeViewBox: false, // https://github.com/svg/svgo/issues/1128
|
||||
sortAttrs: true,
|
||||
removeOffCanvasPaths: true
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
]
|
||||
};
|
||||
23
.trunk/trunk.yaml
Normal file
23
.trunk/trunk.yaml
Normal file
|
|
@ -0,0 +1,23 @@
|
|||
version: 0.1
|
||||
cli:
|
||||
version: 1.3.1
|
||||
plugins:
|
||||
sources:
|
||||
- id: trunk
|
||||
ref: v0.0.8
|
||||
uri: https://github.com/trunk-io/plugins
|
||||
lint:
|
||||
enabled:
|
||||
- markdownlint@0.33.0
|
||||
- actionlint@1.6.22
|
||||
- gitleaks@8.15.2
|
||||
- git-diff-check
|
||||
- shellcheck@0.9.0
|
||||
- prettier@2.8.2
|
||||
- shfmt@3.5.0
|
||||
- eslint@8.31.0
|
||||
- svgo@3.0.2
|
||||
runtimes:
|
||||
enabled:
|
||||
- go@1.18.3
|
||||
- node@18.12.1
|
||||
3
.vscode/extensions.json
vendored
Normal file
3
.vscode/extensions.json
vendored
Normal file
|
|
@ -0,0 +1,3 @@
|
|||
{
|
||||
"recommendations": ["trunk.io"]
|
||||
}
|
||||
7
.vscode/settings.json
vendored
Normal file
7
.vscode/settings.json
vendored
Normal file
|
|
@ -0,0 +1,7 @@
|
|||
{
|
||||
"editor.formatOnSave": true,
|
||||
"editor.defaultFormatter": "trunk.io",
|
||||
"files.associations": {
|
||||
"*.mdx": "markdown"
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
|
@ -11,7 +11,7 @@ Website and documentation source for the Meshtastic project.
|
|||
|
||||
## Stats
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
## Development & Building
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -4,4 +4,4 @@ collapsible: true # make the category collapsible
|
|||
link:
|
||||
type: generated-index
|
||||
title: About Meshtastic
|
||||
slug: /about
|
||||
slug: /about
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -23,7 +23,7 @@ There are many technologies (and repositories) used in creating the Meshtastic e
|
|||
|
||||
### Protocol Buffers
|
||||
|
||||
Most communication and interactions happen with protocol buffers. The [Meshtastic Protobuf Definitions](https://github.com/meshtastic/protobufs) repo is where all of the protocol buffer changes happen. See the [Protobuf API Reference](/docs/developers/protobufs/api) for more details.
|
||||
Most communication and interactions happen with protocol buffers. The [Meshtastic Protobuf Definitions](https://github.com/meshtastic/protobufs) repo is where all of the protocol buffer changes happen. See the [Protobuf API Reference](https://buf.build/meshtastic/protobufs/) for more details.
|
||||
|
||||
### Device Firmware
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -44,10 +44,10 @@ The [firmware](https://github.com/meshtastic/firmware) is where all of the firmw
|
|||
|
||||
@sachaw has been making tons of progress on the web app and would love help with:
|
||||
|
||||
* Saving of preferences
|
||||
* Better loading state indicators
|
||||
* Chat scroll lock
|
||||
* Various module support
|
||||
- Saving of preferences
|
||||
- Better loading state indicators
|
||||
- Chat scroll lock
|
||||
- Various module support
|
||||
|
||||
### Mobile Apps (Device Interface)
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -59,4 +59,3 @@ There are two phone apps that interact with the Meshtastic devices:
|
|||
### Documentation
|
||||
|
||||
This website is in the [Meshtastic](https://github.com/meshtastic/meshtastic) repository.
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -21,13 +21,13 @@ Everyone contributes in a different way. Join the [Meshtastic Discord](https://d
|
|||
|
||||
### What versions of Android does the Meshtastic Android App require?
|
||||
|
||||
Minimum requirement is Android 5 (Lollipop 2014, first BLE support), however at least Android 6 (Marshmallow 2015) is recommended as Bluetooth is more stable. While Android 5/6 are officially supported by Meshtastic, it is *not* recommended that you purchase devices with these versions due to their limited OS support and limited battery life due to age. Many newer models exist that are very affordable. A good resource to use when researching affordable devices is the [LineageOS Supported Devices List](https://wiki.lineageos.org/devices/).
|
||||
Minimum requirement is Android 5 (Lollipop 2014, first BLE support), however at least Android 6 (Marshmallow 2015) is recommended as Bluetooth is more stable. While Android 5/6 are officially supported by Meshtastic, it is _not_ recommended that you purchase devices with these versions due to their limited OS support and limited battery life due to age. Many newer models exist that are very affordable. A good resource to use when researching affordable devices is the [LineageOS Supported Devices List](https://wiki.lineageos.org/devices/).
|
||||
|
||||
### What does the icon next to the message mean?
|
||||
|
||||
- Cloud with an up arrow - Queued on the app to be sent to your device.
|
||||
- Cloud only - Queued on the device to be sent over the mesh.
|
||||
- Cloud with a check mark - At least one other node on the mesh acknowledged the message.
|
||||
- Cloud with a check mark - At least one other node on the mesh acknowledged the message.
|
||||
- Person with a check mark - The intended recipient of your direct message acknowledged the message.
|
||||
- Cloud crossed out - Not acknowledged or message error.
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -91,7 +91,7 @@ Hold down the left PWR button for about 10 seconds and the display should turn o
|
|||
|
||||
Push the left PWR button for about 1 second.
|
||||
|
||||
### Functionality of the T-Beam Buttons ###
|
||||
### Functionality of the T-Beam Buttons
|
||||
|
||||
[T-Beam Buttons](/docs/hardware/devices/tbeam/buttons) explained here
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -120,9 +120,9 @@ Once the node wakes up from sleep, your phone will relay any delayed messages th
|
|||
- Android instructions see: [Android Usage](/docs/software/android/usage#configuration-options)
|
||||
- Python CLI instructions see: [Python Usage](/docs/software/python/cli/usage#changing-settings)
|
||||
|
||||
### I am in Europe and my device seems to stop transmitting after a while, what is going on?
|
||||
### I am in Europe and my device seems to stop transmitting after a while, what is going on?
|
||||
|
||||
Europe has an hourly duty cycle limit of 10% in the frequency band that Meshtastic uses. It might be that you hit this limit if you are sending a lot. You can confirm this by checking whether you see duty cycle limit errors in the serial log, Mesh Log (Apple apps) or Debug Panel (Android).
|
||||
Europe has an hourly duty cycle limit of 10% in the frequency band that Meshtastic uses. It might be that you hit this limit if you are sending a lot. You can confirm this by checking whether you see duty cycle limit errors in the serial log, Mesh Log (Apple apps) or Debug Panel (Android).
|
||||
To limit traffic, you can consider setting the device metrics and position update intervals higher. Alternatively, the device can be configured to override the duty cycle limit, but then you will violate the regulations.
|
||||
|
||||
### Why does only one RAK Meshtastic Starter kit show up in my node list?
|
||||
|
|
@ -133,23 +133,24 @@ There was a bug where Meshtastic Starter kits were sent out with the same MAC ad
|
|||
|
||||
## Amateur Radio (HAM)
|
||||
|
||||
Meshtastic can be used by both unlicensed people and licensed HAM operators.
|
||||
Meshtastic can be used by both unlicensed people and licensed HAM operators.
|
||||
|
||||
### What is the benefit of using a HAM license with Meshtastic?
|
||||
|
||||
If you use your HAM radio license with Meshtastic, consider both the privileges and restrictions:
|
||||
|
||||
#### Privileges
|
||||
|
||||
- Increased Transmit Power
|
||||
- Up to 1500W transmit power! [FCC Part 97.313](https://www.ecfr.gov/current/title-47/chapter-I/subchapter-D/part-97/subpart-D/section-97.313)
|
||||
- Up to 1500W transmit power! [FCC Part 97.313](https://www.ecfr.gov/current/title-47/chapter-I/subchapter-D/part-97/subpart-D/section-97.313)
|
||||
- Higher Gain Antennas
|
||||
|
||||
#### Restrictions
|
||||
- Plain-Text Only
|
||||
- On amateur radio bands, encryption is illegal. [FCC Part 97.113.C](https://www.ecfr.gov/current/title-47/chapter-I/subchapter-D/part-97/subpart-B/section-97.113)
|
||||
- Lack of Privacy
|
||||
- As a HAM operator, it is a requirement that you identify yourself by your call sign periodically when transmitting. Your call sign will be publicly transmitted at least once every 10 minutes at minimum. [FCC Part 97.119.A](https://www.ecfr.gov/current/title-47/chapter-I/subchapter-D/part-97/subpart-B/section-97.119)
|
||||
|
||||
- Plain-Text Only
|
||||
- On amateur radio bands, encryption is illegal. [FCC Part 97.113.C](https://www.ecfr.gov/current/title-47/chapter-I/subchapter-D/part-97/subpart-B/section-97.113)
|
||||
- Lack of Privacy
|
||||
- As a HAM operator, it is a requirement that you identify yourself by your call sign periodically when transmitting. Your call sign will be publicly transmitted at least once every 10 minutes at minimum. [FCC Part 97.119.A](https://www.ecfr.gov/current/title-47/chapter-I/subchapter-D/part-97/subpart-B/section-97.119)
|
||||
|
||||
### How do I set my HAM call sign?
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -5,7 +5,7 @@ slug: /introduction
|
|||
sidebar_position: 1
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
import Link from '@docusaurus/Link';
|
||||
import Link from "@docusaurus/Link";
|
||||
|
||||
Meshtastic® is a project that enables you to use inexpensive LoRa radios as a long range off-grid communication platform in areas without existing or reliable communications infrastructure. This project is 100% community driven and open source!
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -32,8 +32,8 @@ If you are interested in a more technical overview of how Meshtastic works, visi
|
|||
|
||||
<div className="indexCtasBody">
|
||||
<Link
|
||||
className={'button button--outline button--lg cta--button'}
|
||||
to={'/docs/overview'}
|
||||
className={"button button--outline button--lg cta--button"}
|
||||
to={"/docs/overview"}
|
||||
>
|
||||
Technical Overview
|
||||
</Link>
|
||||
|
|
@ -45,8 +45,8 @@ Meshtastic is an open source project available on GitHub. Our generous volunteer
|
|||
|
||||
<div className="indexCtasBody">
|
||||
<Link
|
||||
className={'button button--outline button--lg cta--button'}
|
||||
to={'/docs/contributing'}
|
||||
className={"button button--outline button--lg cta--button"}
|
||||
to={"/docs/contributing"}
|
||||
>
|
||||
Contribute!
|
||||
</Link>
|
||||
|
|
@ -54,16 +54,16 @@ Meshtastic is an open source project available on GitHub. Our generous volunteer
|
|||
|
||||
<!--- FIXME add Github organization list/contributor list --->
|
||||
|
||||
## Start using Meshtastic!
|
||||
## Start using Meshtastic
|
||||
|
||||
Hopefully your "Getting Started" experience is straight forward and headache free. If you encounter any issues, please consider updating our documentation to improve future user experiences or reach out on the forum or Discord.
|
||||
Hopefully your "Getting Started" experience is straight forward and headache free. If you encounter any issues, please consider updating our documentation to improve future user experiences or reach out on the forum or Discord.
|
||||
|
||||
Our support is 100% volunteer based. We are passionate about the project and hope to help newcomers become Meshtastic experts!
|
||||
|
||||
<div className="indexCtasBody">
|
||||
<Link
|
||||
className={'button button--outline button--lg cta--button'}
|
||||
to={'/docs/getting-started'}
|
||||
className={"button button--outline button--lg cta--button"}
|
||||
to={"/docs/getting-started"}
|
||||
>
|
||||
Getting Started
|
||||
</Link>
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -55,62 +55,59 @@ I'm assuming that meshtastic is being used to hike in places where someone capab
|
|||
|
||||
I'm guessing that the network behaves somewhat like a store-and-forward network - or, at least, that the goal is to avoid establishing a two-way connection to transmit data. I'm afraid I haven't worked with mesh networks much, but remember studying them briefly in school about ten years ago.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
## Phased Proposal for the Meshtastic Security Framework
|
||||
|
||||
### Phase 1 - Fixed network encryption with AES-CTR
|
||||
|
||||
The current implementation provides optional confidentiality to members of a configured network:
|
||||
* Encryption is implemented in devices/nodes with network-wide encryption keys.
|
||||
* Encryption is optional and is turned off when devices are in 'Ham mode'.
|
||||
* There is no encryption supported in the clients (iOS, Android) to facilitate distribution as mass market software.
|
||||
* Pairing from client-to-device is by:
|
||||
* direct USB cable
|
||||
* BT pairing
|
||||
* Devices are 'promiscuous' and will pair with any near-by client. Network confidentiality requires physical protextion of all nodes.
|
||||
|
||||
- Encryption is implemented in devices/nodes with network-wide encryption keys.
|
||||
- Encryption is optional and is turned off when devices are in 'Ham mode'.
|
||||
- There is no encryption supported in the clients (iOS, Android) to facilitate distribution as mass market software.
|
||||
- Pairing from client-to-device is by:
|
||||
- direct USB cable
|
||||
- BT pairing
|
||||
- Devices are 'promiscuous' and will pair with any near-by client. Network confidentiality requires physical protextion of all nodes.
|
||||
|
||||
### Phase 2 - Strong device and client identity
|
||||
|
||||
**Phase 2 security goals:**
|
||||
* Know who sent a message (strong binding of messages to a particular node and/or terminal device)
|
||||
* This would be an optional feature for a message
|
||||
* Optionaly enforce identity based restrictions on some actions performed at nodes and/or clients
|
||||
* Optional support of strong pairing of a client to a device/node and restrict ability to manage and receive messages based on the pairing.
|
||||
* The BT paring and the cryptographic paring are separate (to simplify pahse 1 deployment and testing)
|
||||
* Above features should be architected to be ‘cryptographically strong’ and algorithm agile.
|
||||
|
||||
- Know who sent a message (strong binding of messages to a particular node and/or terminal device)
|
||||
- This would be an optional feature for a message
|
||||
- Optionaly enforce identity based restrictions on some actions performed at nodes and/or clients
|
||||
- Optional support of strong pairing of a client to a device/node and restrict ability to manage and receive messages based on the pairing.
|
||||
- The BT paring and the cryptographic paring are separate (to simplify pahse 1 deployment and testing)
|
||||
- Above features should be architected to be ‘cryptographically strong’ and algorithm agile.
|
||||
|
||||
**Phase 2 Proposed mechanisms:**
|
||||
* Proposed initial algorithms
|
||||
- Ed25519 for signatures based on NaCl libraries and iOS support for Ed25519
|
||||
* Clients and nodes to generate local identity Ed25519 keys
|
||||
* Devices maintain knowledge of owner public key
|
||||
* Devices maintain knowledge of some peers public keys and associated information (name, etc.)
|
||||
* Experimental protobuf message type with
|
||||
* cipher suite indicator (csi)
|
||||
* wrapped data using a cipher suite identifier to indicate use of Ed25519 wrapping identified algorithms.
|
||||
Wrapped data to contain any of the existing message types.
|
||||
* initial ‘cipher suite’ **only** signs a message
|
||||
* new signed/authenticated messages to:
|
||||
* device->client: provide ownership status of device (owner is identifed by a public key)
|
||||
* client->device: set owner key (must be existing device owner or owner null)
|
||||
* any->all. Broadcast public key and associated info (crude initial key distribution)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
- Proposed initial algorithms
|
||||
- Ed25519 for signatures based on NaCl libraries and iOS support for Ed25519
|
||||
- Clients and nodes to generate local identity Ed25519 keys
|
||||
- Devices maintain knowledge of owner public key
|
||||
- Devices maintain knowledge of some peers public keys and associated information (name, etc.)
|
||||
- Experimental protobuf message type with
|
||||
- cipher suite indicator (csi)
|
||||
- wrapped data using a cipher suite identifier to indicate use of Ed25519 wrapping identified algorithms.
|
||||
Wrapped data to contain any of the existing message types.
|
||||
- initial ‘cipher suite’ **only** signs a message
|
||||
- new signed/authenticated messages to:
|
||||
- device->client: provide ownership status of device (owner is identifed by a public key)
|
||||
- client->device: set owner key (must be existing device owner or owner null)
|
||||
- any->all. Broadcast public key and associated info (crude initial key distribution)
|
||||
|
||||
### Phase 3 and 3+:
|
||||
* Device/node e2e message confidentiality (1-to-1)
|
||||
* NO client side encryption
|
||||
* All encryption turned off for a network in 'Ham mode'
|
||||
* Protect messages sent over LoRa from eavesdroppers outside of a well identified group
|
||||
- multicast group key distribution / discovery (1-to-n)
|
||||
* Privacy
|
||||
* BT MAC layer address privatization
|
||||
* Node address privatization (Use use if based on device public key and schedule based aliasing)
|
||||
* Private peer discovery
|
||||
* Private service announcement and discovery
|
||||
* Device/node security (hardening key storage, tamper resistance, side channel protection, etc.)
|
||||
* Public key pairing process for client-to-device also sets up BT (no BT pin)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
- Device/node e2e message confidentiality (1-to-1)
|
||||
- NO client side encryption
|
||||
- All encryption turned off for a network in 'Ham mode'
|
||||
- Protect messages sent over LoRa from eavesdroppers outside of a well identified group
|
||||
- multicast group key distribution / discovery (1-to-n)
|
||||
- Privacy
|
||||
- BT MAC layer address privatization
|
||||
- Node address privatization (Use use if based on device public key and schedule based aliasing)
|
||||
- Private peer discovery
|
||||
- Private service announcement and discovery
|
||||
- Device/node security (hardening key storage, tamper resistance, side channel protection, etc.)
|
||||
- Public key pairing process for client-to-device also sets up BT (no BT pin)
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -11,4 +11,4 @@ When you send a message on your Meshtastic companion app, it is relayed to the r
|
|||
|
||||
When a receiving radio captures a packet, it checks to see if it has heard that message before. If it has it ignores the message. If it hasn't heard the message, it will rebroadcast it.
|
||||
|
||||
For each message a radio rebroadcasts, it marks the "hop limit" down by one. When a radio receives a packet with a hop limit of zero, it will not rebroadcast the message.
|
||||
For each message a radio rebroadcasts, it marks the "hop limit" down by one. When a radio receives a packet with a hop limit of zero, it will not rebroadcast the message.
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -25,23 +25,23 @@ This preamble allows receiving radios to synchronize clocks and start framing. W
|
|||
|
||||
This layer is conventional non-reliable LoRa packet transmission. The transmitted packet has the following representation before encoding for transmission:
|
||||
|
||||
| Offset | Length | Type | Usage |
|
||||
|:------------:|:-----------------------------:|:-------:|:---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- |
|
||||
| 0x00 | 1 byte | Integer | syncWord, always `0x2B`. |
|
||||
| 0x01 | 4 bytes | Integer | Packet header: Destination. The destination's unique NodeID. `0xFFFFFFFF` for broadcast. |
|
||||
| 0x05 | 4 bytes | Integer | Packet Header: Sender. The sender's unique NodeID. |
|
||||
| 0x09 | 4 bytes | Integer | Packet Header: The sending node's unique packet ID for this packet. |
|
||||
| 0x0D | 32 bits | Bits | Packet Header: Flags. See the [header flags](#packet-header-flags) for usage. |
|
||||
| 0x11 .. 0xFD | Varies, maximum of 237 bytes. | Bytes | Actual packet data. Unused bytes are not transmitted. |
|
||||
| 0xFE .. 0xFF | 2 Bytes | Bytes | Unused. |
|
||||
| Offset | Length | Type | Usage |
|
||||
| :----------: | :---------------------------: | :-----: | :--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- |
|
||||
| 0x00 | 1 byte | Integer | syncWord, always `0x2B`. |
|
||||
| 0x01 | 4 bytes | Integer | Packet header: Destination. The destination's unique NodeID. `0xFFFFFFFF` for broadcast. |
|
||||
| 0x05 | 4 bytes | Integer | Packet Header: Sender. The sender's unique NodeID. |
|
||||
| 0x09 | 4 bytes | Integer | Packet Header: The sending node's unique packet ID for this packet. |
|
||||
| 0x0D | 32 bits | Bits | Packet Header: Flags. See the [header flags](#packet-header-flags) for usage. |
|
||||
| 0x11 .. 0xFD | Varies, maximum of 237 bytes. | Bytes | Actual packet data. Unused bytes are not transmitted. |
|
||||
| 0xFE .. 0xFF | 2 Bytes | Bytes | Unused. |
|
||||
|
||||
#### Packet Header Flags
|
||||
|
||||
| Index | # of Bits | Usage |
|
||||
|:-------:|:---------:|:------------------------------|
|
||||
| 0 | 3 | HopLimit (see note in Layer 3) |
|
||||
| 3 | 1 | WantAck |
|
||||
| 4 .. 32 | 28 | Currently unused |
|
||||
| Index | # of Bits | Usage |
|
||||
| :-----: | :-------: | :----------------------------- |
|
||||
| 0 | 3 | HopLimit (see note in Layer 3) |
|
||||
| 3 | 1 | WantAck |
|
||||
| 4 .. 32 | 28 | Currently unused |
|
||||
|
||||
#### Usage Details
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -51,7 +51,7 @@ This layer is conventional non-reliable LoRa packet transmission. The transmitte
|
|||
|
||||
- **Packet Header - Unique ID:** The ID is a large, 32 bit ID to ensure there is enough unique state to protect an encrypted payload from attack.
|
||||
|
||||
- **Payload:** An encrypted and packed protobuf encoding of the SubPacket protobuf. Only the SubPacket is encrypted, while headers are not. This allows the option of eventually allowing nodes to route packets without knowing anything about the encrypted payload. For more information, see the [encryption](/docs/overview/encryption) and [protobufs](/docs/developers/protobufs/api) documentation. Any data past the maximum length is truncated.
|
||||
- **Payload:** An encrypted and packed protobuf encoding of the SubPacket protobuf. Only the SubPacket is encrypted, while headers are not. This allows the option of eventually allowing nodes to route packets without knowing anything about the encrypted payload. For more information, see the [encryption](/docs/overview/encryption) and [Protobuf API Reference](https://buf.build/meshtastic/protobufs/). Any data past the maximum length is truncated.
|
||||
|
||||
#### Carrier-Sense Multiple Access with Collision Avoidance (CSMA/CA)
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -46,7 +46,7 @@ There are 104 channels defined with the standard radio preset `LongFast`. After
|
|||
|
||||
### Considerations
|
||||
|
||||
Various data-rate options are available when configuring a channel and are inversely proportional to the theoretical range of the devices.
|
||||
Various data-rate options are available when configuring a channel and are inversely proportional to the theoretical range of the devices.
|
||||
|
||||
- **Spreading Factor** - How much we "spread" our data over time.
|
||||
- Each step up in Spreading Factor doubles the airtime to transmit.
|
||||
|
|
@ -65,16 +65,16 @@ Various data-rate options are available when configuring a channel and are inver
|
|||
|
||||
We have six predefined channels. These are the most common settings and have been proven to work well:
|
||||
|
||||
| Channel setting | Alt Channel Name | Data-Rate | SF / Symbols | Coding Rate | Bandwidth | Link Budget |
|
||||
| :------------------: | :---------------: | :------------------: | :-----------: | :----------: | :--------:| :---------- :|
|
||||
| Short Range / Fast | Short Fast | 6.8 kbps | 7 / 128 | 4/8 | 250 | 137dB |
|
||||
| Short Range / Slow | Short Slow | 3.9 kbps | 8 / 256 | 4/8 | 250 | 140dB |
|
||||
| Medium Range / Fast | Medium Fast | 2.2 kbps | 9 / 512 | 4/8 | 250 | 143dB |
|
||||
| Medium Range / Slow | Medium Slow | 1.2 kbps | 10 / 1024 | 4/8 | 250 | 146dB |
|
||||
| Long Range / Fast | Long Fast | 0.67 kbps (default) | 11 / 2048 | 4/8 | 250 | 148.5dB |
|
||||
| Long Range / Slow | Long Slow | 0.18 kbps | 12 / 4096 | 4/8 | 125 | 154dB |
|
||||
| Very Long Range - Slow | Very Long Slow | 0.05 kbps | 12 / 4096 | 4/8 | 31.25 | 160.1dB |
|
||||
|
||||
| Channel setting | Alt Channel Name | Data-Rate | SF / Symbols | Coding Rate | Bandwidth | Link Budget |
|
||||
| :--------------------: | :--------------: | :-----------------: | :----------: | :---------: | :-------: | :---------: |
|
||||
| Short Range / Fast | Short Fast | 6.8 kbps | 7 / 128 | 4/8 | 250 | 137dB |
|
||||
| Short Range / Slow | Short Slow | 3.9 kbps | 8 / 256 | 4/8 | 250 | 140dB |
|
||||
| Medium Range / Fast | Medium Fast | 2.2 kbps | 9 / 512 | 4/8 | 250 | 143dB |
|
||||
| Medium Range / Slow | Medium Slow | 1.2 kbps | 10 / 1024 | 4/8 | 250 | 146dB |
|
||||
| Long Range / Fast | Long Fast | 0.67 kbps (default) | 11 / 2048 | 4/8 | 250 | 148.5dB |
|
||||
| Long Range / Moderate | Long Moderate | 0.335 kbps | 11 / 2048 | 4/8 | 125 | 151dB |
|
||||
| Long Range / Slow | Long Slow | 0.18 kbps | 12 / 4096 | 4/8 | 125 | 154dB |
|
||||
| Very Long Range / Slow | Very Long Slow | 0.09 kbps | 12 / 4096 | 4/8 | 62.5 | 157dB |
|
||||
|
||||
:::note
|
||||
The link budget used by these calculations assumes a transmit power of 17dBm and an antenna with 0dB gain. Adjust your link budget assumptions based on your actual devices. Data-rate in this table is actual measured but doesn't count mesh overhead, hops and re-transmissions.
|
||||
|
|
@ -93,18 +93,17 @@ After applying the settings, you will need to restart the device. After your dev
|
|||
Some example settings:
|
||||
|
||||
| Data-rate | SF / Symbols | Coding Rate | Bandwidth | Link Budget | Note |
|
||||
| :---------:| :-----------:| :----------:| :--------:| :----------:| :----------------------------------------------------------------------- |
|
||||
| 37.50 kbps | 6 / 64 | 4/5 | 500 | 129dB | Fastest possible speed |
|
||||
| 3.125 kbps | 8 / 256 | 4/5 | 125 | 143dB | |
|
||||
| 1.953 kbps | 8 / 256 | 4/8 | 125 | 143dB | |
|
||||
| 1.343 kbps | 11 / 2048 | 4/8 | 500 | 145dB | |
|
||||
| 1.099 kbps | 9 / 512 | 4/8 | 125 | 146dB | |
|
||||
| 0.814 kbps | 10 / 1024 | 4/6 | 125 | 149dB | |
|
||||
| 0.610 kbps | 10 / 1024 | 4/8 | 125 | 149dB | |
|
||||
| 0.488 kbps | 11 / 2048 | 4/6 | 125 | 152dB | |
|
||||
| 0.336 kbps | 11 / 2048 | 4/8 | 125 | 152dB | |
|
||||
| 0.073 kbps | 12 / 4096 | 4/5 | 31 | 160dB | Twice the range and/or coverage of "Long Slow", low resilience to noise |
|
||||
| 0.046 kbps | 12 / 4096 | 4/8 | 31 | 160dB | Twice the range and/or coverage of "Long Slow", high resilience to noise |
|
||||
| :--------: | :----------: | :---------: | :-------: | :---------: | :----------------------------------------------------------------------- |
|
||||
| 37.50 kbps | 6 / 64 | 4/5 | 500 | 129dB | Fastest possible speed |
|
||||
| 3.125 kbps | 8 / 256 | 4/5 | 125 | 143dB | |
|
||||
| 1.953 kbps | 8 / 256 | 4/8 | 125 | 143dB | |
|
||||
| 1.343 kbps | 11 / 2048 | 4/8 | 500 | 145dB | |
|
||||
| 1.099 kbps | 9 / 512 | 4/8 | 125 | 146dB | |
|
||||
| 0.814 kbps | 10 / 1024 | 4/6 | 125 | 149dB | |
|
||||
| 0.610 kbps | 10 / 1024 | 4/8 | 125 | 149dB | |
|
||||
| 0.488 kbps | 11 / 2048 | 4/6 | 125 | 152dB | |
|
||||
| 0.073 kbps | 12 / 4096 | 4/5 | 31 | 160dB | Twice the range and/or coverage of "Long Slow", low resilience to noise |
|
||||
| 0.046 kbps | 12 / 4096 | 4/8 | 31 | 160dB | Twice the range and/or coverage of "Long Slow", high resilience to noise |
|
||||
|
||||
The link budget used by these calculations assumes a transmit power of 17dBm and an antenna with 0dB gain. Adjust your link budget assumptions based on your actual devices.
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -12,18 +12,21 @@ sidebar_position: 4
|
|||
- **Record Holder:** _PuzzledPancake_
|
||||
- **Source:** [Meshtastic Discourse](https://meshtastic.discourse.group/t/practical-range-test-results/692/44)
|
||||
|
||||
**Modem Settings**
|
||||
### Modem Settings
|
||||
|
||||
- **Frequency:** 868MHz
|
||||
- **Bandwidth:** 125
|
||||
- **Spread Factor:** 12
|
||||
- **Coding Rate:** 4/8
|
||||
|
||||
**Node A**
|
||||
### Node A
|
||||
|
||||
- **Device:** [LILYGO TTGO T-Beam w/ SX1262](/docs/hardware/devices/tbeam)
|
||||
- **Firmware Version:** 1.2
|
||||
- **Antenna:** [868MHz 5dBi Antenna](https://ivent.co.nz/product/category/1000/868mhz%205dbi%20antenna%20193mm%20black%20sma%20%28m%29/38646)
|
||||
|
||||
**Node B**
|
||||
### Node B
|
||||
|
||||
- **Device:** [LILYGO TTGO T-Beam w/ SX1262](/docs/hardware/devices/tbeam)
|
||||
- **Firmware Version:** 1.2
|
||||
- **Antenna:** [868MHz Vertical 6dBi](https://ivent.co.nz/product/category/1000/868mhz%20vertical%206dbi%20antenna/38606)
|
||||
|
|
@ -34,5 +37,6 @@ sidebar_position: 4
|
|||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
**Resources Used**
|
||||
- http://www.heywhatsthat.com
|
||||
### Resources Used
|
||||
|
||||
- http://www.heywhatsthat.com
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -1,21 +1,22 @@
|
|||
|
||||
| Region Code | Description |
|
||||
| :-------: | :--------: |
|
||||
| `UNSET` | Unset |
|
||||
| `US` | United States |
|
||||
| `EU_433` | European Union 433MHz |
|
||||
| `EU_868` | European Union 868MHz |
|
||||
| `CN` | China |
|
||||
| `JP` | Japan |
|
||||
| `ANZ` | Australia & New Zealand |
|
||||
| `KR` | Korea |
|
||||
| `TW` | Taiwan |
|
||||
| `RU` | Russia |
|
||||
| `IN` | India |
|
||||
| `NZ_865` | New Zealand 865MHz |
|
||||
| `TH` | Thailand |
|
||||
| `LORA_24` | 2.4 GHz band worldwide |
|
||||
| Region Code | Description |
|
||||
| :---------: | :---------------------: |
|
||||
| `UNSET` | Unset |
|
||||
| `US` | United States |
|
||||
| `EU_433` | European Union 433MHz |
|
||||
| `EU_868` | European Union 868MHz |
|
||||
| `CN` | China |
|
||||
| `JP` | Japan |
|
||||
| `ANZ` | Australia & New Zealand |
|
||||
| `KR` | Korea |
|
||||
| `TW` | Taiwan |
|
||||
| `RU` | Russia |
|
||||
| `IN` | India |
|
||||
| `NZ_865` | New Zealand 865MHz |
|
||||
| `UA_433` | Ukraine 433MHz |
|
||||
| `UA_868` | Ukraine 868MHz |
|
||||
| `TH` | Thailand |
|
||||
| `LORA_24` | 2.4 GHz band worldwide |
|
||||
|
||||
:::info
|
||||
EU_433 and EU_868 have to adhere to an hourly duty cycle limitation of 10%. Your device will stop transmitting if you reach it, until it is allowed again.
|
||||
:::
|
||||
:::
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -4,4 +4,4 @@ position: 4
|
|||
link:
|
||||
type: generated-index
|
||||
title: Configuration
|
||||
slug: /settings
|
||||
slug: /settings
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -5,10 +5,10 @@ slug: /settings/config/bluetooth
|
|||
sidebar_label: Bluetooth
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
import Tabs from '@theme/Tabs';
|
||||
import TabItem from '@theme/TabItem';
|
||||
import Tabs from "@theme/Tabs";
|
||||
import TabItem from "@theme/TabItem";
|
||||
|
||||
The Bluetooth config options are: Enabled, Pairing Mode and Fixed PIN Value. Bluetooth config uses an admin message sending a `Config.Bluetooth` protobuf.
|
||||
The Bluetooth config options are: Enabled, Pairing Mode and Fixed PIN Value. Bluetooth config uses an admin message sending a `Config.Bluetooth` protobuf.
|
||||
|
||||
:::info
|
||||
ESP32 Devices: Bluetooth will be disabled if WiFi is enabled. The WiFi setting takes precedence.
|
||||
|
|
@ -82,11 +82,11 @@ All Bluetooth module config options are available in the python CLI. Example com
|
|||
|
||||
:::
|
||||
|
||||
| Setting | Acceptable Values | Default |
|
||||
| :-----------------------: | :-----------------: | :-----: |
|
||||
| `bluetooth.enabled` | `true`, `false` | `true` |
|
||||
| `bluetooth.mode` | `RANDOM_PIN`, `FIXED_PIN`, `NO_PIN` | `RANDOM_PIN` |
|
||||
| `bluetooth.fixedPin` | `integer` (6 digits) | `123456` |
|
||||
| Setting | Acceptable Values | Default |
|
||||
| :------------------: | :---------------------------------: | :----------: |
|
||||
| `bluetooth.enabled` | `true`, `false` | `true` |
|
||||
| `bluetooth.mode` | `RANDOM_PIN`, `FIXED_PIN`, `NO_PIN` | `RANDOM_PIN` |
|
||||
| `bluetooth.fixedPin` | `integer` (6 digits) | `123456` |
|
||||
|
||||
:::tip
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -107,6 +107,7 @@ meshtastic --set bluetooth.enabled false
|
|||
meshtastic --set bluetooth.mode FIXED_PIN
|
||||
meshtastic --set bluetooth.fixed_pin 111111
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
</TabItem>
|
||||
<TabItem value="web">
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -120,4 +121,4 @@ All Bluetooth module config options are available for the Web UI.
|
|||
:::
|
||||
|
||||
</TabItem>
|
||||
</Tabs>
|
||||
</Tabs>
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -5,8 +5,8 @@ slug: /settings/config/channels
|
|||
sidebar_label: Channels
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
import Tabs from '@theme/Tabs';
|
||||
import TabItem from '@theme/TabItem';
|
||||
import Tabs from "@theme/Tabs";
|
||||
import TabItem from "@theme/TabItem";
|
||||
|
||||
The Channels config options are: Index, Roles, and Settings. Channel config uses an admin message sending a `Channel` protobuf which also consists of a `ChannelSettings` protobuf.
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -26,16 +26,16 @@ The channel index begins at 0 and ends at 7.
|
|||
|
||||
_Indexing_ can not be modified.
|
||||
|
||||
| Index | Channel | Default Role | Purpose |
|
||||
| :--------------------: | :----------------: | :----------------: | :----------------: |
|
||||
| 0 | 1 | `PRIMARY` | Used as `default` channel |
|
||||
| 1 | 2 | `DISABLED` | User defined |
|
||||
| 2 | 3 | `DISABLED` | User defined |
|
||||
| 3 | 4 | `DISABLED` | User defined |
|
||||
| 4 | 5 | `DISABLED` | User defined |
|
||||
| 5 | 6 | `DISABLED` | User defined |
|
||||
| 6 | 7 | `DISABLED` | User defined |
|
||||
| 7 | 8 | `DISABLED` | User defined |
|
||||
| Index | Channel | Default Role | Purpose |
|
||||
| :---: | :-----: | :----------: | :-----------------------: |
|
||||
| 0 | 1 | `PRIMARY` | Used as `default` channel |
|
||||
| 1 | 2 | `DISABLED` | User defined |
|
||||
| 2 | 3 | `DISABLED` | User defined |
|
||||
| 3 | 4 | `DISABLED` | User defined |
|
||||
| 4 | 5 | `DISABLED` | User defined |
|
||||
| 5 | 6 | `DISABLED` | User defined |
|
||||
| 6 | 7 | `DISABLED` | User defined |
|
||||
| 7 | 8 | `DISABLED` | User defined |
|
||||
|
||||
:::note
|
||||
You can **not** have `DISABLED` channels in-between active channels such as `PRIMARY` and `SECONDARY`. Active channels must be consecutive.
|
||||
|
|
@ -45,15 +45,20 @@ You can **not** have `DISABLED` channels in-between active channels such as `PRI
|
|||
|
||||
Each channel is assigned one of 3 roles:
|
||||
|
||||
1. `PRIMARY` or `1`
|
||||
- This is the first channel that is created for you on initial setup.
|
||||
- Only one primary channel can exist and can not be disabled.
|
||||
- Direct messages are only available on this channel.
|
||||
1. `PRIMARY` or `1`
|
||||
- This is the first channel that is created for you on initial setup.
|
||||
- Only one primary channel can exist and can not be disabled.
|
||||
- Direct messages are only available on this channel.
|
||||
2. `SECONDARY` or `2`
|
||||
- Can modify the encryption key (PSK).
|
||||
3. `DISABLED` or `0`
|
||||
- The channel is no longer available for use.
|
||||
- The channel settings are set to default.
|
||||
- Can modify the encryption key (PSK).
|
||||
3. `DISABLED` or `0`
|
||||
- The channel is no longer available for use.
|
||||
- The channel settings are set to default.
|
||||
|
||||
:::note
|
||||
While you can have a different PRIMARY channel and communicate over SECONDARY channels with the same PSK, a hash of the PRIMARY channel's name sets the LoRa channel number, which determines the actual frequency you are transmitting on in the band.
|
||||
To ensure devices with different PRIMARY channel name transmit on the same frequency, you must explicitly set the LoRa channel number.
|
||||
:::
|
||||
|
||||
## Channel Settings Values
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -71,12 +76,12 @@ Set to `0` by default.
|
|||
|
||||
### Name
|
||||
|
||||
A short identifier for the channel. _(< 12 bytes)_
|
||||
A short identifier for the channel. _(< 12 bytes)_
|
||||
|
||||
| Reserved Name | Purpose |
|
||||
| :--------------------: | :----------------: |
|
||||
| `""` (default) | If left empty on the Primary channel, this designates the `default` channel. |
|
||||
| `admin` | On Secondary channels, the name `admin` (case sensitive) designates the `admin` channel used to administer nodes over the mesh |
|
||||
| Reserved Name | Purpose |
|
||||
| :------------: | :----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------: |
|
||||
| `""` (default) | If left empty on the Primary channel, this designates the `default` channel. |
|
||||
| `admin` | On Secondary channels, the name `admin` (case sensitive) designates the `admin` channel used to administer nodes over the mesh |
|
||||
|
||||
### PSK
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -140,13 +145,13 @@ meshtastic --ch-set name "My Channel" --ch-set psk random --ch-set uplink_enable
|
|||
|
||||
:::
|
||||
|
||||
**Id**
|
||||
### Id
|
||||
|
||||
```shell title="Set the PRIMARY channel ID"
|
||||
meshtastic --ch-set id 1234 --ch-index 0
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
**Name**
|
||||
### Name
|
||||
|
||||
```shell title="Set channel name for the PRIMARY channel"
|
||||
# without spaces
|
||||
|
|
@ -155,7 +160,7 @@ meshtastic --ch-set name MyChannel --ch-index 0
|
|||
meshtastic --ch-set name "My Channel" --ch-index 0
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
**PSK**
|
||||
### PSK
|
||||
|
||||
If you use Meshtastic for exchanging messages you don't want other people to see, `random` is the setting you should use. Selecting `default` or any of the `simple` values from the following table will use publicly known encryption keys. They're shipped with Meshtastic source code and thus, anyone can listen to messages encrypted by them. They're great for testing and public channels.
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -186,7 +191,7 @@ meshtastic --ch-set psk 0x1a1a1a1a2b2b2b2b1a1a1a1a2b2b2b2b1a1a1a1a2b2b2b2b1a1a1a
|
|||
meshtastic --ch-set psk none --ch-index 0
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
**Uplink / Downlink**
|
||||
### Uplink / Downlink
|
||||
|
||||
For configuring gateways, please see [MQTT](/docs/settings/moduleconfig/mqtt)
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -209,4 +214,4 @@ All Channel config options are available in the Web UI.
|
|||
:::
|
||||
|
||||
</TabItem>
|
||||
</Tabs>
|
||||
</Tabs>
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -5,36 +5,66 @@ slug: /settings/config/device
|
|||
sidebar_label: Device
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
import Tabs from '@theme/Tabs';
|
||||
import TabItem from '@theme/TabItem';
|
||||
import Tabs from "@theme/Tabs";
|
||||
import TabItem from "@theme/TabItem";
|
||||
|
||||
The device config options are: Role, Serial Output, and Debug Log. Device config uses an admin message sending a `Config.Device` protobuf.
|
||||
The device config options are: Role, Serial Output, and Debug Log. Device config uses an admin message sending a `Config.Device` protobuf.
|
||||
|
||||
## Device Config Values
|
||||
|
||||
### Role
|
||||
Sets the role of node.
|
||||
|
||||
Sets the role of the node.
|
||||
|
||||
Acceptable values:
|
||||
|
||||
| Value | Description |
|
||||
| :-------: | :---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------: |
|
||||
| `CLIENT` | Client (default) - App connected client. |
|
||||
| `CLIENT_MUTE` | Client Mute - Same as a client except packets will not hop over this node, does not contribute to routing packets for mesh. |
|
||||
| `ROUTER` | Router - Mesh packets will prefer to be routed over this node. This node will not be used by client apps. The WiFi/BLE radios and the OLED screen will be put to sleep. |
|
||||
| `ROUTER_CLIENT` | Router Client - Mesh packets will prefer to be routed over this node. The Router Client can be used as both a Router and an app connected Client. |
|
||||
| Value | Description |
|
||||
| :-------------: | :----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------: |
|
||||
| `CLIENT` | Client (default) - This role will follow the standard routing rules while also allowing the device to interact with client applications via BLE/Wi-Fi (Android/Apple/Web). |
|
||||
| `CLIENT_MUTE` | Client Mute - Same as a client except packets will not hop over this node, does not contribute to routing packets for mesh. |
|
||||
| `ROUTER` | Router - Mesh packets will prefer to be routed over this node. The assumption is that Router-type devices will be placed in locations with a height/range/antenna advantage, and therefore have better overall coverage. This node will not be used by client apps. The BLE/Wi-Fi radios and the OLED screen will be put to sleep. Please note: Due to the preferred routing, this role may cause higher power usage due to more frequent transmission. |
|
||||
| `ROUTER_CLIENT` | Router Client - Hybrid of the Client and Router roles. Similar to Router, except the Router Client can be used as both a Router and an app connected Client. BLE/Wi-Fi and OLED screen will not be put to sleep. |
|
||||
| `REPEATER`[^1] | Repeater - Mesh packets will prefer to be routed over this node. This role eliminates unnecessary overhead such as NodeInfo, DeviceTelemetry, and any other mesh packet, resulting in the device not appearing as part of the network. As such, direct messaging this node is not available, as it will not appear in your nodes list which results in a cleaner mesh network. Channel and modem settings of the mesh packets being repeated must be identical to the repeater's configuration. Please see Rebroadcast Mode for additional settings specific to this role.[^1] |
|
||||
| `TRACKER`[^1] | Tracker - For use with devices intended as a GPS tracker. Position packets sent from this device will be higher priority, with position broadcasting every two minutes. Smart Position Broadcast will default to off.[^1] |
|
||||
|
||||
[^1]: These roles are new as of the 2.0.15 alpha release. They are still a work in progress and as such features and functionality may not work as described and can evolve or change as development continues.
|
||||
|
||||
### Rebroadcast Mode
|
||||
|
||||
This setting defines the device's behavior for how messages are rebroadcasted. [^2]
|
||||
|
||||
[^2]: This setting is new as of the 2.0.16 alpha release. It is still a work in progress and as such features and functionality may not work as described and can evolve or change as development continues.
|
||||
|
||||
| Value | Description |
|
||||
| :-----------------: | :-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------: |
|
||||
| `ALL` | ALL (Default) - This setting will rebroadcast ALL messages from its primary mesh as well as other meshes with the same modem settings, including when encryption settings differ. |
|
||||
| `All_SKIP_DECODING` | ALL_SKIP_DECODING - Same as behavior as ALL, but skips packet decoding and simply rebroadcasts them. **Only available with Repeater role.** |
|
||||
| `LOCAL_ONLY` | LOCAL_ONLY - Ignores observed messages from foreign meshes that are open or those which it cannot decrypt. Only rebroadcasts message on the nodes local primary / secondary channels. |
|
||||
|
||||
### Serial Console
|
||||
|
||||
### Serial Console
|
||||
Acceptable values: `true` or `false`
|
||||
|
||||
Disabling this will disable the SerialConsole by not initializing the StreamAPI.
|
||||
|
||||
### Debug Log
|
||||
|
||||
Acceptable values: `true` or `false`
|
||||
|
||||
By default we turn off logging as soon as an API client connects. Set this to true to leave the debug log outputting even when API is active.
|
||||
|
||||
### GPIO for user button
|
||||
|
||||
This is the GPIO pin number that will be used for the user button, if your device does not come with a predefined user button.
|
||||
|
||||
### GPIO for PWM Buzzer
|
||||
|
||||
This is the GPIO pin number that will be used for the PWM buzzer, if your device does not come with a predefined buzzer.
|
||||
|
||||
### Node Info Broadcast Seconds
|
||||
|
||||
This is the number of seconds between NodeInfo message broadcasts from the device. The device will still respond ad-hoc to NodeInfo messages when a response is wanted.
|
||||
|
||||
## Device Config Client Availability
|
||||
|
||||
<Tabs
|
||||
|
|
@ -73,11 +103,15 @@ All device config options are available in the python CLI. Example commands are
|
|||
|
||||
:::
|
||||
|
||||
| Setting | Acceptable Values | Default |
|
||||
|--------------------------|----------------------------------------------------|----------|
|
||||
| device.debug_log_enabled | `true`, `false` | `false` |
|
||||
| device.role | `CLIENT`, `CLIENT_MUTE`, `ROUTER`, `ROUTER_CLIENT` | `CLIENT` |
|
||||
| device.serial_enabled | `true`, `false` | `true` |
|
||||
| Setting | Acceptable Values | Default |
|
||||
| ------------------------------- | ------------------------------------------------------------------------- | ----------------- |
|
||||
| device.debug_log_enabled | `true`, `false` | `false` |
|
||||
| device.role | `CLIENT`, `CLIENT_MUTE`, `ROUTER`, `ROUTER_CLIENT`, `REPEATER`, `TRACKER` | `CLIENT` |
|
||||
| device.rebroadcast_mode | `ALL`, `ALL_SKIP_DECODING`, `LOCAL_ONLY` | `ALL` |
|
||||
| device.serial_enabled | `true`, `false` | `true` |
|
||||
| device.button_gpio | `0` - `34` | `0` |
|
||||
| device.buzzer_gpio | `0` - `34` | `0` |
|
||||
| device.node_info_broadcast_secs | `0` - `UINT MAX` | `10800` (3 hours) |
|
||||
|
||||
:::tip
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -107,6 +141,6 @@ meshtastic --set device.debug_log_enabled true
|
|||
:::info
|
||||
All device config options are available in the Web UI.
|
||||
:::
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
</TabItem>
|
||||
</Tabs>
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -5,52 +5,68 @@ slug: /settings/config/display
|
|||
sidebar_label: Display
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
import Tabs from '@theme/Tabs';
|
||||
import TabItem from '@theme/TabItem';
|
||||
import Tabs from "@theme/Tabs";
|
||||
import TabItem from "@theme/TabItem";
|
||||
|
||||
The display config options are: Screen On Duration, Auto Carousel Interval, Always Point North and GPS Format. Display config uses an admin message sending a `Config.Display` protobuf.
|
||||
The display config options are: Screen On Duration, Auto Carousel Interval, Always Point North and GPS Format. Display config uses an admin message sending a `Config.Display` protobuf.
|
||||
|
||||
## Device Config Values
|
||||
|
||||
### Screen On Duration
|
||||
|
||||
How long the screen remains on after the user button is pressed or messages are received.
|
||||
|
||||
### Auto Carousel Interval
|
||||
|
||||
Automatically toggles to the next page on the screen like a carousel, based the specified interval.
|
||||
|
||||
### Always Point North
|
||||
|
||||
If this is set, the compass heading on the screen outside of the circle will always point north. This feature is off by default and the top of display represents your heading direction, the North indicator will move around the circle.
|
||||
|
||||
### GPS Format
|
||||
|
||||
The format used to display GPS coordinates on the device screen.
|
||||
|
||||
Acceptable values:
|
||||
|
||||
| Value | Description |
|
||||
| :-------: | :--------------------------: |
|
||||
| `DEC` | Decimal Degrees |
|
||||
| `DMS` | Degrees Minutes Seconds |
|
||||
| `UTM` | Universal Transverse Mercator |
|
||||
| `MGRS` | Military Grid Reference System |
|
||||
| `OLC` | Open Location Code (Plus Codes) |
|
||||
| `OSGR` | Ordnance Survey Grid Reference |
|
||||
| Value | Description |
|
||||
| :----: | :-----------------------------: |
|
||||
| `DEC` | Decimal Degrees |
|
||||
| `DMS` | Degrees Minutes Seconds |
|
||||
| `UTM` | Universal Transverse Mercator |
|
||||
| `MGRS` | Military Grid Reference System |
|
||||
| `OLC` | Open Location Code (Plus Codes) |
|
||||
| `OSGR` | Ordnance Survey Grid Reference |
|
||||
|
||||
### Prefered display units
|
||||
|
||||
switch between `METRIC` (default) and `IMPERIAL` units
|
||||
|
||||
### Flip Screen
|
||||
|
||||
If enabled, the screen will be rotated 180 degrees, for cases that mount the screen upside down
|
||||
|
||||
### OLED Defintion
|
||||
The type of OLED Controller is auto-detected by default, but can be defined with this setting if the auto-detection fails.
|
||||
|
||||
The type of OLED Controller is auto-detected by default, but can be defined with this setting if the auto-detection fails. For the SH1107, we assume a square display with 128x128 Pixels like the GME128128-1.
|
||||
|
||||
Acceptable values:
|
||||
|
||||
| Value | Description |
|
||||
| :-------: | :--------------------------: |
|
||||
| `OLED_AUTO` | Auto detect display controller |
|
||||
| `OLED_SSD1306` | Always use SSD1306 driver |
|
||||
| `OLED_SH1106` | Always use SH1106 driver |
|
||||
| Value | Description |
|
||||
| :------------: | :-----------------------------------------: |
|
||||
| `OLED_AUTO` | Auto detect display controller |
|
||||
| `OLED_SSD1306` | Always use SSD1306 driver |
|
||||
| `OLED_SH1106` | Always use SH1106 driver |
|
||||
| `OLED_SH1107` | Always use SH1107 driver (Geometry 128x128) |
|
||||
|
||||
### Display Mode
|
||||
|
||||
The display mode can be set to `NORMAL` (default), `TWOCOLOR` or `INVERTED`. The `TWOCOLOR` mode is intended for OLED displays with the first line of output being a different color than the rest of the display. The `INVERTED` mode will invert that bicolor area, resulting in a white background headline on monochrome displays.
|
||||
|
||||
### Heading Bold
|
||||
|
||||
The heading can be hard to read when 'INVERTED' or 'TWOCOLOR' display mode is used. This setting will make the heading bold, so it is easier to read.
|
||||
|
||||
## Device Config Client Availability
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -90,15 +106,17 @@ All display config options are available in the python CLI. Example commands are
|
|||
|
||||
:::
|
||||
|
||||
| Setting | Acceptable Values | Default |
|
||||
|-----------------------------------|--------------------------------------------|------------------------------|
|
||||
| display.auto_screen_carousel_secs | `integer` | Default of `0` is 10 minutes |
|
||||
| display.compass_north_top | `false`, `true` | `false` |
|
||||
| display.flip_screen | `fasle`, `true` | `false` |
|
||||
| display.gps_format | `DEC`, `DMS`, `UTM`, `MGRS`, `OLC`, `OSGR` | `DEC` |
|
||||
| display.oled | `OLED_AUTO`, `OLED_SSD1306`, `OLED_SH1106` | `OLED_AUTO` |
|
||||
| display.screen_on_secs | `integer` | Default of `0` is off. |
|
||||
| display.units | `METRIC`, `IMPERIAL` | `METRIC` |
|
||||
| Setting | Acceptable Values | Default |
|
||||
| --------------------------------- | --------------------------------------------------------- | ----------------------------- |
|
||||
| display.auto_screen_carousel_secs | `integer` | Default of `0` is off. |
|
||||
| display.compass_north_top | `false`, `true` | `false` |
|
||||
| display.flip_screen | `fasle`, `true` | `false` |
|
||||
| display.gps_format | `DEC`, `DMS`, `UTM`, `MGRS`, `OLC`, `OSGR` | `DEC` |
|
||||
| display.oled | `OLED_AUTO`, `OLED_SSD1306`, `OLED_SH1106`, `OLED_SH1107` | `OLED_AUTO` |
|
||||
| display.screen_on_secs | `integer` | Default of `0` is 10 minutes. |
|
||||
| display.units | `METRIC`, `IMPERIAL` | `METRIC` |
|
||||
| display.displaymode | `NORMAL`, `TWOCOLOR`, `INVERTED` | `NORMAL` |
|
||||
| display.heading_bold | `false`, `true` | `false` |
|
||||
|
||||
:::tip
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -131,6 +149,6 @@ meshtastic --set display.gps_format UTM
|
|||
:::info
|
||||
All display config options are available in the Web UI.
|
||||
:::
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
</TabItem>
|
||||
</Tabs>
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -8,14 +8,14 @@ sidebar_position: 1
|
|||
|
||||
There are several config sections in the Meshtastic firmware, these are broken out so they can be sent as small admin messages over the mesh.
|
||||
|
||||
| Name | Description |
|
||||
|:----:|:-----------:|
|
||||
| [Bluetooth](/docs/settings/config/bluetooth) | Bluetooth config options are: Enabled, Pairing Mode and Fixed PIN. |
|
||||
| [Channels](/docs/settings/config/channels) | Channels config options are: Index, Role and Settings. |
|
||||
| [Device](/docs/settings/config/device) | Device config options are: Device Role, Serial Output, Debug Log and Factory Reset. |
|
||||
| [Display](/docs/settings/config/display) | Display config options are: Screen On Duration, Auto Carousel Interval, Always Point North, and GPS Format. |
|
||||
| [LoRa](/docs/settings/config/lora) | The LoRa config options are: Region, Modem Preset, Max Hops, Transmit Power, Bandwidth, Spread Factor, Coding Rate, Frequency Offset, Transmit Disabled and Ignore Incoming Array. |
|
||||
| [Network](/docs/settings/config/network) | Network config options are: WiFi Enabled, WiFi SSID, WiFi PSK, WiFi Mode and NTP Server. |
|
||||
| [Position](/docs/settings/config/position) | Position config options are: GPS Enabled, GPS Update Interval, GPS Attempt Time, Fixed Position, Smart Broadcast, Broadcast Interval and Position Packet Flags. |
|
||||
| [Power](/docs/settings/config/power) | Power config options are: Charge Current, Power Saving, Shutdown after losing power, ADC Multiplier Override Wait Bluetooth Interval, Mesh Super Deep Sleep Timeout, Super Deep Sleep Interval, Light Sleep Interval and Minimum Wake Interval. |
|
||||
| [User](/docs/settings/config/user) | The user config options are: Long Name, Short Name, and Is Licensed |
|
||||
| Name | Description |
|
||||
| :------------------------------------------: | :---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------: |
|
||||
| [Bluetooth](/docs/settings/config/bluetooth) | Bluetooth config options are: Enabled, Pairing Mode and Fixed PIN. |
|
||||
| [Channels](/docs/settings/config/channels) | Channels config options are: Index, Role and Settings. |
|
||||
| [Device](/docs/settings/config/device) | Device config options are: Device Role, Serial Output, Debug Log and Factory Reset. |
|
||||
| [Display](/docs/settings/config/display) | Display config options are: Screen On Duration, Auto Carousel Interval, Always Point North, and GPS Format. |
|
||||
| [LoRa](/docs/settings/config/lora) | The LoRa config options are: Region, Modem Preset, Max Hops, Transmit Power, Bandwidth, Spread Factor, Coding Rate, Frequency Offset, Transmit Disabled and Ignore Incoming Array. |
|
||||
| [Network](/docs/settings/config/network) | Network config options are: WiFi Enabled, WiFi SSID, WiFi PSK, WiFi Mode and NTP Server. |
|
||||
| [Position](/docs/settings/config/position) | Position config options are: GPS Enabled, GPS Update Interval, GPS Attempt Time, Fixed Position, Smart Broadcast, Broadcast Interval and Position Packet Flags. |
|
||||
| [Power](/docs/settings/config/power) | Power config options are: Charge Current, Power Saving, Shutdown after losing power, ADC Multiplier Override Wait Bluetooth Interval, Mesh Super Deep Sleep Timeout, Super Deep Sleep Interval, Light Sleep Interval and Minimum Wake Interval. |
|
||||
| [User](/docs/settings/config/user) | The user config options are: Long Name, Short Name, and Is Licensed |
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -5,11 +5,15 @@ slug: /settings/config/lora
|
|||
sidebar_label: LoRa
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
import Tabs from '@theme/Tabs';
|
||||
import TabItem from '@theme/TabItem';
|
||||
import LoRaRegions from '../../blocks/_lora-regions.mdx';
|
||||
import Tabs from "@theme/Tabs";
|
||||
import TabItem from "@theme/TabItem";
|
||||
import LoRaRegions from "../../blocks/_lora-regions.mdx";
|
||||
|
||||
The LoRa config options are: Region, Modem Preset, Max Hops, Transmit Power, Bandwidth, Spread Factor, Coding Rate, Frequency Offset, Transmit Enabled, Channel Number and Ignore Incoming Array. LoRa config uses an admin message sending a `Config.LoRa` protobuf.
|
||||
The LoRa config options are: Region, Modem Preset, Max Hops, Transmit Power, Bandwidth, Spread Factor, Coding Rate, Frequency Offset, Transmit Enabled, Channel Number and Ignore Incoming Array. LoRa config uses an admin message sending a `Config.LoRa` protobuf.
|
||||
|
||||
:::note
|
||||
In order to communicate fully, devices within a mesh must have identical settings for Region and Modem Preset, or identical custom Modem settings.
|
||||
:::
|
||||
|
||||
## LoRa Config Values
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -18,14 +22,40 @@ You must set your device's `lora.region` setting. This will ensure that you are
|
|||
:::
|
||||
|
||||
### Region
|
||||
|
||||
Sets the region for your node. Default is `unset`. As long as this is not set, the node screen will display a message and not transmit any packets.
|
||||
|
||||
<LoRaRegions />
|
||||
|
||||
### Modem Preset
|
||||
Use a sensible default for the modem. Default is `unset` which equates to `LONG_FAST`. Also 'Use Presets' has to be defined, which is the default. If 'Use Presets' is not defined, the modem will be configured manually with Bandwidth, Spread Factor, and Coding Rate.
|
||||
|
||||
Default is `unset` which equates to `LONG_FAST`. Presets are pre-defined modem settings (Bandwidth, Spread Factor, and Coding Rate) which influence both message speed and range. The default will provide a strong mixture of speed and range, for most users.
|
||||
|
||||
The presets are designed to provide further options for optimizing either speed (and reduced network congestion) or range, which can be useful for two real world scenarios:
|
||||
|
||||
1. A high number of devices exist in the mesh, or messages are sent very frequently. Faster speeds (and therefore lower radio time per device) can help with mesh network congestion.
|
||||
2. Maximum range is desired, for long range scenarios where a several second delay in message receipt is acceptable (for instance, attempting to send messages from a town to a distant mountain top).
|
||||
|
||||
The Presets available are as follows, and follow a linear pattern of Fastest <--> Slowest, and Shortest <--> Longest range:
|
||||
|
||||
1. `SHORT_FAST` (Fastest, highest bandwidth, lowest airtime, shortest range)
|
||||
|
||||
2. `SHORT_SLOW`
|
||||
|
||||
3. `MEDIUM_FAST`
|
||||
|
||||
4. `MEDIUM_SLOW`
|
||||
|
||||
5. `LONG_FAST` (Default)
|
||||
|
||||
6. `LONG_MODERATE`
|
||||
|
||||
7. `LONG_SLOW`
|
||||
|
||||
8. `VERY_LONG_SLOW` (Slowest, lowest bandwidth, highest airtime, longest range)
|
||||
|
||||
### Max Hops
|
||||
|
||||
Maximum number of hops. This can't be greater than 7. Default is 3 which should be fine for most applications. _**Really, 3 is fine.**_
|
||||
|
||||
### Transmit Power
|
||||
|
|
@ -61,6 +91,7 @@ Allows you to enable and disable transmit (TX) from the LoRa radio. Useful for h
|
|||
Defaults to true
|
||||
|
||||
### Channel Number
|
||||
|
||||
This is controlling the actual hardware frequency the radio is transmitting on. A channel number between 1 and NUM_CHANNELS (whatever the max is in the current region). If this is ZERO/UNSET then the rule is "use the old channel name hash based algorithm to derive the channel number".
|
||||
|
||||
### Ignore Incoming Array
|
||||
|
|
@ -110,18 +141,27 @@ LoRa config commands are available in the python CLI. Example commands are below
|
|||
|
||||
:::
|
||||
|
||||
| Setting | Acceptable Values | Default |
|
||||
| :----------: | :---------------------------------------------------------------------------: | :---------------: |
|
||||
| lora.modem_preset | `LONG_FAST`, `LONG_SLOW`, `VERY_LONG_SLOW`, `MEDIUM_SLOW`, `MEDIUM_FAST`, `SHORT_SLOW`, `SHORT_FAST` | `LONG_FAST` |
|
||||
| lora.region | `UNSET`, `US`, `EU_433`, `EU_868`, `CN`, `JP`, `ANZ`, `KR`, `TW`, `RU` ,`IN`, `NZ_865`, `TH`, `LORA_24` | `UNSET` |
|
||||
| lora.hop_limit | `1`,`2`,`3`,`4`,`5`,`6`,`7` | `3` |
|
||||
| lora.override_duty_cycle | `false`, `true` | `false` |
|
||||
| Setting | Acceptable Values | Default |
|
||||
| :-------------------------: | :-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------: | :---------: |
|
||||
| lora.modem_preset | `LONG_FAST`, `LONG_SLOW`, `VERY_LONG_SLOW`, `MEDIUM_SLOW`, `MEDIUM_FAST`, `SHORT_SLOW`, `SHORT_FAST` | `LONG_FAST` |
|
||||
| lora.use_preset | `false`, `true` | `false` |
|
||||
| lora.region | `UNSET`, `US`, `EU_433`, `EU_868`, `CN`, `JP`, `ANZ`, `KR`, `TW`, `RU` ,`IN`, `NZ_865`, `TH`, `LORA_24`, `UA_433`, `UA_868` | `UNSET` |
|
||||
| lora.bandwidth | `31`, `62`, `125`, `250`, `500` | `250` |
|
||||
| lora.spread_factor | `7`, `8`, `9`, `10`, `11`, `12` | `12` |
|
||||
| lora.coding_rate | `5`, `6`, `7`, `8` | `8` |
|
||||
| lora.frequency_offset | `0` to `1000000` | `0` |
|
||||
| lora.hop_limit | `1`,`2`,`3`,`4`,`5`,`6`,`7` | `3` |
|
||||
| lora.tx_power | `0` to `30` | `0` |
|
||||
| lora.tx_enabled | `false`, `false` | `true` |
|
||||
| lora.channel_num | `0`, `1` to `NUM_CHANNELS` | `0` |
|
||||
| lora.override_duty_cycle | `false`, `true` | `false` |
|
||||
| lora.sx126x_rx_boosted_gain | `false`, `true` | `false` |
|
||||
| lora.override_frequency | Any supported frequency the LoRA radio is capable of. Please respect local rules and regulations | `0` |
|
||||
|
||||
:::tip
|
||||
|
||||
Because the device will reboot after each command is sent via CLI, it is recommended when setting multiple values in a config section that commands be chained together as one.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
```shell title="Example:"
|
||||
meshtastic --set lora.region US --set lora.modem_preset LONG_FAST
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -5,8 +5,8 @@ slug: /settings/config/network
|
|||
sidebar_label: Network
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
import Tabs from '@theme/Tabs';
|
||||
import TabItem from '@theme/TabItem';
|
||||
import Tabs from "@theme/Tabs";
|
||||
import TabItem from "@theme/TabItem";
|
||||
|
||||
The Network config options are: WiFi Enabled, WiFi SSID, WiFi PSK, Ethernet Enabled, IPv4 Networking Mode, Static Address and NTP Server. Network config uses an admin message sending a `Config.Network` protobuf.
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -56,7 +56,6 @@ Set to `DHCP` by default. Change to `STATIC` to use a static IP address. Applies
|
|||
|
||||
contains ip, gateway, subnet and dns server in case you want a static configuration.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
:::tip
|
||||
The first time your device restarts after enabling WiFi or Ethernet, it will take an additional 20-30 seconds to boot. This is to generate self-signed SSL keys. The keys will be saved for future reuse.
|
||||
:::
|
||||
|
|
@ -103,12 +102,12 @@ All Network config options are available in the python CLI.
|
|||
|
||||
:::
|
||||
|
||||
| Setting | Acceptable Values | Default |
|
||||
| :-----------: | :---------------: | :-----: |
|
||||
| network.ntp_server | string | `0.pool.ntp.org` |
|
||||
| network.wifi_enabled | `true`, `false` | `false` |
|
||||
| network.wifi_psk | string | `""` |
|
||||
| network.wifi_ssid | string | `""` |
|
||||
| Setting | Acceptable Values | Default |
|
||||
| :------------------: | :---------------: | :--------------: |
|
||||
| network.ntp_server | string | `0.pool.ntp.org` |
|
||||
| network.wifi_enabled | `true`, `false` | `false` |
|
||||
| network.wifi_psk | string | `""` |
|
||||
| network.wifi_ssid | string | `""` |
|
||||
|
||||
:::tip
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -149,7 +148,7 @@ meshtastic --set network.wifi_psk "my password"
|
|||
:::info
|
||||
All Network config options are available in the Web UI.
|
||||
:::
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
</TabItem>
|
||||
|
||||
</Tabs>
|
||||
|
|
@ -160,18 +159,6 @@ All Network config options are available in the Web UI.
|
|||
|
||||
With `network.wifi_ssid` & `network.wifi_psk` populated, the device will know to connect to your network. Make sure you are in range of your WiFi. If you have a single Meshtastic device on your local network it's easy to connect to your device with DNS `http://meshtastic.local`. If you have multiple Meshtastic devices you will need to connect using their respective IP addresses.
|
||||
|
||||
If you have a screen attached to your device, the final page will display something similar to the following:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
WiFi: Software AP (Admin)
|
||||
IP: 192.168.42.1 (0/4)
|
||||
SSID: myNetwork
|
||||
http://meshtastic.local
|
||||
* * * * *
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
You should then be able to connect to the node using either the displayed IP address or the HTTP link.
|
||||
|
||||
### Disable WiFi
|
||||
|
||||
To disable WiFi completely, set `network.wifi_enabled` to `false`.
|
||||
To disable WiFi completely, set `network.wifi_enabled` to `false`.
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -5,17 +5,18 @@ slug: /settings/config/position
|
|||
sidebar_label: Position
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
import Tabs from '@theme/Tabs';
|
||||
import TabItem from '@theme/TabItem';
|
||||
import Tabs from "@theme/Tabs";
|
||||
import TabItem from "@theme/TabItem";
|
||||
|
||||
The position config options are: GPS Enabled, GPS Update Interval, GPS Attempt Time, Fixed Position, Smart Broadcast, Broadcast Interval and Position Packet Flags. Position config uses an admin message sending a `Config.Position` protobuf.
|
||||
The position config options are: GPS Enabled, GPS Update Interval, GPS Attempt Time, Fixed Position, Smart Broadcast, Broadcast Interval and Position Packet Flags. Position config uses an admin message sending a `Config.Position` protobuf.
|
||||
|
||||
Position data from GPS is provided by either the radio or your paired phone. Position data is not required to use Meshtastic but time calculations require at least one device on the mesh have either a GPS or internet connection for time.
|
||||
|
||||
## Position Config Values
|
||||
|
||||
### GPS Disabled
|
||||
Acceptable values: `true` or `false`
|
||||
|
||||
Acceptable values: `true` or `false`
|
||||
|
||||
Defaults to false. Should the device GPS be disabled for this node?
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -25,18 +26,19 @@ How often should we try to get GPS position (in seconds), or zero for the defaul
|
|||
|
||||
### GPS Attempt Time
|
||||
|
||||
How long should we try to get our position during each GPS update interval attempt? (in seconds) Or if zero, use the default of 30 seconds.
|
||||
How long should we try to get our position during each GPS update interval attempt? (in seconds) Or if zero, use the default of 30 seconds.
|
||||
|
||||
### Fixed Position
|
||||
|
||||
Acceptable values: `true` or `false`
|
||||
Acceptable values: `true` or `false`
|
||||
|
||||
Off by default
|
||||
|
||||
If set, this node is at a fixed position. The device will generate GPS updates at the regular GPS update interval, but use whatever the last lat/lon/alt it saved for the node. The lat/lon/alt can be set by an internal GPS or with the help of the mobile device's GPS.
|
||||
|
||||
### Smart Broadcast
|
||||
Acceptable values: `true` or `false`
|
||||
|
||||
Acceptable values: `true` or `false`
|
||||
|
||||
On by default
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -54,27 +56,29 @@ If smart broadcast is of we should send our position this often (but only if it
|
|||
|
||||
The GPS updates will be sent out every Broadcast Interval, with either the actual GPS location, or an empty location if no GPS fix was achieved. This defaults to broadcast every 15 minutes.
|
||||
|
||||
### Position Flags
|
||||
### Position Flags
|
||||
|
||||
Bit field of boolean configuration options for POSITION messages (bitwise OR of PositionFlags)
|
||||
Bit field of boolean configuration options for POSITION messages (bitwise OR of PositionFlags)
|
||||
|
||||
| Value | Description |
|
||||
| :-----------: | :---------------------------------------------------------: |
|
||||
| UNSET | Required for compilation |
|
||||
| ALTITUDE | Include an altitude value (if available) |
|
||||
| ALTITUDE_MSL | Altitude value is MSL |
|
||||
| GEOIDAL_SEPARATION | Include geoidal separation |
|
||||
| DOP | Include the DOP value ; PDOP used by default, see below |
|
||||
| HVDOP | If POS_DOP set, send separate HDOP / VDOP values instead of PDOP |
|
||||
| SATINVIEW | Include number of "satellites in view" |
|
||||
| SEQ_NO | Include a sequence number incremented per packet |
|
||||
| TIMESTAMP | Include positional timestamp (from GPS solution) |
|
||||
| HEADING | Include positional heading (from GPS solution) |
|
||||
| SPEED | Include positional speed (from GPS solution) |
|
||||
| Value | Description |
|
||||
| :----------------: | :--------------------------------------------------------------: |
|
||||
| UNSET | Required for compilation |
|
||||
| ALTITUDE | Include an altitude value (if available) |
|
||||
| ALTITUDE_MSL | Altitude value is MSL |
|
||||
| GEOIDAL_SEPARATION | Include geoidal separation |
|
||||
| DOP | Include the DOP value ; PDOP used by default, see below |
|
||||
| HVDOP | If POS_DOP set, send separate HDOP / VDOP values instead of PDOP |
|
||||
| SATINVIEW | Include number of "satellites in view" |
|
||||
| SEQ_NO | Include a sequence number incremented per packet |
|
||||
| TIMESTAMP | Include positional timestamp (from GPS solution) |
|
||||
| HEADING | Include positional heading (from GPS solution) |
|
||||
| SPEED | Include positional speed (from GPS solution) |
|
||||
|
||||
### GPIO RX/TX for GPS Module
|
||||
|
||||
If your device does not have a fixed GPS chip, you can define the GPIO pins for the RX and TX pins of a GPS module.
|
||||
|
||||
## Position Config Client Availability
|
||||
## Position Config Client Availability
|
||||
|
||||
<Tabs
|
||||
groupId="settings"
|
||||
|
|
@ -106,21 +110,23 @@ All position config values are available on iOS, iPadOS and macOS at Settings >
|
|||
</TabItem>
|
||||
<TabItem value="cli">
|
||||
|
||||
:::info
|
||||
:::info
|
||||
|
||||
All Position config commands are available in the python CLI. Example commands are below:
|
||||
|
||||
:::
|
||||
|
||||
| Setting | Acceptable Values | Default |
|
||||
| :----------------------------: | :-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------: | :-------------: |
|
||||
| position.gps_enabled | `true`, `false` | `true` |
|
||||
| position.gps_update_interval | `integer` (seconds) | Default `0` is 30 Seconds |
|
||||
| position.gps_attempt_time | `integer` (seconds) | Default of `0` is 30 Seconds |
|
||||
| position.fixed_position | `true`, `false` | `false` |
|
||||
| position.position_broadcast_smart_enabled | `true`, `false` | `true` |
|
||||
| position.position_broadcast_secs | `integer` (seconds) | Default of `0` is 15 Minutes |
|
||||
| position.flags | `UNSET`, `ALTITUDE`, `ALTITUDE_MSL`, `GEOIDAL_SEPARATION`, `DOP`, `HVDOP`, `PDOP`, `SATINVIEW`, `SEQ_NO`, `TIMESTAMP`, `HEADING`, `SPEED` | `UNSET` |
|
||||
| Setting | Acceptable Values | Default |
|
||||
| :---------------------------------------: | :---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------: | :--------------------------: |
|
||||
| position.gps_enabled | `true`, `false` | `true` |
|
||||
| position.gps_update_interval | `integer` (seconds) | Default `0` is 30 Seconds |
|
||||
| position.gps_attempt_time | `integer` (seconds) | Default of `0` is 30 Seconds |
|
||||
| position.fixed_position | `true`, `false` | `false` |
|
||||
| position.position_broadcast_smart_enabled | `true`, `false` | `true` |
|
||||
| position.position_broadcast_secs | `integer` (seconds) | Default of `0` is 15 Minutes |
|
||||
| position.flags | `UNSET`, `ALTITUDE`, `ALTITUDE_MSL`, `GEOIDAL_SEPARATION`, `DOP`, `HVDOP`, `PDOP`, `SATINVIEW`, `SEQ_NO`, `TIMESTAMP`, `HEADING`, `SPEED` | `UNSET` |
|
||||
| position.rx_gpio | `integer` (0-39) | `UNSET` |
|
||||
| position.tx_gpio | `integer` (0-34) | `UNSET` |
|
||||
|
||||
:::tip
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -183,7 +189,7 @@ meshtastic --pos-fields UNSET
|
|||
:::info
|
||||
All position config options are available in the Web UI.
|
||||
:::
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
</TabItem>
|
||||
</Tabs>
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -5,10 +5,10 @@ slug: /settings/config/power
|
|||
sidebar_label: Power
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
import Tabs from '@theme/Tabs';
|
||||
import TabItem from '@theme/TabItem';
|
||||
import Tabs from "@theme/Tabs";
|
||||
import TabItem from "@theme/TabItem";
|
||||
|
||||
The power config options are: Power Saving, Shutdown after losing power, ADC Multiplier Override Wait Bluetooth Interval, Mesh Super Deep Sleep Timeout, Super Deep Sleep Interval, Light Sleep Interval and Minimum Wake Interval. Power config uses an admin message sending a `Config.Power` protobuf.
|
||||
The power config options are: Power Saving, Shutdown after losing power, ADC Multiplier Override Wait Bluetooth Interval, Mesh Super Deep Sleep Timeout, Super Deep Sleep Interval, Light Sleep Interval and Minimum Wake Interval. Power config uses an admin message sending a `Config.Power` protobuf.
|
||||
|
||||
Power settings are advanced configuration, most users should choose a role under Device Config to manage power for their device and should never need to touch any of these settings.
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -16,14 +16,13 @@ Power settings are advanced configuration, most users should choose a role under
|
|||
|
||||
### Power Saving
|
||||
|
||||
If set, we are powered from a low-current source (i.e. solar), so even if it looks like we have power flowing in we should try to minimize power consumption as much as possible.
|
||||
If set, Bluetooth, Wifi, and screen (if applicable) are turned off. When using the Router device role, this setting is on by default. The assumption for a Router is that the device will be used in a standalone manner where these features are not needed, and will be shut off to conserve power. This is especially useful when a device is powered from a low-current source (i.e. solar).
|
||||
|
||||
### Shutdown after losing power
|
||||
|
||||
Automatically shut down a device after a defined time period if power is lost.
|
||||
|
||||
### ADC Multiplier Override
|
||||
**Fixes issues on Heltec v2**
|
||||
### ADC Multiplier Override `Fixes issues on Heltec v2`
|
||||
|
||||
Ratio of voltage divider for battery pin e.g. 3.20 (R1=100k, R2=220k)
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -39,21 +38,19 @@ How long wait before turning off BLE in no Bluetooth states
|
|||
|
||||
### Mesh Super Deep Sleep Timeout
|
||||
|
||||
While in Light Sleep if this value is exceeded we will lower into super deep sleep
|
||||
While in Light Sleep if this value is exceeded we will lower into super deep sleep
|
||||
|
||||
or Super Deep Sleep Interval (default 1 year) or a button press
|
||||
|
||||
`0` for default of two hours, MAXUINT for disabled
|
||||
|
||||
### Super Deep Sleep Interval
|
||||
### Super Deep Sleep Interval
|
||||
|
||||
While in Light Sleep if Mesh Super Deep Sleep Timeout Seconds is exceeded we will lower into super deep sleep or this value (default 1 year) or a button press
|
||||
|
||||
`0` for default of one year
|
||||
|
||||
### Light Sleep Interval
|
||||
|
||||
**ESP32 Only Setting**
|
||||
### Light Sleep Interval `ESP32 Only Setting`
|
||||
|
||||
In light sleep the CPU is suspended, LoRa radio is on, BLE is off an GPS is on
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -98,22 +95,22 @@ Power config is not available on Apple OS's.
|
|||
</TabItem>
|
||||
<TabItem value="cli">
|
||||
|
||||
:::info
|
||||
:::info
|
||||
|
||||
All Power config options are available in the python CLI.
|
||||
|
||||
:::
|
||||
|
||||
| Setting | Acceptable Values | Default |
|
||||
| :----------------------------------: | :-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------: | :-------: |
|
||||
| power.is_power_saving | `true`, `false` | `false` |
|
||||
| power.on_battery_shutdown_after_secs | `integer` (seconds) | Default of `0` is off |
|
||||
| power.adc_multiplier_override | `2-4` (floating point value) | Default of `0` uses firmware values |
|
||||
| power.wait_bluetooth_secs | `integer` (seconds) | Default of `0` is 1 minute |
|
||||
| power.mesh_sds_timeout_secs | `integer` (seconds) | Default of `0` is 2 hours |
|
||||
| power.sds_secs | `integer` (seconds) | Default of `0` is 1 year |
|
||||
| power.ls_secs | `integer` (seconds) | Default of `0` is 1 hour |
|
||||
| power.min_wake_secs | `integer` (seconds) | Default of `0` is 10 seconds |
|
||||
| Setting | Acceptable Values | Default |
|
||||
| :----------------------------------: | :--------------------------: | :---------------------------------: |
|
||||
| power.is_power_saving | `true`, `false` | `false` |
|
||||
| power.on_battery_shutdown_after_secs | `integer` (seconds) | Default of `0` is off |
|
||||
| power.adc_multiplier_override | `2-4` (floating point value) | Default of `0` uses firmware values |
|
||||
| power.wait_bluetooth_secs | `integer` (seconds) | Default of `0` is 1 minute |
|
||||
| power.mesh_sds_timeout_secs | `integer` (seconds) | Default of `0` is 2 hours |
|
||||
| power.sds_secs | `integer` (seconds) | Default of `0` is 1 year |
|
||||
| power.ls_secs | `integer` (seconds) | Default of `0` is 1 hour |
|
||||
| power.min_wake_secs | `integer` (seconds) | Default of `0` is 10 seconds |
|
||||
|
||||
:::tip
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -161,12 +158,13 @@ meshtastic --set power.ls_secs 120
|
|||
meshtastic --set power.min_wake_secs 0
|
||||
meshtastic --set power.min_wake_secs 120
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
</TabItem>
|
||||
<TabItem value="web">
|
||||
|
||||
:::info
|
||||
All power config options are available in the Web UI.
|
||||
:::
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
</TabItem>
|
||||
</Tabs>
|
||||
</Tabs>
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -5,8 +5,8 @@ slug: /settings/config/user
|
|||
sidebar_label: User
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
import Tabs from '@theme/Tabs';
|
||||
import TabItem from '@theme/TabItem';
|
||||
import Tabs from "@theme/Tabs";
|
||||
import TabItem from "@theme/TabItem";
|
||||
|
||||
The user config options are: Long Name, Short Name, and Is Licensed. User config uses an admin message sending a `User` protobuf.
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -51,7 +51,7 @@ values={[
|
|||
|
||||
:::info
|
||||
|
||||
User Config options are available for Android.
|
||||
User Config options are available for Android.
|
||||
|
||||
1. Open the Meshtastic App
|
||||
2. Navigate to: **Vertical Ellipsis (3 dots top right) > Device Settings > User Config**
|
||||
|
|
@ -109,4 +109,4 @@ All User config options are available in the Web UI.
|
|||
:::
|
||||
|
||||
</TabItem>
|
||||
</Tabs>
|
||||
</Tabs>
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -6,7 +6,6 @@ slug: /hardware/peripheral/
|
|||
sidebar_position: 6
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
## Firmware Versions
|
||||
|
||||
:::warning
|
||||
|
|
@ -47,7 +46,7 @@ The procedure using the python command line tool is:
|
|||
meshtastic --ch-add gpio
|
||||
```
|
||||
3. If doing local testing, you may also want to change the speed of the channel:
|
||||
```sh
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
meshtastic --ch-mediumfast
|
||||
```
|
||||
4. Check the channel has been created and copy the long "Complete URL" that contains all the channels on that device:
|
||||
|
|
@ -144,7 +143,6 @@ By default, the pin may be "off" or "on". (It will most likely "off".) See the s
|
|||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
## Using GPIOs from the Python CLI
|
||||
|
||||
### Writing a GPIO
|
||||
|
|
@ -178,4 +176,4 @@ meshtastic --port /dev/ttyUSB0 --gpio-watch 0x10 --dest 28979058
|
|||
# Received RemoteHardware typ=GPIOS_CHANGED, gpio_value=0
|
||||
# Received RemoteHardware typ=GPIOS_CHANGED, gpio_value=16
|
||||
# < press ctrl-c to exit >
|
||||
```
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -5,8 +5,8 @@ slug: /settings/moduleconfig/audio
|
|||
sidebar_label: Audio
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
import Tabs from '@theme/Tabs';
|
||||
import TabItem from '@theme/TabItem';
|
||||
import Tabs from "@theme/Tabs";
|
||||
import TabItem from "@theme/TabItem";
|
||||
|
||||
The audio module config options are: Codec2 Enabled, PTT GPIO, Audio Bitrate/Codec Mode, I2S Word Select, I2S Data IN, I2S Data OUT and I2S Clock. Audio Module config uses an admin message sending a `ConfigModule.Audio` protobuf.
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -26,15 +26,15 @@ The GPIO to use for the Push-To-Talk button. The default is GPIO 39 on the ESP32
|
|||
|
||||
The bitrate to use for audio. The default is `CODEC2_700B`. The available options are:
|
||||
|
||||
* CODEC2_DEFAULT
|
||||
* CODEC2_3200
|
||||
* CODEC2_2400
|
||||
* CODEC2_1600
|
||||
* CODEC2_1400
|
||||
* CODEC2_1300
|
||||
* CODEC2_1200
|
||||
* CODEC2_700B
|
||||
* CODEC2_700
|
||||
- CODEC2_DEFAULT
|
||||
- CODEC2_3200
|
||||
- CODEC2_2400
|
||||
- CODEC2_1600
|
||||
- CODEC2_1400
|
||||
- CODEC2_1300
|
||||
- CODEC2_1200
|
||||
- CODEC2_700B
|
||||
- CODEC2_700
|
||||
|
||||
### I2S Word Select
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -53,7 +53,7 @@ The GPIO to use for the DIN signal in the I2S interface.
|
|||
The GPIO to use for the SCK signal in the I2S interface.
|
||||
|
||||
:::info What is this?
|
||||
These Pins comprise an I2S digital audio interface. Meshtastic uses it in monoaural mode. The software will use the logical 'LEFT' Stereo channel for the microphone and the logical 'RIGHT' Stereo channel for the speaker, so configure your breakouts accordingly. Audio is Half-Duplex, so we can re-use part of the pins for a bi-directional configuration. There's __no__ default pin assigment, setting these is mandatory.
|
||||
These Pins comprise an I2S digital audio interface. Meshtastic uses it in monoaural mode. The software will use the logical 'LEFT' Stereo channel for the microphone and the logical 'RIGHT' Stereo channel for the speaker, so configure your breakouts accordingly. Audio is Half-Duplex, so we can re-use part of the pins for a bi-directional configuration. There's **no** default pin assigment, setting these is mandatory.
|
||||
:::
|
||||
|
||||
## Audio Module Config Client Availability
|
||||
|
|
@ -88,21 +88,21 @@ Audio module config is not available on iOS, iPadOS and macOS.
|
|||
</TabItem>
|
||||
<TabItem value="cli">
|
||||
|
||||
:::info
|
||||
:::info
|
||||
|
||||
All audio module config options are available in the python CLI. Example commands are below:
|
||||
|
||||
:::
|
||||
|
||||
| Setting | Acceptable Values | Default |
|
||||
| :-------------------: | :-----------------: | :-----: |
|
||||
| audio.enabled | `true`, `false` | `false` |
|
||||
| audio.ptt_pin | GPIO Pin Number 1-39 | Default of `39` is Unset |
|
||||
| audio.bitrate | `CODEC2_DEFAULT` `CODEC2_3200` `CODEC2_2400` `CODEC2_1600` `CODEC2_1400` `CODEC2_1300` `CODEC2_1200` `CODEC2_700B` `CODEC2_700` | `CODEC2_DEFAULT` |
|
||||
| audio.i2s_ws | GPIO Pin Number 1-34 | no Default |
|
||||
| audio.i2s_sd | GPIO Pin Number 1-39 | no Default |
|
||||
| audio.i2s_din | GPIO Pin Number 1-34 | no Default |
|
||||
| audio.i2s_sck | GPIO Pin Number 1-34 | no Default |
|
||||
| Setting | Acceptable Values | Default |
|
||||
| :-----------: | :-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------: | :----------------------: |
|
||||
| audio.enabled | `true`, `false` | `false` |
|
||||
| audio.ptt_pin | GPIO Pin Number 1-39 | Default of `39` is Unset |
|
||||
| audio.bitrate | `CODEC2_DEFAULT` `CODEC2_3200` `CODEC2_2400` `CODEC2_1600` `CODEC2_1400` `CODEC2_1300` `CODEC2_1200` `CODEC2_700B` `CODEC2_700` | `CODEC2_DEFAULT` |
|
||||
| audio.i2s_ws | GPIO Pin Number 1-34 | no Default |
|
||||
| audio.i2s_sd | GPIO Pin Number 1-39 | no Default |
|
||||
| audio.i2s_din | GPIO Pin Number 1-34 | no Default |
|
||||
| audio.i2s_sck | GPIO Pin Number 1-34 | no Default |
|
||||
|
||||
:::tip
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -142,7 +142,7 @@ meshtastic --set audio.bitrate CODEC2_1400
|
|||
:::info
|
||||
All audio module config options are available in the Web UI.
|
||||
:::
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
</TabItem>
|
||||
</Tabs>
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -5,12 +5,12 @@ slug: /settings/moduleconfig/canned-message
|
|||
sidebar_label: Canned Message
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
import Tabs from '@theme/Tabs';
|
||||
import TabItem from '@theme/TabItem';
|
||||
import Tabs from "@theme/Tabs";
|
||||
import TabItem from "@theme/TabItem";
|
||||
|
||||
The Canned Message Module will allow you to send messages to the mesh network from the device without using the phone app. You can predefine text messages to choose from.
|
||||
|
||||
The canned message module config options are: Enabled, Save, and Sender. Range Test Module config uses an admin message sending a `ConfigModule.CannedMessage` protobuf.
|
||||
The canned message module config options are: Enabled, Save, and Sender. Range Test Module config uses an admin message sending a `ConfigModule.CannedMessage` protobuf.
|
||||
|
||||
## Canned Message Module Config Values
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -23,7 +23,7 @@ Enables the canned message module.
|
|||
Sends a bell character with each message.
|
||||
|
||||
The [External Notification Module](external-notification) can be set up to beep when a new message arrives.
|
||||
This module can also be configured to beep only when message contains the bell character.
|
||||
This module can also be configured to beep only when message contains the bell character.
|
||||
|
||||
### Messages
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -33,12 +33,12 @@ The list of pre-set messages, up to 200 bytes.
|
|||
|
||||
Input event sources accepted by the canned message module.
|
||||
|
||||
| Value | Description |
|
||||
| :----------: | :---------------------------------------------------------------------: |
|
||||
| `_any` | Default. Allows any peripheral input device connected to the device. |
|
||||
| `rotEnc1` | Basic Rotary Encoder |
|
||||
| `upDownEnc1` | Up Down Encoder (use this also for RAK14006 Rotary Encoder) |
|
||||
| `cardkb` | M5 Stack CardKB (this covers RAK14004 Keymatrix) |
|
||||
| Value | Description |
|
||||
| :----------: | :------------------------------------------------------------------: |
|
||||
| `_any` | Default. Allows any peripheral input device connected to the device. |
|
||||
| `rotEnc1` | Basic Rotary Encoder |
|
||||
| `upDownEnc1` | Up Down Encoder (use this also for RAK14006 Rotary Encoder) |
|
||||
| `cardkb` | M5 Stack CardKB (this covers RAK14004 Keymatrix) |
|
||||
|
||||
### Rotary Encoder Enabled
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -106,25 +106,25 @@ All canned message module config options are available on iOS, iPadOS and macOS
|
|||
|
||||
:::info
|
||||
|
||||
All canned message module config options are available in the python CLI.
|
||||
All canned message module config options are available in the python CLI.
|
||||
|
||||
:::
|
||||
|
||||
Example commands are below:
|
||||
|
||||
| Setting | Acceptable Values | Default |
|
||||
| :--------------------------------------: | :---------------: | :-----------: |
|
||||
| canned_message.enabled | `true`, `false` | `false` |
|
||||
| canned_message.send_bell | `true`, `false` | `false` |
|
||||
| canned_message.allow_input_source | `rotEnc1`, `_any`, `upDownEnc1`, `cardkb` | `_any` |
|
||||
| canned_message.messages | `string` | `""` |
|
||||
| (Messages)\* | `string` | `""` |
|
||||
| canned_message.inputbroker_event_cw | `InputEventChar` | (not defined) |
|
||||
| canned_message.inputbroker_event_ccw | `InputEventChar` | (not defined) |
|
||||
| canned_message.inputbroker_event_press | `InputEventChar` | (not defined) |
|
||||
| canned_message.inputbroker_pin_a | `integer` | (not defined) |
|
||||
| canned_message.inputbroker_pin_b | `integer` | (not defined) |
|
||||
| canned_message.inputbroker_pin_press | `integer` | (not defined) |
|
||||
| Setting | Acceptable Values | Default |
|
||||
| :------------------------------------: | :---------------------------------------: | :-----------: |
|
||||
| canned_message.enabled | `true`, `false` | `false` |
|
||||
| canned_message.send_bell | `true`, `false` | `false` |
|
||||
| canned_message.allow_input_source | `rotEnc1`, `_any`, `upDownEnc1`, `cardkb` | `_any` |
|
||||
| canned_message.messages | `string` | `""` |
|
||||
| (Messages)\* | `string` | `""` |
|
||||
| canned_message.inputbroker_event_cw | `InputEventChar` | (not defined) |
|
||||
| canned_message.inputbroker_event_ccw | `InputEventChar` | (not defined) |
|
||||
| canned_message.inputbroker_event_press | `InputEventChar` | (not defined) |
|
||||
| canned_message.inputbroker_pin_a | `integer` | (not defined) |
|
||||
| canned_message.inputbroker_pin_b | `integer` | (not defined) |
|
||||
| canned_message.inputbroker_pin_press | `integer` | (not defined) |
|
||||
|
||||
:::tip
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -188,13 +188,14 @@ meshtastic --set canned_message.inputbroker_event_ccw ""
|
|||
meshtastic --set canned_message.inputbroker_event_press KEY_SELECT
|
||||
meshtastic --set canned_message.inputbroker_event_press ""
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
</TabItem>
|
||||
<TabItem value="web">
|
||||
|
||||
:::info
|
||||
All canned message module config options are available in the Web UI.
|
||||
:::
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
</TabItem>
|
||||
</Tabs>
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -227,7 +228,7 @@ Just use UP/DOWN/ENTER to select a predefined message and send it.
|
|||
|
||||
### Rotary encoder
|
||||
|
||||
Meshtastic supports hardwired rotary encoders as input devices.
|
||||
Meshtastic supports hardwired rotary encoders as input devices.
|
||||
|
||||
You will need a generic rotary encoder. The types listed below has five legs where two is dedicated to a "press" action, but any other types will likely do the job. You can also use a three-legged version, where the "press" action should be wired from an independent switch.
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -241,7 +242,7 @@ You will need a generic rotary encoder. The types listed below has five legs whe
|
|||
|
||||
Connect your rotary encoder as follows. The rotary encoder has two rows of legs. One of the rows contains two legs, the other contains three legs. Bottom side view:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
```text
|
||||
B o --- o PRESS
|
||||
GND o | |
|
||||
A o --- o GND
|
||||
|
|
@ -251,7 +252,7 @@ The two legs is to sense the press action (or push). Connect one of the two to G
|
|||
|
||||
The three legs is to sense the rotation action. Connect the middle leg to GROUND and the ones on the side to GPIO pins. Let's call these ports 'A' and 'B', according to the scheme below.
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
```text
|
||||
A --||
|
||||
GND --||]========
|
||||
B --||
|
||||
|
|
@ -267,7 +268,6 @@ Recommended GPIO pins for connecting a rotary encoder.
|
|||
There is a reference case 3D-design utilizing the rotary encoder for TTGO LoRa V1:
|
||||
[Case for TTGO-ESP32-LORA-OLED-v1.0 with rotary encoder](https://www.thingiverse.com/thing:5178495)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
## Examples
|
||||
|
||||
- Attach a compatible peripheral device. Take note of the GPIO numbers you use, as they will be used in the following step.
|
||||
|
|
@ -286,6 +286,4 @@ meshtastic --set canned_message.inputbroker_event_press KEY_SELECT
|
|||
meshtastic --set canned_message.rotary1_enabled True
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
That's it! With a functioning and enabled rotary encoder, you're ready to begin configuring the Canned Message Module.
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -5,32 +5,33 @@ slug: /settings/moduleconfig/external-notification
|
|||
sidebar_label: External Notification
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
import Tabs from '@theme/Tabs';
|
||||
import TabItem from '@theme/TabItem';
|
||||
import Tabs from "@theme/Tabs";
|
||||
import TabItem from "@theme/TabItem";
|
||||
|
||||
The External Notification Module will allow you to connect a buzzer, speaker, LED, or other device to notify you when a message has been received from the mesh network.
|
||||
The External Notification Module will allow you to connect a buzzer, speaker, LED, or other device to notify you when a message has been received from the mesh network. You can enable up to 3 pins independently from each other.
|
||||
|
||||
## External Notification Module Config Values
|
||||
## External Notification Module Config Values
|
||||
|
||||
### Enabled
|
||||
|
||||
Enables the external notification module.
|
||||
|
||||
### Alert when receiving a bell
|
||||
### Alert when receiving a bell (general / LED, Vibra and Buzzer)
|
||||
|
||||
Specifies if an alert should be triggered when receiving an incoming bell.
|
||||
|
||||
### Alert when receiving a message
|
||||
### Alert when receiving a message (general / LED, Vibra and Buzzer)
|
||||
|
||||
Specifies if an alert should be triggered when receiving an incoming message.
|
||||
|
||||
### Active
|
||||
### Active (general / LED only)
|
||||
|
||||
Specifies whether the external circuit is triggered when the device's GPIO is low or high.
|
||||
Specifies whether the external circuit is active when the device's GPIO is low or high.
|
||||
|
||||
### GPIO to monitor
|
||||
### GPIO Pins (general / LED, Vibra and Buzzer)
|
||||
|
||||
Specifies the GPIO that your external circuit is attached to on the device. On devices that have a PWM buzzer, you can use the buzzer for notifications by setting this to the same pin the buzzer uses.
|
||||
Specifies the GPIO that your external circuit is attached to on the device. On devices that have a PWM buzzer, you can use the buzzer for notifications by setting the use_pwm property to TRUE. The Buzzer Pin will be ignored and the device.buzzer_gpio is used instead. If you enable PWM mode, the device will use
|
||||
so-called RTTTL ring tones for notification. You can find examples of RTTTL ring tones [here](https://www.laub-home.de/wiki/RTTTL_Songs) and upload them to the device via a client application.
|
||||
|
||||
:::info
|
||||
On ESP32 based boards, GPIOs 34 to 39 are GPIs – input only pins. These pins do not have internal pull-up or pull-down resistors. They can not be used as outputs, so you can NOT use these pins as outputs.
|
||||
|
|
@ -38,10 +39,14 @@ On ESP32 based boards, GPIOs 34 to 39 are GPIs – input only pins. These pins d
|
|||
|
||||
### How long monitored GPIO is triggered
|
||||
|
||||
Specifies how long in milliseconds you would like your external circuit to be triggered.
|
||||
Specifies how long in milliseconds you would like your GPIOs to be active. In case of the repeat option, this is the duration of every tone and pause.
|
||||
|
||||
Default of 0 is 1000ms
|
||||
|
||||
### Repeat (Nag Timeout) (general / LED, Vibra and Buzzer)
|
||||
|
||||
Specifies if the alert should be repeated. If set to a value greater than zero, the alert will be repeated until the user button is pressed or 'value' number of seconds have past.
|
||||
|
||||
## External Notification Module Config Client Availability
|
||||
|
||||
<Tabs
|
||||
|
|
@ -80,14 +85,22 @@ All external notification module config options are available in the python CLI.
|
|||
|
||||
:::
|
||||
|
||||
| Setting | Acceptable Values | Default |
|
||||
| :----------------------------: | :----------------------: | :-----: |
|
||||
| external_notification.enabled | `true`, `false` | `false` |
|
||||
| external_notification.active | `true`, `false` | `false` |
|
||||
| external_notification.alert_bell | `true`, `false` | `false` |
|
||||
| external_notification.alert_message | `true`, `false` | `false` |
|
||||
| external_notification.output | `integer` | `0` |
|
||||
| external_notification.output_ms | `integer` (milliseconds) | `0` |
|
||||
| Setting | Acceptable Values | Default |
|
||||
| :----------------------------------------: | :----------------------: | :-----: |
|
||||
| external_notification.enabled | `true`, `false` | `false` |
|
||||
| external_notification.active | `true`, `false` | `false` |
|
||||
| external_notification.alert_bell | `true`, `false` | `false` |
|
||||
| external_notification.alert_bell_vibra | `true`, `false` | `false` |
|
||||
| external_notification.alert_bell_buzzer | `true`, `false` | `false` |
|
||||
| external_notification.alert_message | `true`, `false` | `false` |
|
||||
| external_notification.alert_message_vibra | `true`, `false` | `false` |
|
||||
| external_notification.alert_message_buzzer | `true`, `false` | `false` |
|
||||
| external_notification.output | `integer` | `0` |
|
||||
| external_notification.output_vibra | `integer` | `0` |
|
||||
| external_notification.output_buzzer | `integer` | `0` |
|
||||
| external_notification.output_ms | `integer` (milliseconds) | `0` |
|
||||
| external_notification.use_pwm | `true`, `false` | `false` |
|
||||
| external_notification.nag_timeout | `integer` (seconds) | `0` |
|
||||
|
||||
:::tip
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -127,13 +140,14 @@ meshtastic --set external_notification.output 21
|
|||
meshtastic --set external_notification.output_ms 0
|
||||
meshtastic --set external_notification.output_ms 1500
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
</TabItem>
|
||||
<TabItem value="web">
|
||||
|
||||
:::info
|
||||
All External Notification module config is available for the Web UI.
|
||||
:::
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
</TabItem>
|
||||
</Tabs>
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -8,13 +8,13 @@ sidebar_position: 3
|
|||
|
||||
Modules are included in the firmware and allow users to extend the functionality of their mesh or device.
|
||||
|
||||
| Name | Description |
|
||||
|:----:|:-----------:|
|
||||
| [Audio](/docs/settings/moduleconfig/audio) | enable Support for Codec2 Voice Comms on certain devices |
|
||||
| [Canned Message](/docs/settings/moduleconfig/canned-message) | Set a number of predefined messages to send out directly from the device with the use of an input device like a rotary encoder. |
|
||||
| [External Notification](/docs/settings/moduleconfig/external-notification) | Incoming messages are able to alert you using circuits you attach to the device (LEDs, Buzzers, etc) |
|
||||
| [MQTT](/docs/settings/moduleconfig/mqtt) | Forward packets along to an MQTT server. This allows users on the local mesh to communicate with users on another mesh over the internet. |
|
||||
| [Range Test](/docs/settings/moduleconfig/range-test) | Send messages with GPS location at an interval to test the distance your devices can communicate. Requires (at least) one device set up as a sender and one as a receiver. The receiver(s) will log all incoming messages to a CSV. |
|
||||
| [Serial Module](/docs/settings/moduleconfig/serial) | Send messages across the mesh by sending strings over a serial port. |
|
||||
| [Telemetry](/docs/settings/moduleconfig/telemetry) | Attach sensors to the device and transmit readings on a regular interval to the mesh. |
|
||||
| [Traceroute](/docs/settings/moduleconfig/traceroute) | Track which nodes are used to hop a message to a certain destination. |
|
||||
| Name | Description |
|
||||
| :------------------------------------------------------------------------: | :---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------: |
|
||||
| [Audio](/docs/settings/moduleconfig/audio) | enable Support for Codec2 Voice Comms on certain devices |
|
||||
| [Canned Message](/docs/settings/moduleconfig/canned-message) | Set a number of predefined messages to send out directly from the device with the use of an input device like a rotary encoder. |
|
||||
| [External Notification](/docs/settings/moduleconfig/external-notification) | Incoming messages are able to alert you using circuits you attach to the device (LEDs, Buzzers, etc) |
|
||||
| [MQTT](/docs/settings/moduleconfig/mqtt) | Forward packets along to an MQTT server. This allows users on the local mesh to communicate with users on another mesh over the internet. |
|
||||
| [Range Test](/docs/settings/moduleconfig/range-test) | Send messages with GPS location at an interval to test the distance your devices can communicate. Requires (at least) one device set up as a sender and one as a receiver. The receiver(s) will log all incoming messages to a CSV. |
|
||||
| [Serial Module](/docs/settings/moduleconfig/serial) | Send messages across the mesh by sending strings over a serial port. |
|
||||
| [Telemetry](/docs/settings/moduleconfig/telemetry) | Attach sensors to the device and transmit readings on a regular interval to the mesh. |
|
||||
| [Traceroute](/docs/settings/moduleconfig/traceroute) | Track which nodes are used to hop a message to a certain destination. |
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -5,8 +5,8 @@ slug: /settings/moduleconfig/mqtt
|
|||
sidebar_label: MQTT
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
import Tabs from '@theme/Tabs';
|
||||
import TabItem from '@theme/TabItem';
|
||||
import Tabs from "@theme/Tabs";
|
||||
import TabItem from "@theme/TabItem";
|
||||
|
||||
If your device is connected to Internet via wifi or ethernet, you can enable it to forward packets along to an MQTT server. This allows users on the local mesh to communicate with users on the internet. One or more channels must be enabled as uplink and/or downlink for protobufs to be transmitted from and/or to the mesh (See [channels](/docs/settings/config/channels#downlink-enabled)). Without these settings the node will still connect to MQTT server and send status messages.
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -14,7 +14,7 @@ The MQTT module config options are: Enabled, Server Address, Username, Password,
|
|||
|
||||
## Settings
|
||||
|
||||
## MQTT Module Config Values
|
||||
## MQTT Module Config Values
|
||||
|
||||
### Enabled
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -78,14 +78,14 @@ All MQTT module config options are available in the python CLI. Example commands
|
|||
|
||||
:::
|
||||
|
||||
| Setting | Acceptable Values | Default |
|
||||
| :--------------------------: | :----------------------: | :-----: |
|
||||
| mqtt.enabled | `true`, `false` | `false` |
|
||||
| mqtt.address | `string` | |
|
||||
| mqtt.username | `string` | |
|
||||
| mqtt.password | `string` | |
|
||||
| mqtt.encryption_enabled | `string` | |
|
||||
| mqtt.json_enabled | `true`, `false` | `false` |
|
||||
| Setting | Acceptable Values | Default |
|
||||
| :---------------------: | :---------------: | :-----: |
|
||||
| mqtt.enabled | `true`, `false` | `false` |
|
||||
| mqtt.address | `string` | |
|
||||
| mqtt.username | `string` | |
|
||||
| mqtt.password | `string` | |
|
||||
| mqtt.encryption_enabled | `string` | |
|
||||
| mqtt.json_enabled | `true`, `false` | `false` |
|
||||
|
||||
:::tip
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -113,6 +113,6 @@ meshtastic --set mqtt.json_enabled false
|
|||
:::info
|
||||
All MQTT module config options are available for the Web UI.
|
||||
:::
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
</TabItem>
|
||||
</Tabs>
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -5,12 +5,12 @@ slug: /settings/moduleconfig/range-test
|
|||
sidebar_label: Range Test
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
import Tabs from '@theme/Tabs';
|
||||
import TabItem from '@theme/TabItem';
|
||||
import Tabs from "@theme/Tabs";
|
||||
import TabItem from "@theme/TabItem";
|
||||
|
||||
This module allows you to test the range of your Meshtastic nodes. It requires at least two nodes, a sender and a receiver. The receiving node then saves the messages along with the GPS coordinates at which they were received into a .csv file. This .csv file can then be integrated into [Google Earth](https://earth.google.com), [Google Maps - My Maps](https://mymaps.google.com), or any other program capable of processing .csv files. This can enable you to visualize your mesh.
|
||||
|
||||
The range test module config options are: Enabled, Save, and Sender. Range Test Module config uses an admin message sending a `ConfigModule.RangeTest` protobuf.
|
||||
The range test module config options are: Enabled, Save, and Sender. Range Test Module config uses an admin message sending a `ConfigModule.RangeTest` protobuf.
|
||||
|
||||
## Range Test Module Config Values
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -18,9 +18,7 @@ The range test module config options are: Enabled, Save, and Sender. Range Test
|
|||
|
||||
Enables the range test module.
|
||||
|
||||
### Save CSV File
|
||||
|
||||
**ESP32 Only Setting**
|
||||
### Save CSV File `ESP32 Only Setting`
|
||||
|
||||
If enabled, we will save a log of all received messages to a file named rangetest.csv which you can access from the web server Extensions > File Browser > rangetest.csv. The file will be created after receiving messages. The device will abort writing if there is less than 50k of space on the filesystem to prevent filling up the storage.
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -66,8 +64,8 @@ Range Test module config options are available in the python CLI. Example comman
|
|||
|
||||
:::
|
||||
|
||||
| Setting | Acceptable Values | Default |
|
||||
| :-----------------------: | :-----------------: | :-----: |
|
||||
| Setting | Acceptable Values | Default |
|
||||
| :----------------: | :-----------------: | :-----: |
|
||||
| range_test.enabled | `true`, `false` | `false` |
|
||||
| range_test.save | `true`, `false` | `false` |
|
||||
| range_test.sender | `integer` (Seconds) | `0` |
|
||||
|
|
@ -121,7 +119,7 @@ Be sure to turn off either the module configured as a sender or the device where
|
|||
Also be mindful of your space usage on the file system. It has protections from filling up the space but it's best to delete old range test results.
|
||||
|
||||
:::note
|
||||
Leaving this module on can slow down your mesh. Currently, the messages are sent using the same `TEXT_MESSAGE_APP` [port that all other messages](/docs/developers/protobufs/api#portnumsproto) are sent on.
|
||||
Leaving this module on can slow down your mesh. Currently, the messages are sent using the same `TEXT_MESSAGE_APP` [port that all other messages](https://buf.build/meshtastic/protobufs/docs/main:meshtastic#meshtastic.PortNum) are sent on.
|
||||
:::
|
||||
|
||||
### Accessing your CSV
|
||||
|
|
@ -137,12 +135,10 @@ http://198.168.0.15
|
|||
|
||||
| Radio Setting | `range_test.sender` |
|
||||
| :-----------: | :-----------------: |
|
||||
| Long Slow | 60 |
|
||||
| Long Alt | 30 |
|
||||
| Medium | 15 |
|
||||
| Short Fast | 15 |
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
| Long Slow | 60 |
|
||||
| Long Alt | 30 |
|
||||
| Medium | 15 |
|
||||
| Short Fast | 15 |
|
||||
|
||||
## Application Examples
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -5,16 +5,15 @@ slug: /settings/moduleconfig/serial
|
|||
sidebar_label: Serial
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
import Tabs from '@theme/Tabs';
|
||||
import TabItem from '@theme/TabItem';
|
||||
import Tabs from "@theme/Tabs";
|
||||
import TabItem from "@theme/TabItem";
|
||||
|
||||
The serial module config options are: Enabled, Echo, Mode, Receive GPIO, Transmit GPIO and Sender. Serial Module config uses an admin message sending a `ConfigModule.Serial` protobuf.
|
||||
The serial module config options are: Enabled, Echo, Mode, Receive GPIO, Transmit GPIO and Sender. Serial Module config uses an admin message sending a `ConfigModule.Serial` protobuf.
|
||||
|
||||
This is a simple interface to send messages over the mesh network by sending strings over a serial port. Anything you send the node will be turned into a message sent out over the mesh, and anything received from the mesh will be sent to the serial port. Note that this module does not (yet) allow arbitrary protobuf commands to be sent over the serial connection.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
## Serial Module Config Values
|
||||
|
||||
### Enabled
|
||||
|
|
@ -31,11 +30,11 @@ Defaults to 'Simple'.
|
|||
|
||||
Available Values:
|
||||
|
||||
* `DEFAULT`
|
||||
* `SIMPLE` operate as an dumb UART tunnel. What goes in will come out, Requires a channel named 'serial'.
|
||||
* `PROTO` Exposes the Protobuf Client API on this serial port. You can use this to connect from another device. [API Reference](/docs/development/device/client-api)
|
||||
* `TEXTMSG` Will send the string received over the serial port as a Text Message for Display on the other devices.
|
||||
* `NMEA` Will output a NMEA 0183 Data stream containing the internal GPS or fixed position and other node locations as Waypoints (WPL).
|
||||
- `DEFAULT`
|
||||
- `SIMPLE` operate as an dumb UART tunnel. What goes in will come out, Requires a channel named 'serial'.
|
||||
- `PROTO` Exposes the Protobuf Client API on this serial port. You can use this to connect from another device. [API Reference](/docs/development/device/client-api)
|
||||
- `TEXTMSG` Will send the string received over the serial port as a Text Message for Display on the other devices.
|
||||
- `NMEA` Will output a NMEA 0183 Data stream containing the internal GPS or fixed position and other node locations as Waypoints (WPL).
|
||||
|
||||
### Receive GPIO Pin
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -93,21 +92,21 @@ All serial module config options are available on iOS, iPadOS and macOS at Setti
|
|||
</TabItem>
|
||||
<TabItem value="cli">
|
||||
|
||||
:::info
|
||||
:::info
|
||||
|
||||
All serial module config options are available in the python CLI. Example commands are below:
|
||||
|
||||
:::
|
||||
|
||||
| Setting | Acceptable Values | Default |
|
||||
| :-------------------: | :-----------------: | :-----: |
|
||||
| serial.enabled | `true`, `false` | `false` |
|
||||
| serial.echo | `true`, `false` | `false` |
|
||||
| serial.mode | `DEFAULT` `SIMPLE` `PROTO` `TEXTMSG`, `NMEA` | `DEFAULT` |
|
||||
| serial.rxd | GPIO Pin Number 1-39 | Default of `0` is Unset |
|
||||
| serial.txd | GPIO Pin Number 1-33 | Default of `0` is Unset |
|
||||
| serial.baud | `BAUD_DEFAULT` `BAUD_110` `BAUD_300` `BAUD_600` `BAUD_1200` `BAUD_2400` `BAUD_4800` `BAUD_9600` `BAUD_19200` `BAUD_38400` `BAUD_57600` `BAUD_115200` `BAUD_230400` `BAUD_460800` `BAUD_576000` `BAUD_921600` | `BAUD_DEFAULT` |
|
||||
| serial.timeout | `integer` (seconds) | `0` |
|
||||
| Setting | Acceptable Values | Default |
|
||||
| :------------: | :----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------: | :----------------------------------: |
|
||||
| serial.enabled | `true`, `false` | `false` |
|
||||
| serial.echo | `true`, `false` | `false` |
|
||||
| serial.mode | `DEFAULT` `SIMPLE` `PROTO` `TEXTMSG`, `NMEA` | `DEFAULT` |
|
||||
| serial.rxd | GPIO Pin Number 1-39 | Default of `0` is Unset |
|
||||
| serial.txd | GPIO Pin Number 1-33 | Default of `0` is Unset |
|
||||
| serial.baud | `BAUD_DEFAULT` `BAUD_110` `BAUD_300` `BAUD_600` `BAUD_1200` `BAUD_2400` `BAUD_4800` `BAUD_9600` `BAUD_19200` `BAUD_38400` `BAUD_57600` `BAUD_115200` `BAUD_230400` `BAUD_460800` `BAUD_576000` `BAUD_921600` | `BAUD_DEFAULT` |
|
||||
| serial.timeout | `integer` (milli seconds) | Default of `0` corresponds to 250 ms |
|
||||
|
||||
:::tip
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -132,7 +131,7 @@ meshtastic --set serial.echo false
|
|||
```shell title="Set Mode"
|
||||
meshtastic --set serial.mode DEFAULT
|
||||
meshtastic --set serial.mode PROTO
|
||||
```
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
```shell title="Set RXD to GPIO pin number 7"
|
||||
meshtastic --set serial.rxd 7
|
||||
|
|
@ -147,7 +146,7 @@ meshtastic --set serial.baud BAUD_DEFAULT
|
|||
meshtastic --set serial.baud BAUD_576000
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
```shell title="Set Timeout to 15 seconds"
|
||||
```shell title="Set Timeout to 15 milli seconds"
|
||||
meshtastic --set serial.timeout 15
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -157,7 +156,7 @@ meshtastic --set serial.timeout 15
|
|||
:::info
|
||||
All serial module config options are available in the Web UI.
|
||||
:::
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
</TabItem>
|
||||
</Tabs>
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -170,7 +169,8 @@ This module requires attaching a peripheral accessory to your device. It will no
|
|||
## Examples
|
||||
|
||||
Default is to use RX GPIO 16 and TX GPIO 17.
|
||||
### Basic Usage:
|
||||
|
||||
### Basic Usage
|
||||
|
||||
1. Enable the module by setting `serial.enabled` to `1`.
|
||||
2. Set the pins (`serial.rxd` / `serial.txd`) for your preferred RX and TX GPIO pins. On tbeam boards it is recommended to use:
|
||||
|
|
@ -180,24 +180,28 @@ Default is to use RX GPIO 16 and TX GPIO 17.
|
|||
4. (Optional) set serial.mode to TEXTMSG if you want to send messages to/from the general text message channel
|
||||
5. Connect to your device over the serial interface at `38400 8N1`.
|
||||
|
||||
With [tio](https://github.com/tio/tio) – `tio -e -b 38400 -f none /dev/myserialport`
|
||||
7. Send a packet up to 237 bytes in length. This will get relayed over the mesh network.
|
||||
8. (Optional) Set `serial.echo` to `1` and any message you send out will be echoed back to your device.
|
||||
With [tio](https://github.com/tio/tio) – `tio -e -b 38400 -f none /dev/myserialport`
|
||||
|
||||
6. Send a packet up to 237 bytes in length. This will get relayed over the mesh network.
|
||||
7. (Optional) Set `serial.echo` to `1` and any message you send out will be echoed back to your device.
|
||||
|
||||
### Interfacing PIR Sensor With External Microcontroller
|
||||
The following is an example of using a Raspberry Pi Pico connected to a PIR sensor to detect motion. When motion is detected, a message is sent via. serial to the T-Beam. The T-Beam transmits the message as text over the default channel by utilizing the serial module in TXTMSG mode.
|
||||
|
||||
The following is an example of using a Raspberry Pi Pico connected to a PIR sensor to detect motion. When motion is detected, a message is sent via. serial to the T-Beam. The T-Beam transmits the message as text over the default channel by utilizing the serial module in TXTMSG mode.
|
||||
|
||||
#### BOM
|
||||
|
||||
- Raspberry Pi Pico running [CircuitPython](https://learn.adafruit.com/getting-started-with-raspberry-pi-pico-circuitpython)
|
||||
- T-Beam V1.1 running Meshtastic
|
||||
- PIR Sensor ([Adafruit Breadboard Model](https://www.adafruit.com/product/4871))
|
||||
|
||||
#### Meshtastic Software Configuration:
|
||||
#### Meshtastic Software Configuration
|
||||
|
||||
- Serial module enabled, mode: TXTMSG
|
||||
- GPIO Pins (For T-Beam) RX 13, TX 14
|
||||
- 38400 Baud
|
||||
|
||||
#### Wiring:
|
||||
#### Wiring
|
||||
|
||||
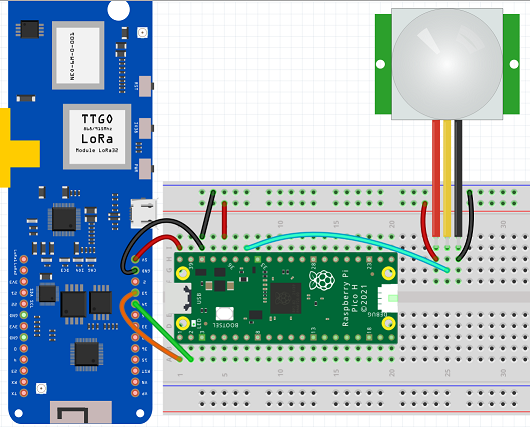
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -209,9 +213,10 @@ The following is an example of using a Raspberry Pi Pico connected to a PIR sens
|
|||
- GND pin 38 on the Pico to breadboard ground rail
|
||||
- 3V3 pin 36 on the Pico to the breadboard positive voltage rail
|
||||
- Optional, to power the Pico off of the T-Beam instead of USB:
|
||||
- Connect 5V pin on T-Beam to Vbus pin 40 on the Pico
|
||||
- Connect 5V pin on T-Beam to Vbus pin 40 on the Pico
|
||||
|
||||
#### Circuit Python Code
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
import time
|
||||
import board
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -5,10 +5,10 @@ slug: /settings/moduleconfig/telemetry
|
|||
sidebar_label: Telemetry
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
import Tabs from '@theme/Tabs';
|
||||
import TabItem from '@theme/TabItem';
|
||||
import Tabs from "@theme/Tabs";
|
||||
import TabItem from "@theme/TabItem";
|
||||
|
||||
The Telemetry Module provides two types of data over the mesh. Device metrics (Battery Level, Voltage, Channel Utilization and Airtime) from your meshtastic device and Environment Metrics from attached I2C sensors.
|
||||
The Telemetry Module provides two types of data over the mesh. Device metrics (Battery Level, Voltage, Channel Utilization and Airtime) from your meshtastic device and Environment Metrics from attached I2C sensors.
|
||||
|
||||
Supported sensors connected to the I2C bus of the device will be automatically detected at startup. Environment Telemetry must be enabled for them to be instrumented and their readings sent over the mesh.
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -16,19 +16,19 @@ The telemetry module config options are: Device Metrics Update Interval, Environ
|
|||
|
||||
### Currently Supported Sensor Types
|
||||
|
||||
| Sensor | I<sup>2</sup>C Address | Data Points |
|
||||
| Sensor | I<sup>2</sup>C Address | Data Points |
|
||||
| :-----: | :--------------------: | :-----------------------------------------------------------: |
|
||||
| BMP280 | 0x76, 0x77 | Temperature and barometric pressure |
|
||||
| BME280 | 0x76, 0x77 | Temperature, barometric pressure and humidity |
|
||||
| BME680 | 0x76, 0x77 | Temperature, barometric pressure, humidity and air resistance |
|
||||
| MCP9808 | 0x18 | Temperature |
|
||||
| INA260 | 0x40, 0x41 | Current and Voltage |
|
||||
| INA219 | 0x40, 0x41 | Current and Voltage |
|
||||
| LPS22 | 0x5D, 0x5c | Barometric pressure |
|
||||
| SHTC3 | 0x70 | Temperature and humidity |
|
||||
| SHT31 | 0x44 | Temperature and humidity |
|
||||
| BMP280 | 0x76, 0x77 | Temperature and barometric pressure |
|
||||
| BME280 | 0x76, 0x77 | Temperature, barometric pressure and humidity |
|
||||
| BME680 | 0x76, 0x77 | Temperature, barometric pressure, humidity and air resistance |
|
||||
| MCP9808 | 0x18 | Temperature |
|
||||
| INA260 | 0x40, 0x41 | Current and Voltage |
|
||||
| INA219 | 0x40, 0x41 | Current and Voltage |
|
||||
| LPS22 | 0x5D, 0x5c | Barometric pressure |
|
||||
| SHTC3 | 0x70 | Temperature and humidity |
|
||||
| SHT31 | 0x44 | Temperature and humidity |
|
||||
|
||||
## Module Config Values
|
||||
## Module Config Values
|
||||
|
||||
### Update Intervals
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -101,13 +101,13 @@ All telemetry module config options are available in the python CLI. Example com
|
|||
|
||||
## Settings
|
||||
|
||||
| Setting | Acceptable Values | Default |
|
||||
| :-----------------------------------------------------: | :-----------------: | :-----: |
|
||||
| telemetry.device_update_interval | `integer` (seconds) | Default `0` is 15 minutes(`900` seconds). |
|
||||
| telemetry.environment_display_fahrenheit | `true`, `false` | `false` |
|
||||
| telemetry.environment_measurement_enabled | `true`, `false` | `false` |
|
||||
| telemetry.environment_screen_enabled | `true`, `false` | `0` |
|
||||
| telemetry.environment_update_interval | `integer` (seconds) | Default `0` is 15 minutes(`900` seconds). |
|
||||
| Setting | Acceptable Values | Default |
|
||||
| :---------------------------------------: | :-----------------: | :---------------------------------------: |
|
||||
| telemetry.device_update_interval | `integer` (seconds) | Default `0` is 15 minutes(`900` seconds). |
|
||||
| telemetry.environment_display_fahrenheit | `true`, `false` | `false` |
|
||||
| telemetry.environment_measurement_enabled | `true`, `false` | `false` |
|
||||
| telemetry.environment_screen_enabled | `true`, `false` | `0` |
|
||||
| telemetry.environment_update_interval | `integer` (seconds) | Default `0` is 15 minutes(`900` seconds). |
|
||||
|
||||
:::tip
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -125,7 +125,7 @@ meshtastic --set telemetry.device_update_interval 0
|
|||
meshtastic --set telemetry.device_update_interval 0
|
||||
// Environment Metrics Two Minutes
|
||||
meshtastic --set telemetry.environment_update_interval 120
|
||||
````
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
```shell title="Enable/Disable Environment Module"
|
||||
meshtastic --set telemetry.environment_measurement_enabled true
|
||||
|
|
@ -140,7 +140,7 @@ meshtastic --set telemetry.environment_screen_enabled false
|
|||
```shell title="Enable / Disable Display Fahrenheit"
|
||||
meshtastic --set telemetry.environment_display_fahrenheit true
|
||||
meshtastic --set telemetry.environment_display_fahrenheit false
|
||||
````
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
</TabItem>
|
||||
<TabItem value="web">
|
||||
|
|
@ -150,7 +150,7 @@ meshtastic --set telemetry.environment_display_fahrenheit false
|
|||
All telemetry module config options are available in the Web UI.
|
||||
|
||||
:::
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
</TabItem>
|
||||
</Tabs>
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -195,15 +195,15 @@ And examine the serial logs for Telemetry diagnostic information.
|
|||
|
||||
### Environment Metrics
|
||||
|
||||
The environment metrics in the telemetry module supports a limited amount of fields as they are stored in memory on the device. Support for sensors that provide one or more of the following fields can potentially be added to the main firmware provided there is a GPL licensed library for us to include to support it, and the library size is not prohibitive.
|
||||
The environment metrics in the telemetry module supports a limited amount of fields as they are stored in memory on the device. Support for sensors that provide one or more of the following fields can potentially be added to the main firmware provided there is a GPL licensed library for us to include to support it, and the library size is not prohibitive.
|
||||
|
||||
* Temperature
|
||||
* Relative Humidity
|
||||
* Barometric Pressure
|
||||
* Gas Resistance (AQI)
|
||||
* Voltage
|
||||
* Current
|
||||
- Temperature
|
||||
- Relative Humidity
|
||||
- Barometric Pressure
|
||||
- Gas Resistance (AQI)
|
||||
- Voltage
|
||||
- Current
|
||||
|
||||
### Supporting Other Sensor types
|
||||
|
||||
For other interesting sensor types and use cases we need to add a portnum for more generic telemetry packets and a second MCU will be required to interact with the sensor and process the data to be sent over the mesh. This data will not be stored in the nodedb on the device.
|
||||
For other interesting sensor types and use cases we need to add a portnum for more generic telemetry packets and a second MCU will be required to interact with the sensor and process the data to be sent over the mesh. This data will not be stored in the nodedb on the device.
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -5,14 +5,14 @@ slug: /settings/moduleconfig/traceroute
|
|||
sidebar_label: Traceroute
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
import Tabs from '@theme/Tabs';
|
||||
import TabItem from '@theme/TabItem';
|
||||
import Tabs from "@theme/Tabs";
|
||||
import TabItem from "@theme/TabItem";
|
||||
|
||||
Due to the limited bandwidth of LoRa, Meshtastic does not keep track of the nodes a message used to hop to the destination. However, from firmware 2.0.8 on, there is a Traceroute Module that can show you this.
|
||||
|
||||
Only nodes that know the encryption key of the channel you use can be tracked. Also note that a message may arrive via multiple routes due to duplication because of rebroadcasting. This module will only track the hops of the first packet containing the traceroute request that arrived at the destination.
|
||||
|
||||
In order to use it, make sure your devices use firmware version 2.0.8 or higher.
|
||||
In order to use it, make sure your devices use firmware version 2.0.8 or higher.
|
||||
|
||||
## Traceroute Module Client Availability
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -32,7 +32,7 @@ Not yet implemented.
|
|||
</TabItem>
|
||||
<TabItem value="apple">
|
||||
|
||||
Make sure the app is at least version 2.0.9.
|
||||
Make sure the app is at least version 2.0.9.
|
||||
|
||||
Under Contacts > Direct Messages, long hold a destination node and select 'Trace Route' to send the request. Depending on the amount of hops that is needed, this might take a while. The result will be shown in the Mesh Log.
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -61,6 +61,6 @@ The first ID shown is the device you are connected to with the CLI. As you can s
|
|||
<TabItem value="web">
|
||||
|
||||
Not yet implemented.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
</TabItem>
|
||||
</Tabs>
|
||||
</Tabs>
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -9,28 +9,28 @@ sidebar_position: 5
|
|||
|
||||
The RAK4631 uses symbolic labels for its I/O Pins on the module and baseboard silk screens. The following table shows the mapping of the RAK4631 GPIO pins to the corresponding Arduino pins and the MCU Port numbers.
|
||||
|
||||
| RAK Pin | nRF52840 Pin | Arduino GPIO | Remark |
|
||||
| ------- | ------------ | ------------ | ------ |
|
||||
| IO1 | P0.17 | 17 | used for GPS PPM signal if GPS module is connected |
|
||||
| IO2 | P1.02 | 34 | used to power all peripheral modules, not available for user application |
|
||||
| IO3 | P0.21 | 21 |
|
||||
| IO4 | P0.04 | 4 |
|
||||
| IO5 | P0.09 | 9 | The 'User Button' is mapped here. |
|
||||
| IO6 | P0.10 | 10 |
|
||||
| IO7 | P0.28 | 28 |
|
||||
| SW1 | P0.01 | 1 |
|
||||
| A0 | P0.04/AIN2 | A2 |
|
||||
| A1 | P0.31/AIN7 | A7 |
|
||||
| SPI_CS | P0.26 | 26 |
|
||||
| RAK Pin | nRF52840 Pin | Arduino GPIO | Remark |
|
||||
| ------- | ------------ | ------------ | ------------------------------------------------------------------------ |
|
||||
| IO1 | P0.17 | 17 | used for GPS PPM signal if GPS module is connected |
|
||||
| IO2 | P1.02 | 34 | used to power all peripheral modules, not available for user application |
|
||||
| IO3 | P0.21 | 21 |
|
||||
| IO4 | P0.04 | 4 |
|
||||
| IO5 | P0.09 | 9 | The 'User Button' is mapped here. |
|
||||
| IO6 | P0.10 | 10 |
|
||||
| IO7 | P0.28 | 28 |
|
||||
| SW1 | P0.01 | 1 |
|
||||
| A0 | P0.04/AIN2 | A2 |
|
||||
| A1 | P0.31/AIN7 | A7 |
|
||||
| SPI_CS | P0.26 | 26 |
|
||||
|
||||
When configuring GPIO pins in your device settings, the Arduino GPIO numbers should be used.
|
||||
|
||||
```shell title="Example"
|
||||
meshtastic --set external_notification.output 10
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
This will use IO6 on a RAK4631
|
||||
|
||||
:::caution Note
|
||||
There is no usable GPIO pin on any RAK base board except the 'big' baseboard RAK19001 without adding a RAK13002 IO module or a third party IO sensor breakout.
|
||||
:::
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -151,7 +151,7 @@ Completed getting preferences
|
|||
For further reading, I recommend starting out with [Meshtastic-python](/docs/software/python/cli/) if you haven't already gone through this (hopefully you have since you are reading this). But for a full reference to the settings you can change, please see:
|
||||
|
||||
[Settings Overview](/docs/settings) and
|
||||
[Complete list of user settings in Protobufs](/docs/developers/protobufs/api#radioconfiguserpreferences)
|
||||
[Complete list of user settings in Protobufs](https://buf.build/meshtastic/protobufs/docs/main:meshtastic#meshtastic.User)
|
||||
|
||||
## Areas for future development
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -4,4 +4,4 @@ position: 7
|
|||
link:
|
||||
type: generated-index
|
||||
title: Developers
|
||||
slug: /developers
|
||||
slug: /developers
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -12,12 +12,12 @@ If you would like to develop this application we'd love your help! These build i
|
|||
1. Use Android Studio to build/debug
|
||||
2. Use `git submodule update --init --recursive` to pull in the various sub-modules we depend on.
|
||||
3. There are a few config files which you'll need to copy from templates included in the project. Run the following commands to do so:
|
||||
```sh
|
||||
rm ./app/google-services.json
|
||||
cp ./app/google-services-example.json ./app/google-services.json
|
||||
rm ./app/src/main/res/values/curfirmwareversion.xml
|
||||
cp ./app/special/curfirmwareversion.xml ./app/src/main/res/values/
|
||||
```
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
rm ./app/google-services.json
|
||||
cp ./app/google-services-example.json ./app/google-services.json
|
||||
rm ./app/src/main/res/values/curfirmwareversion.xml
|
||||
cp ./app/special/curfirmwareversion.xml ./app/src/main/res/values/
|
||||
```
|
||||
4. Now you should be able to select "Run / Run" in the IDE and it will happily start running on your phone or the emulator.
|
||||
|
||||
:::note
|
||||
|
|
@ -30,15 +30,16 @@ Analytics are included but can be disabled by the user on the settings screen.
|
|||
|
||||
1. Configure analytics for development device
|
||||
|
||||
```sh
|
||||
adb shell setprop debug.firebase.analytics.app com.geeksville.mesh
|
||||
adb shell setprop log.tag.FirebaseCrashlytics DEBUG
|
||||
```
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
adb shell setprop debug.firebase.analytics.app com.geeksville.mesh
|
||||
adb shell setprop log.tag.FirebaseCrashlytics DEBUG
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
2. Set verbose logging
|
||||
|
||||
```sh
|
||||
adb shell setprop log.tag.FA VERBOSE
|
||||
```
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
adb shell setprop log.tag.FA VERBOSE
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## Publish to Google Play
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -47,20 +48,19 @@ Only available for core developers that publish releases.
|
|||
:::
|
||||
|
||||
1. Add repository secrets:
|
||||
- **KEYSTORE_FILENAME**
|
||||
- Name of the `.jks`
|
||||
- **KEYSTORE**
|
||||
- Convert the `.jks` to base64:
|
||||
```sh
|
||||
openssl base64 < filename.jks | tr -d '\n' | tee filename.txt
|
||||
```
|
||||
- **KEYSTORE_PROPERTIES**
|
||||
- `storePassword=nononononono`
|
||||
- `keyPassword=nononononono`
|
||||
- `keyAlias=upload`
|
||||
- `storeFile=nononononono.jks`
|
||||
- **KEYSTORE_FILENAME**
|
||||
- Name of the `.jks`
|
||||
- **KEYSTORE**
|
||||
- Convert the `.jks` to base64:
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
openssl base64 < filename.jks | tr -d '\n' | tee filename.txt
|
||||
```
|
||||
- **KEYSTORE_PROPERTIES**
|
||||
- `storePassword=nononononono`
|
||||
- `keyPassword=nononononono`
|
||||
- `keyAlias=upload`
|
||||
- `storeFile=nononononono.jks`
|
||||
2. Update protobufs
|
||||
3. Go to Actions / Make Release / Run Workflow
|
||||
4. Pick the Releases branch
|
||||
5. Enter the version found in `app/gradle.build`
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -4,4 +4,4 @@ position: 1
|
|||
link:
|
||||
slug: /development/device
|
||||
type: generated-index
|
||||
title: Device
|
||||
title: Device
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -27,7 +27,6 @@ The 4 byte header is constructed to both provide framing and to not look line 'n
|
|||
|
||||
The receiver will validate length and if >512 it will assume the packet is corrupted and return to looking for START1. While looking for START1 any other characters are printed as "debug output". For small example implementation of this reader see the python implementation.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
## Bluetooth (MeshBluetoothService)
|
||||
|
||||
This is the main Bluetooth service for the device and provides the API your app should use to get information about the mesh, send packets, or provision the radio.
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -8,19 +8,19 @@ sidebar_position: 4
|
|||
The device might report these fault codes on the screen, but it will also be outputted on the device serial output. If you encounter a fault code, please post on the forum and we'll try to help.
|
||||
|
||||
:::note
|
||||
This table is derived from the [protobufs](/docs/developers/protobufs/api#criticalerrorcode)
|
||||
This table is derived from the [protobufs](https://buf.build/meshtastic/protobufs/docs/main:meshtastic#meshtastic.CriticalErrorCode)
|
||||
:::
|
||||
|
||||
| Name | Number | Description |
|
||||
|:------------------- :|:------:|:----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- |
|
||||
| TxWatchdog | 1 | A software bug was detected while trying to send LoRa |
|
||||
| SleepEnterWait | 2 | A software bug was detected on entry to sleep |
|
||||
| NoRadio | 3 | No LoRa radio hardware could be found |
|
||||
| Unspecified | 4 | Not normally used |
|
||||
| UBloxInitFailed | 5 | We failed while configuring a UBlox GPS |
|
||||
| NoAXP192 | 6 | This board was expected to have a power management chip and it is missing or broken |
|
||||
| InvalidRadioSetting | 7 | The channel tried to set a radio setting which is not supported by this chipset, radio comms settings are now undefined |
|
||||
| TransmitFailed | 8 | Radio transmit hardware failure. We sent data to the radio chip, but it did not reply with an interrupt |
|
||||
| Brownout | 9 | We detected that the main CPU voltage dropped below the minimum acceptable value |
|
||||
| SX1262Failure | 10 | Selftest of SX1262 radio chip failed |
|
||||
| RadioSpiBug | 11 | A (likely software but possibly hardware) failure was detected while trying to send packets. If this occurs on your board, please post in the forum so that we can ask you to collect some information to allow fixing this bug |
|
||||
| Name | Number | Description |
|
||||
| :-----------------: | :----: | :------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------ |
|
||||
| TxWatchdog | 1 | A software bug was detected while trying to send LoRa |
|
||||
| SleepEnterWait | 2 | A software bug was detected on entry to sleep |
|
||||
| NoRadio | 3 | No LoRa radio hardware could be found |
|
||||
| Unspecified | 4 | Not normally used |
|
||||
| UBloxInitFailed | 5 | We failed while configuring a UBlox GPS |
|
||||
| NoAXP192 | 6 | This board was expected to have a power management chip and it is missing or broken |
|
||||
| InvalidRadioSetting | 7 | The channel tried to set a radio setting which is not supported by this chipset, radio comms settings are now undefined |
|
||||
| TransmitFailed | 8 | Radio transmit hardware failure. We sent data to the radio chip, but it did not reply with an interrupt |
|
||||
| Brownout | 9 | We detected that the main CPU voltage dropped below the minimum acceptable value |
|
||||
| SX1262Failure | 10 | Selftest of SX1262 radio chip failed |
|
||||
| RadioSpiBug | 11 | A (likely software but possibly hardware) failure was detected while trying to send packets. If this occurs on your board, please post in the forum so that we can ask you to collect some information to allow fixing this bug |
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -36,15 +36,15 @@ Two endpoints are specified:
|
|||
|
||||
Allows `PUT` and `OPTION` requests.
|
||||
|
||||
#### PUT
|
||||
#### PUT
|
||||
|
||||
A `PUT` request to this endpoint will be expected to contain a series of ToRadio protobuf payloads.
|
||||
A `PUT` request to this endpoint will be expected to contain a series of ToRadio protobuf payloads.
|
||||
|
||||
The protobufs will be sent in binary as the body for the request.
|
||||
|
||||
For the initial implementation, only one ToRadio message per request is supported, but future optimizations to improve throughput might add support for multiple ToRadios in a single request.
|
||||
|
||||
#### OPTIONS
|
||||
#### OPTIONS
|
||||
|
||||
An `OPTIONS`request to this endpoint will return a response status code `204` and headers only.
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -52,7 +52,7 @@ An `OPTIONS`request to this endpoint will return a response status code `204` an
|
|||
|
||||
Allows `GET` requests.
|
||||
|
||||
#### GET
|
||||
#### GET
|
||||
|
||||
A `GET` request from this endpoint will return a series of FromRadio protobufs.
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -61,12 +61,14 @@ The protobufs will be sent in binary as the body for the request.
|
|||
**Parameters**
|
||||
|
||||
##### **/api/v1/fromradio?all**
|
||||
|
||||
- `all=false` (unset default)
|
||||
- Only one protobuf is returned.
|
||||
- `all=true`
|
||||
- Only one protobuf is returned.
|
||||
- `all=true`
|
||||
- All available protobufs are returned.
|
||||
|
||||
##### **/api/v1/fromradio?chunked**
|
||||
|
||||
- `chunked=false` (unset default, not yet implemented)
|
||||
- The request returns all protobufs that can be delivered for the client's session (this would allow the client to poll by doing a series of requests). This is the only option that is supported in the initial release.
|
||||
- `chunked=true` (not yet implemented)
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -27,7 +27,7 @@ The relevant bits of the class hierarchy are as follows:
|
|||
### First Level: MeshModule
|
||||
|
||||
- [src/mesh/MeshModule.h](http://github.com/meshtastic/firmware/tree/master/src/mesh/MeshModule.h) - you probably don't want to use this base-class directly.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
### Second Level: SinglePortModule
|
||||
|
||||
- [src/mesh/SinglePortModule.h](http://github.com/meshtastic/firmware/tree/master/src/mesh/SinglePortModule.h) - for modules that send/receive from a single port number (the normal case).
|
||||
|
|
@ -66,10 +66,10 @@ A number of [key services](http://github.com/meshtastic/firmware/tree/master/src
|
|||
The easiest way to get started is:
|
||||
|
||||
1. [Build the firmware](/docs/development/firmware/build) codebase.
|
||||
2. Copy the [ReplyModule](http://github.com/meshtastic/firmware/tree/master/src/modules/ReplyModule.cpp) as a template into `src/modules/`.
|
||||
```sh
|
||||
cp src/modules/ReplyModule.* src/modules/YourModule.*
|
||||
```
|
||||
2. Copy the [ReplyModule](http://github.com/meshtastic/firmware/tree/master/src/modules/ReplyModule.cpp) as a template into `src/modules/`.
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
cp src/modules/ReplyModule.* src/modules/YourModule.*
|
||||
```
|
||||
3. Change the port number from `PortNum_REPLY_APP` to `PortNum_PRIVATE_APP`.
|
||||
4. Edit the `setupModules()` function located at `modules/Moduless.cpp` to add a call to create an instance of your module (see comment at head of that function).
|
||||
5. Rebuild with your new module and install on the device.
|
||||
|
|
@ -96,4 +96,3 @@ If you would like to use protocol buffers to define the structures you send over
|
|||
1. Create a new `.proto` file in the protos directory.
|
||||
2. Run `./bin/regen-protos.sh` to regenerate the C code for accessing the protocol buffers. If you don't have the required nanopb tool, follow the instructions printed by the script to get it.
|
||||
3. Done! You can now use your new protobuf just like any of the existing protobufs in Meshtastic.
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -25,7 +25,7 @@ Another component that we use is [Vercel](https://vercel.com) — a platform for
|
|||
| Getting Started | `docs/getting-started` | Instructions on how to get the Meshtastic firmware onto a users device. |
|
||||
| Device Settings | `docs/software/settings` | Details each user setting and provides explanations for what the setting does and how to configure the device using the various clients available (Android, CLI, iOS, Web) |
|
||||
| Hardware Details | `docs/hardware` | Any hardware related content. Any time a user is attaching a peripheral accessory to their device. That includes 3D printed cases, antennas, buttons, chimes, rotary encoders, and screens. |
|
||||
| Radio Mesh Details | `docs/mesh` | This section discusses everything relating to the Meshtastic mesh. Mesh health metrics will be discussed here as well as topics such as signal strength, range and anything else pertaining to "over the air". |
|
||||
| Radio Mesh Details | `docs/mesh` | This section discusses everything relating to the Meshtastic mesh. Mesh health metrics will be discussed here as well as topics such as signal strength, range and anything else pertaining to "over the air". |
|
||||
| Contribute to Meshtastic | `docs/developers` | Details each of the projects and how they work together to give a developer an idea of how the Meshtastic ecosystem operates. |
|
||||
| About the Documentation | `docs/maintaining-documentation` | This section explains how our documentation is organized, how to make edits to the documentation, view a local copy of your fork of the project. Style guides and tips will also be included here. |
|
||||
| Legal | `docs/legal` | Any legal information. Most changes here will be handled by developers actually working on the projects that require any legal disclosures. Examples include: the Meshtastic trademark, terms of service, and privacy policy. |
|
||||
|
|
@ -34,31 +34,31 @@ Another component that we use is [Vercel](https://vercel.com) — a platform for
|
|||
|
||||
Assuming you have the [prerequisites installed](/docs/development/documentation/local-dev#prerequisites), running a local instance of Docusaurus takes three steps:
|
||||
|
||||
1. Fork/Clone the [meshtastic/meshtastic](https://github.com/meshtastic/meshtastic) repository and navigate to the root directory of the project.
|
||||
1. Fork/Clone the [meshtastic/meshtastic](https://github.com/meshtastic/meshtastic) repository and navigate to the root directory of the project.
|
||||
|
||||
```shell title="Clone the project"
|
||||
git clone https://github.com/meshtastic/meshtastic.git
|
||||
```
|
||||
```shell title="Clone the project"
|
||||
git clone https://github.com/meshtastic/meshtastic.git
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
```shell title="Clone fork of the project"
|
||||
git clone https://github.com/[username]/meshtastic.git
|
||||
```
|
||||
```shell title="Clone fork of the project"
|
||||
git clone https://github.com/[username]/meshtastic.git
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
```shell title="Change Directory"
|
||||
cd ~/Meshtastic
|
||||
```
|
||||
```shell title="Change Directory"
|
||||
cd ~/Meshtastic
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
2. Install Dependencies
|
||||
2. Install Dependencies
|
||||
|
||||
```shell title="Install dependencies using Yarn"
|
||||
yarn install
|
||||
```
|
||||
```shell title="Install dependencies using Yarn"
|
||||
yarn install
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
3. Run Docusaurus
|
||||
3. Run Docusaurus
|
||||
|
||||
```shell title="Run node.js server"
|
||||
yarn start
|
||||
```
|
||||
```shell title="Run node.js server"
|
||||
yarn start
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
:::tip
|
||||
Before submitting a pull request, it's helpful to run the following command to ensure there are no broken links or errors:
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -7,14 +7,18 @@ sidebar_label: Publish
|
|||
## Publish Live
|
||||
|
||||
1. Generate protobuf docs
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
cd meshtastic
|
||||
./scripts/gen-proto-docs.sh
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
cd meshtastic
|
||||
./scripts/gen-proto-docs.sh
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
2. Build
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
pnpm build
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
pnpm build
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
3. Submit Pull Request
|
||||
|
||||
## Publish to Vercel
|
||||
|
|
@ -48,4 +52,3 @@ There is a limited number of branch urls that you will be able to view. If you n
|
|||
|
||||
Branch urls are helpful in PRs because they will remain constant, and you won't need to resubmit a new url for review each new commit if changes are requested.
|
||||
:::
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -1,8 +1,7 @@
|
|||
|
||||
position: 1 # float position is supported
|
||||
label: 'Style Guides'
|
||||
label: "Style Guides"
|
||||
collapsible: true # make the category collapsible
|
||||
link:
|
||||
slug: /development/docs/style-guide
|
||||
type: generated-index
|
||||
title: Style Guides
|
||||
title: Style Guides
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -4,7 +4,7 @@ title: Markdown Features
|
|||
sidebar_label: Markdown Features
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
import { Dark, Light } from '/src/components/ColorMode';
|
||||
import { Dark, Light } from "/src/components/ColorMode";
|
||||
|
||||
## Overview
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -14,7 +14,7 @@ We have developed several [React](https://reactjs.org/) components for assisting
|
|||
|
||||
### Light/Dark Mode Switch
|
||||
|
||||
#### Usage:
|
||||
#### Usage
|
||||
|
||||
```jsx
|
||||
import { Dark, Light } from '/src/components/ColorMode';
|
||||
|
|
@ -27,7 +27,7 @@ import { Dark, Light } from '/src/components/ColorMode';
|
|||
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
#### Demo:
|
||||
#### Demo
|
||||
|
||||
<Dark>
|
||||
<div className="not-prose rounded-lg bg-primary shadow-md">
|
||||
|
|
@ -50,7 +50,7 @@ import { Dark, Light } from '/src/components/ColorMode';
|
|||
|
||||
### Code Blocks
|
||||
|
||||
#### Usage:
|
||||
#### Usage
|
||||
|
||||
Always specify the language used directly after the start of the code block (```).
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -71,13 +71,13 @@ export const typedArrayToBuffer = (array: Uint8Array): ArrayBuffer => {
|
|||
```
|
||||
````
|
||||
|
||||
#### Demo:
|
||||
#### Demo
|
||||
|
||||
```ts title="Demo"
|
||||
export const typedArrayToBuffer = (array: Uint8Array): ArrayBuffer => {
|
||||
return array.buffer.slice(
|
||||
array.byteOffset,
|
||||
array.byteLength + array.byteOffset,
|
||||
array.byteLength + array.byteOffset
|
||||
);
|
||||
};
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -4,4 +4,4 @@ position: 1
|
|||
link:
|
||||
type: generated-index
|
||||
title: Firmware
|
||||
slug: /development/firmware
|
||||
slug: /development/firmware
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -10,7 +10,7 @@ Meshtastic uses [PlatformIO](https://platformio.org), a development environment
|
|||
|
||||
1. [Install PlatformIO](https://platformio.org/platformio-ide)
|
||||
2. Clone the [Meshtastic Firmware](https://github.com/meshtastic/firmware) repository
|
||||
```sh
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
git clone https://github.com/meshtastic/firmware.git
|
||||
```
|
||||
3. Update the repository's [submodules](https://github.com/meshtastic/firmware/blob/master/.gitmodules)
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -4,32 +4,35 @@ title: OLED Localization Guide
|
|||
sidebar_label: OLED Localization
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
1. Create an extended ASCII custom font. Use a glyph editor to create a new font file. The easiest way is to use the online [glyph editor](https://rawgit.com/ThingPulse/esp8266-oled-ssd1306/master/resources/glyphEditor.html) from the OLED library. ([glyph editor source code](https://github.com/ThingPulse/esp8266-oled-ssd1306/tree/master/resources))
|
||||
1. Copy and paste the existing font.
|
||||
2. Modify it according desired codepage and save the new font file in `graphics/font` folder.
|
||||
Please note that the used font file format differs from common Adafruit GFX.
|
||||
1. Create an extended ASCII custom font. Use a glyph editor to create a new font file. The easiest way is to use the online [glyph editor](https://rawgit.com/ThingPulse/esp8266-oled-ssd1306/master/resources/glyphEditor.html) from the OLED library. ([glyph editor source code](https://github.com/ThingPulse/esp8266-oled-ssd1306/tree/master/resources))
|
||||
1. Copy and paste the existing font.
|
||||
2. Modify it according desired codepage and save the new font file in `graphics/font` folder.
|
||||
Please note that the used font file format differs from common Adafruit GFX.
|
||||
2. Update the `customFontTableLookup` function in `Screen.h`
|
||||
1. To map the double-byte UTF-8 code to the corresponding extended ASCII character of the desired codepage update the `customFontTableLookup` function in the `Screen.h` file.
|
||||
2. Modify the `switch (last)` statement: use left byte from UTF-8 code in the `case` label to map charachter's right byte to its extended ASCII code by specifying an offset.
|
||||
1. To map the double-byte UTF-8 code to the corresponding extended ASCII character of the desired codepage update the `customFontTableLookup` function in the `Screen.h` file.
|
||||
2. Modify the `switch (last)` statement: use left byte from UTF-8 code in the `case` label to map charachter's right byte to its extended ASCII code by specifying an offset.
|
||||
3. Define language and font in `Screen.cpp`
|
||||
```c
|
||||
#ifdef OLED_{LANG_NAME}
|
||||
#include "fonts/OLEDDisplayFonts{LANG_NAME}.h"
|
||||
#endif
|
||||
|
||||
...
|
||||
```c
|
||||
#ifdef OLED_{LANG_NAME}
|
||||
#include "fonts/OLEDDisplayFonts{LANG_NAME}.h"
|
||||
#endif
|
||||
|
||||
...
|
||||
|
||||
#ifdef OLED_{LANG_NAME}
|
||||
#define FONT_SMALL ArialMT_Plain_10_{LANG_NAME}
|
||||
#else
|
||||
#define FONT_SMALL ArialMT_Plain_10
|
||||
#endif
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
#ifdef OLED_{LANG_NAME}
|
||||
#define FONT_SMALL ArialMT_Plain_10_{LANG_NAME}
|
||||
#else
|
||||
#define FONT_SMALL ArialMT_Plain_10
|
||||
#endif
|
||||
```
|
||||
4. Define language in `variant/*/platformio.ini`
|
||||
```
|
||||
build_flags =
|
||||
${esp32_base.build_flags}
|
||||
-D xxxxx
|
||||
-D OLED_{LANG_NAME}
|
||||
-I variants/xxxxx
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
```text
|
||||
build_flags =
|
||||
${esp32_base.build_flags}
|
||||
-D xxxxx
|
||||
-D OLED_{LANG_NAME}
|
||||
-I variants/xxxxx
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -6,15 +6,15 @@ sidebar_label: Port Numbers
|
|||
|
||||
Any new app that runs on the device or via sister apps on phones/PCs should pick and use a unique "portnum" for their applications use.
|
||||
|
||||
The current list of port numbers can be found listed in the [protobufs](/docs/developers/protobufs/api#portnumsproto)
|
||||
The current list of port numbers can be found listed in the [protobufs](https://buf.build/meshtastic/protobufs/docs/main:meshtastic#meshtastic.CriticalErrorCode)
|
||||
|
||||
## Assignment
|
||||
|
||||
PortNums should be assigned by the following ranges:
|
||||
|
||||
| Portnum | Usage |
|
||||
|:-------:|:---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- |
|
||||
| 0-63 | Core Meshtastic use, do not use for third party apps. |
|
||||
| :-----: | :--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- |
|
||||
| 0-63 | Core Meshtastic use, do not use for third party apps. |
|
||||
| 64-127 | Registered 3rd party apps, send in a pull request that adds a new entry to portnums.proto to register your application |
|
||||
| 256-511 | Use one of these portnums for your private applications that you do not want to register publicly |
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -22,4 +22,4 @@ All other values are reserved.
|
|||
|
||||
## Integration
|
||||
|
||||
If you are making a new app using Meshtastic, please send a pull request to add your chosen "portnum" to this master table.
|
||||
If you are making a new app using Meshtastic, please send a pull request to add your chosen "portnum" to this master table.
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -14,19 +14,21 @@ You may encounter a situation where your device crashes and are left with a stac
|
|||
This method uses the symbols of the `firmware.elf` file generated from your latest build, you may wish to rebuild to get up-to-date symbols.
|
||||
:::
|
||||
|
||||
1. Save the backtrace string to a text file:
|
||||
```text title="backtrace.txt"
|
||||
Backtrace: 0x....
|
||||
```
|
||||
1. Save the backtrace string to a text file:
|
||||
|
||||
```text title="backtrace.txt"
|
||||
Backtrace: 0x....
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
2. Run the exception decoder:
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
bin/exception_decoder.py backtrace.txt
|
||||
```
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
bin/exception_decoder.py backtrace.txt
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### In Real-Time
|
||||
|
||||
In order to decode stack traces in real time, keep the following command (replacing `DEVICE_PORT` with your device's port) running in your terminal with the target device connected:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
pio device monitor --port DEVICE_PORT -f esp32_exception_decoder
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -5,17 +5,17 @@ sidebar_label: Connecting
|
|||
---
|
||||
|
||||
```tsx
|
||||
import type React from 'React';
|
||||
import type React from "React";
|
||||
|
||||
import { IHTTPConnection } from '@meshtastic/meshtasticjs';
|
||||
import { IHTTPConnection } from "@meshtastic/meshtasticjs";
|
||||
|
||||
export const Connection = (): JSX.Element => {
|
||||
const connection = new IHTTPConnection();
|
||||
|
||||
const connect = (): void => {
|
||||
void connection.connect({
|
||||
address: '10.0.0.10',
|
||||
fetchInterval: 3000,
|
||||
address: "10.0.0.10",
|
||||
fetchInterval: 3000
|
||||
});
|
||||
};
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -13,8 +13,8 @@ import {
|
|||
Client,
|
||||
Types,
|
||||
Protobuf,
|
||||
SettingsManager,
|
||||
} from '@meshtastic/meshtasticjs';
|
||||
SettingsManager
|
||||
} from "@meshtastic/meshtasticjs";
|
||||
|
||||
/**
|
||||
* Connection method
|
||||
|
|
@ -24,7 +24,7 @@ const client = new Client();
|
|||
SettingsManager.setDebugMode(Protobuf.LogLevelEnum.DEBUG);
|
||||
|
||||
const connection = client.createHTTPConnection();
|
||||
connection.connect('192.168.x.x');
|
||||
connection.connect("192.168.x.x");
|
||||
|
||||
const restartDevice: Promise<void> = connection.restartDevice();
|
||||
const getStatistics: Promise<void | Types.WebSPIFFSResponse> =
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -12,7 +12,7 @@ No pre-requisites are needed locally to make a release. All builds are done via
|
|||
|
||||
To test/validate, you will need to run:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
pip3 install -r requirements.txt
|
||||
pip install .
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
|
@ -25,7 +25,7 @@ pip install .
|
|||
|
||||
connect one device to the serial port and run:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
pytest -m smoke1
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -41,8 +41,6 @@ pytest -m smoke1
|
|||
You need permissions in the GitHub project to make a build
|
||||
:::
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
### Meshtastic-flasher
|
||||
|
||||
A `meshtastic-flasher` release consists of publishing the release to PyPi https://pypi.org/project/meshtastic-flasher/ as well as producing single-executable files that are downloadable from Github https://github.com/meshtastic/Meshtastic-gui-installer/releases.
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -9,41 +9,35 @@ sidebar_label: Python
|
|||
|
||||
We use the Visual Studio Code (VScode) default python formatting conventions (autopep8). So if you use that IDE you should be able to use "Format Document" and not generate unrelated diffs. If you use some other editor, please do not change formatting on lines you have not changed yourself.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
### Building
|
||||
|
||||
**To build a new release**
|
||||
|
||||
```sh
|
||||
```shell title="To build a new release"
|
||||
apt install pandoc
|
||||
sudo pip3 install markdown pdoc3 webencodings pyparsing twine autopep8 pylint pytest pytest-cov
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
**For development**
|
||||
|
||||
```sh
|
||||
```shell title="For development"
|
||||
pip3 install -r requirements.txt
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### Linting
|
||||
|
||||
```sh
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
pylint meshtastic
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### Testing
|
||||
|
||||
**Install and run pytest**
|
||||
#### Install and run pytest
|
||||
|
||||
- For more verbosity, add `-v` or even `-vv`
|
||||
- For more verbosity, add `-v` or even `-vv`
|
||||
|
||||
```sh
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
pip3 install .
|
||||
pytest -vv
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
**Run just unit tests**
|
||||
|
||||
```sh
|
||||
```shell title="Run just unit tests"
|
||||
pytest
|
||||
# or (more verbosely)
|
||||
pytest -m unit
|
||||
|
|
@ -51,15 +45,11 @@ pytest -m unit
|
|||
make
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
**Run just integration tests**
|
||||
|
||||
```sh
|
||||
```shell title="Run just integration tests"
|
||||
pytest -m int
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
**Run the smoke test with only one device connected serially (aka smoke1)**
|
||||
|
||||
```sh
|
||||
```shell title="Run the smoke test with only one device connected serially (aka smoke1)"
|
||||
pytest -m smoke1
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -68,21 +58,15 @@ Running `smoke1` will reset values on the device, including the region to 1 (US)
|
|||
Be sure to hit the reset button on the device after the test is completed.
|
||||
:::
|
||||
|
||||
**Run the smoke test with only two device connected serially (aka smoke2)**
|
||||
|
||||
```sh
|
||||
```shell title="Run the smoke test with only two device connected serially (aka smoke2)"
|
||||
pytest -m smoke2
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
**Run the wifi smoke test**
|
||||
|
||||
```sh
|
||||
```shell title="Run the wifi smoke test"
|
||||
pytest -m smokewifi
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
**Run a specific test**
|
||||
|
||||
```sh
|
||||
```shell title="Run a specific test"
|
||||
pytest -msmoke1 meshtastic/tests/test_smoke1.py::test_smoke1_info
|
||||
|
||||
# or to run a specific smoke2 test
|
||||
|
|
@ -96,9 +80,7 @@ pytest -m smokewifi meshtastic/tests/test_smoke_wifi.py::test_smokewifi_info
|
|||
|
||||
See [pytest.ini](https://github.com/meshtastic/Meshtastic-python/blob/master/pytest.ini).
|
||||
|
||||
**To see the unit test code coverage**
|
||||
|
||||
```sh
|
||||
```shell title="To see the unit test code coverage"
|
||||
pytest --cov=meshtastic
|
||||
# or if want html coverage report
|
||||
pytest --cov-report html --cov=meshtastic
|
||||
|
|
@ -106,9 +88,7 @@ pytest --cov-report html --cov=meshtastic
|
|||
make cov
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
**To see slowest unit tests, you can run**
|
||||
|
||||
```sh
|
||||
```shell title="To see slowest unit tests, you can run"
|
||||
pytest --durations=0
|
||||
# or
|
||||
make slow
|
||||
|
|
@ -118,7 +98,7 @@ make slow
|
|||
|
||||
Pre-generated: [API documentation](https://python.meshtastic.org)
|
||||
|
||||
```sh
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
bin/regen-docs.sh
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -4,4 +4,4 @@ position: 20
|
|||
link:
|
||||
type: generated-index
|
||||
slug: /development/reference
|
||||
title: Reference Material
|
||||
title: Reference Material
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -24,6 +24,7 @@ Repobeats images can be generated at [repobeats.axiom.co](https://repobeats.axio
|
|||
|
||||
<!--Project specific badges here-->
|
||||
<!--Crowdin Badge can be generated from https://crowdin.meshtastic.org/u/projects/<project_id>/crowdsource -->
|
||||
|
||||
[](https://crowdin.meshtastic.org/<project>)
|
||||
[](https://github.com/meshtastic/<repo>/actions/workflows/ci.yml)
|
||||
[](https://cla-assistant.io/meshtastic/<repo>)
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -5,4 +5,4 @@ sidebar_label: LoRa Datasheet
|
|||
sidebar_position: 1
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
- [LoRa Design Guide Datasheet](/documents/LoRa_Design_Guide.pdf)
|
||||
- [LoRa Design Guide Datasheet](/documents/LoRa_Design_Guide.pdf)
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
File diff suppressed because it is too large
Load diff
8
docs/development/reference/protobufs.mdx
Normal file
8
docs/development/reference/protobufs.mdx
Normal file
|
|
@ -0,0 +1,8 @@
|
|||
---
|
||||
id: protobufs
|
||||
title: Protobufs
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
Protobufs are used by Meshtastic software to send and receive data between App and Device and Device to Device.
|
||||
|
||||
Documentation on the Meshtastic Protobuf messages can be fund on the [BSR(Buf Schema Registry)](https://buf.build/meshtastic/protobufs).
|
||||
|
|
@ -4,8 +4,7 @@ title: Building
|
|||
sidebar_label: Building
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
Releases are automatically generated for every commit as per out [CI](https://github.com/meshtastic/web/blob/master/.github/workflows/main.yml). This performs two actions:
|
||||
|
||||
1. Generates a perpetually updated [GitHub release](https://github.com/meshtastic/web/releases/tag/latest) with an accompanying `build.tar` that a automatically get's pulled by the firmware CI at build time.
|
||||
2. A hosted version is deployed to [client.meshtastic.org](https://client.meshtastic.org).
|
||||
2. A hosted version is deployed to [client.meshtastic.org](https://client.meshtastic.org).
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -4,4 +4,4 @@ position: 2
|
|||
link:
|
||||
type: generated-index
|
||||
title: Flashing Firmware
|
||||
slug: /getting-started/flashing-firmware
|
||||
slug: /getting-started/flashing-firmware
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -1,12 +1,13 @@
|
|||
---
|
||||
id: cli-script
|
||||
title: Flashing with the CLI
|
||||
sidebar_label: CLI Script
|
||||
sidebar_label: CLI Script (Advanced Users)
|
||||
sidebar_position: 3
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
import Tabs from '@theme/Tabs';
|
||||
import TabItem from '@theme/TabItem';
|
||||
import Tabs from "@theme/Tabs";
|
||||
import TabItem from "@theme/TabItem";
|
||||
import Link from "@docusaurus/Link";
|
||||
|
||||
:::caution
|
||||
Make sure not to power the radio on without first attaching the antenna! You could damage the radio chip!
|
||||
|
|
@ -269,8 +270,15 @@ Be very careful to install the correct load for your board. In particular the po
|
|||
|
||||
Select `Flash ESP`. It may take a minute or two. Once complete, "Done! Flashing is complete!" will be shown.
|
||||
|
||||
## Over the Air Update Instructions
|
||||
## Connect and Configure Device
|
||||
|
||||
OTA updates are only currently available on Android.
|
||||
After flashing the Meshtastic firmware to the device, you can proceed with the initial configuration.
|
||||
|
||||
<!--- TODO --->
|
||||
<div className="indexCtasBody">
|
||||
<Link
|
||||
className={"button button--outline button--lg cta--button"}
|
||||
to={"/docs/getting-started/initial-config"}
|
||||
>
|
||||
Connect and Configure Device
|
||||
</Link>
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -1,12 +1,13 @@
|
|||
---
|
||||
id: external-serial-adapter
|
||||
title: Flashing with an External Serial Adapter
|
||||
sidebar_label: External Serial Adapter
|
||||
sidebar_label: External Serial Adapter (Advanced Users)
|
||||
sidebar_position: 4
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
import Tabs from '@theme/Tabs';
|
||||
import TabItem from '@theme/TabItem';
|
||||
import Tabs from "@theme/Tabs";
|
||||
import TabItem from "@theme/TabItem";
|
||||
import Link from "@docusaurus/Link";
|
||||
|
||||
:::info
|
||||
This information will likely only be helpful if you've already attempted to go through the prerequisites and processes outlined in [meshtastic flasher](/docs/software/python/flasher) or [manually flashing](/docs/getting-started/flashing-firmware/esp32/cli-script)
|
||||
|
|
@ -19,9 +20,10 @@ Make sure not to power the radio on without first attaching the antenna! You cou
|
|||
## Background
|
||||
|
||||
Situations that may require usage an external USB to Serial Adapter:
|
||||
* Due to the chip shortage, recently purchased devices such as the TTGO T-Beam may come with legacy or non-standard USB to Serial adapter chips that are unreliable in some cases.
|
||||
* Certain devices might have defective USB to Serial chip.
|
||||
* Certain devices, such as the [Hydra](https://github.com/Hydra-Designs/project-hydra-meshtastic-pcb) (Meshtastic-DIY target).
|
||||
|
||||
- Due to the chip shortage, recently purchased devices such as the TTGO T-Beam may come with legacy or non-standard USB to Serial adapter chips that are unreliable in some cases.
|
||||
- Certain devices might have defective USB to Serial chip.
|
||||
- Certain devices, such as the [Hydra](https://github.com/Hydra-Designs/project-hydra-meshtastic-pcb) (Meshtastic-DIY target).
|
||||
|
||||
### USB Serial Adapters
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -38,18 +40,18 @@ Plug the adapter into your computer without connecting it to any devices yet. En
|
|||
:::info
|
||||
There are multiple ways to connect the pins of the adapter to the target device: pressing jumpers against contacts, using pogo pin jigs, etc. This tutorial features offset dupont headers soldered onto the operative GPIO pins and connected via jumpers.
|
||||
:::
|
||||
Disconnect your USB to Serial Adapter from the computer before starting this process.
|
||||
Disconnect your USB to Serial Adapter from the computer before starting this process.
|
||||
|
||||
1. Connect the RX pin of the adapter to the TX pin of the devices
|
||||
2. Connect the TX pin of the adapter to the RX pin of the device
|
||||
3. Connect a GND pin of the adapter to the GND pin of the device
|
||||
4. Connect either the 5V pin of the adapter to the 5V pin of the device (illustrated) or the 3.3V pin of the adapter to the 3.3V pin of device.
|
||||
5. Bridge GPIO 0 to GND on the device with a jumper. (This places the device into flash mode when the device is powered up)
|
||||
Example wiring featuring a T-Beam
|
||||
|
||||
Example wiring featuring a T-Beam
|
||||

|
||||
6. Connect the device to a USB port on the computer
|
||||
7. Remove the jumper bridging GPIO 0 to GND
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
### Flashing
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -62,14 +64,26 @@ After flashing the device is complete, reset your device (via the RST button if
|
|||
If you have the Meshtastic Python CLI installed, you can run `meshtastic --noproto` to connect the device again over the adapter and view the serial output to confirm Meshtastic installed correctly.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
### Troubleshooting
|
||||
|
||||
In the Meshtastic Flasher, device detection may not work when using the external USB to Serial adapter. You might need to manually select the correct device type from the drop-down.
|
||||
|
||||
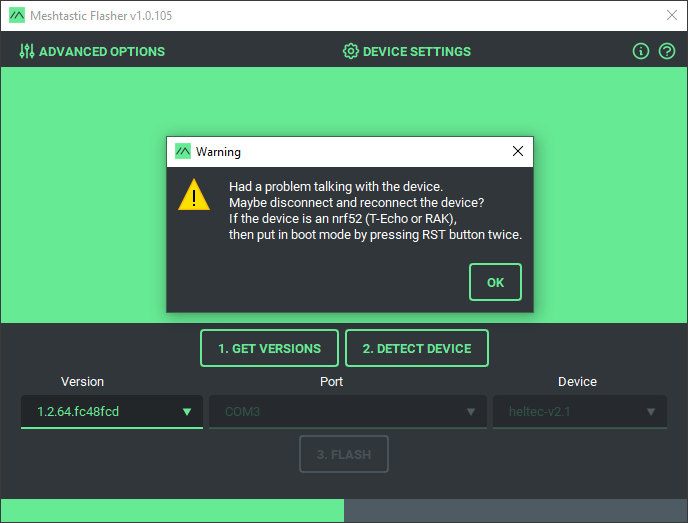
|
||||
|
||||
Sometimes you might receive an error for COM port permission in the Meshtastic Flasher or the manual device install scripts, this can be caused by a number of different issues.
|
||||
Sometimes you might receive an error for COM port permission in the Meshtastic Flasher or the manual device install scripts, this can be caused by a number of different issues.
|
||||
|
||||
You might need to run the process as an administrator, check to ensure software like Cura isn't monopolizing COM ports, or reboot.
|
||||
You might need to run the process as an administrator, check to ensure software like Cura isn't monopolizing COM ports, or reboot.
|
||||
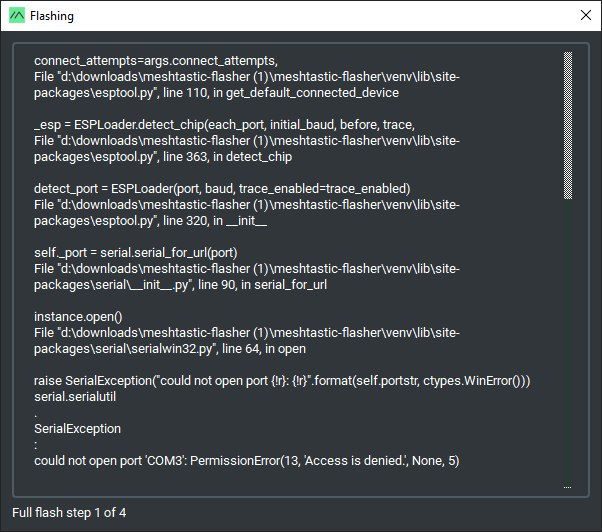
|
||||
|
||||
## Connect and Configure Device
|
||||
|
||||
After flashing the Meshtastic firmware to the device, you can proceed with the initial configuration.
|
||||
|
||||
<div className="indexCtasBody">
|
||||
<Link
|
||||
className={"button button--outline button--lg cta--button"}
|
||||
to={"/docs/getting-started/initial-config"}
|
||||
>
|
||||
Connect and Configure Device
|
||||
</Link>
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -11,7 +11,7 @@ The recommended method for firmware flashing is the [Web-Based Installer.](https
|
|||
|
||||
## Flashing Method for ESP32 Devices
|
||||
|
||||
1. The [Web-Based Installer](https://flasher.meshtastic.org) requires either Chrome or Edge browsers but is an excellent choice for quickly flashing devices. **This is the recommended method for firmware flashing, especially for those new to the project, due to its ease of use.**
|
||||
1. The [Web-Based Installer](/docs/getting-started/flashing-firmware/esp32/web-flasher.mdx) requires either Chrome or Edge browsers but is an excellent choice for quickly flashing devices. **This method is highly recommended for firmware flashing, especially for new users of the project, as it is easy to use.**
|
||||
2. The [Python Flasher](/docs/software/python/flasher) does a lot under the hood to prevent you from needing to use the terminal.
|
||||
3. The [CLI Script](/docs/getting-started/flashing-firmware/esp32/cli-script) is considered the "manual process" for flashing firmware.
|
||||
4. Flashing your device using an [external serial adapter](/docs/getting-started/flashing-firmware/esp32/external-serial-adapter) should only be attempted as a last resort if no other method has been successful.
|
||||
4. Flashing your device using an [external serial adapter](/docs/getting-started/flashing-firmware/esp32/external-serial-adapter) should only be attempted as a last resort if no other method has been successful.
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -5,6 +5,7 @@ sidebar_label: Python Flasher
|
|||
sidebar_position: 2
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
import MFlasher from '../../../software/python-flasher.mdx'
|
||||
import MFlasher from "../../../software/python-flasher.mdx";
|
||||
import Link from "@docusaurus/Link";
|
||||
|
||||
<MFlasher components={props.components} />
|
||||
<MFlasher components={props.components} />
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -5,8 +5,23 @@ sidebar_label: Web Flasher (recommended)
|
|||
sidebar_position: 1
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
import Link from "@docusaurus/Link";
|
||||
|
||||
## Web Flasher
|
||||
|
||||
1. Plug in your device
|
||||
2. Visit [flasher.meshtastic.org](https://flasher.meshtastic.org) _\*requires Chrome or Edge browser_
|
||||
3. Follow the instructions
|
||||
3. Follow the instructions
|
||||
|
||||
## Connect and Configure Device
|
||||
|
||||
After flashing the Meshtastic firmware to the device, you can proceed with the initial configuration.
|
||||
|
||||
<div className="indexCtasBody">
|
||||
<Link
|
||||
className={"button button--outline button--lg cta--button"}
|
||||
to={"/docs/getting-started/initial-config"}
|
||||
>
|
||||
Connect and Configure Device
|
||||
</Link>
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -7,7 +7,7 @@ sidebar_position: 4
|
|||
|
||||
The only difference between the _RAK4631-R_ (RUI3) and the _RAK4631_ (Arduino) is the bootloader it is shipped with - the hardware is the same.
|
||||
|
||||
Meshtastic requires the Arduino bootloader on RAK WisBlock NRF52-based boards. The process of converting the bootloader only needs to be performed once.
|
||||
Meshtastic requires the Arduino bootloader on RAK WisBlock nRF52-based boards. The process of converting the bootloader only needs to be performed once.
|
||||
|
||||
This conversion requires the use of either a [DAPLink](https://daplink.io/) or [J-Link](https://www.segger.com/products/debug-probes/j-link/). The most reasonably priced and available is the [RAKDAP1](https://store.rakwireless.com/products/daplink-tool).
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -25,4 +25,4 @@ This conversion requires the use of either a [DAPLink](https://daplink.io/) or [
|
|||
```
|
||||
6. Continue with the normal [flashing instructions](/docs/getting-started/flashing-firmware/nrf52/drag-n-drop)
|
||||
|
||||
Alternate methods of flashing are outlined [here](https://github.com/RAKWireless/WisBlock/tree/master/bootloader/RAK4630).
|
||||
Alternate methods of flashing are outlined [here](https://github.com/RAKWireless/WisBlock/tree/master/bootloader/RAK4630).
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -1,32 +1,51 @@
|
|||
---
|
||||
id: drag-n-drop
|
||||
title: Drag & Drop NRF52 Firmware Updates
|
||||
title: Drag & Drop nRF52 Firmware Updates
|
||||
sidebar_label: Drag & Drop (recommended)
|
||||
sidebar_position: 1
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
import Tabs from '@theme/Tabs';
|
||||
import TabItem from '@theme/TabItem';
|
||||
import Tabs from "@theme/Tabs";
|
||||
import TabItem from "@theme/TabItem";
|
||||
import Link from "@docusaurus/Link";
|
||||
|
||||
:::info
|
||||
|
||||
Before flashing confirm that you have [RAK4631](https://docs.rakwireless.com/Product-Categories/WisBlock/RAK4631/) and not a [RAK4631-R](https://docs.rakwireless.com/Product-Categories/WisBlock/RAK4631-R/) If this is not the case, fear not. The hardware is identical but requires changing the bootloader. Instructions on how to do this are located [here](/docs/getting-started/flashing-firmware/nrf52/convert-rak4631r).
|
||||
|
||||
:::
|
||||
|
||||
## Upgrading from a previous version of Meshtastic
|
||||
|
||||
If you are upgrading your NRF52 device from a previous version of Meshtastic rather than starting from scratch, you may need to do a full factory reset of the internal flash memory. Stale data saved by previous versions of the Meshtastic firmware can cause devices to get stuck in a crash loop at startup.
|
||||
|
||||
Follow the guide to [factory erase your NRF52](/docs/getting-started/flashing-firmware/nrf52/nrf52-erase) device before continuing to [flash firmware](#flash-firmware).
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
## Flash Firmware
|
||||
|
||||
Download and unzip the latest firmware from [Meshtastic Downloads](https://meshtastic.org/downloads).
|
||||
|
||||
1. Connect your device to your computer with a USB data cable.
|
||||
2. Double click the reset button on your device (this will put it into bootloader mode)
|
||||
2. Double click the reset button on your device (this will put it into bootloader mode)
|
||||
3. Notice a new drive will be mounted on your computer (Windows, Mac, or Linux)
|
||||
4. Open this drive and you should see three files: `CURRENT.UF2`, `INDEX.HTM`, and `INFO_UF2.TXT`
|
||||
5. Drop the appropriate firmware file (`firmware-DEVICE_NAME-vx.x.x-xxxxxxx.uf2`) from the release onto this drive.
|
||||
|
||||
Once the file has finished copying onto the drive, the device will reboot and install the Meshtastic firmware.
|
||||
Once the file has finished copying onto the drive, the device will reboot and install the Meshtastic firmware.
|
||||
|
||||
### Issues When Upgrading from A Previous Version of Meshtastic
|
||||
|
||||
:::info
|
||||
|
||||
Previous versions of the Meshtastic firmware may save stale data, causing devices to get stuck in a crash loop during startup. If you experience issues when upgrading your nRF52 device from a previous version of Meshtastic, you may need to perform a full factory reset of the internal flash memory.
|
||||
|
||||
Follow the guide to [factory erase your nRF52](/docs/getting-started/flashing-firmware/nrf52/nrf52-erase) device before continuing to [flash firmware](#flash-firmware).
|
||||
|
||||
:::
|
||||
|
||||
## Connect and Configure Device
|
||||
|
||||
After flashing the Meshtastic firmware to the device, you can proceed with the initial configuration.
|
||||
|
||||
<div className="indexCtasBody">
|
||||
<Link
|
||||
className={"button button--outline button--lg cta--button"}
|
||||
to={"/docs/getting-started/initial-config"}
|
||||
>
|
||||
Connect and Configure Device
|
||||
</Link>
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -1,13 +1,13 @@
|
|||
---
|
||||
id: flashing-nrf52-devices
|
||||
title: Flash NRF52 Devices
|
||||
sidebar_label: NRF52 Device
|
||||
title: Flash nRF52 Devices
|
||||
sidebar_label: nRF52 Device
|
||||
sidebar_position: 2
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
## Flashing Methods for NRF52 Devices
|
||||
## Flashing Methods for nRF52 Devices
|
||||
|
||||
The NRF52 based devices have the easiest firmware upgrade process. No driver or software install is required on any platform.
|
||||
The nRF52 based devices have the easiest firmware upgrade process. No driver or software install is required on any platform.
|
||||
|
||||
1. The [drag and drop](/docs/getting-started/flashing-firmware/nrf52/drag-n-drop) firmware installation is considered the "manual process" and recommended as the easiest solution.
|
||||
2. The [Python Flasher](/docs/software/python/flasher) application does a lot under the hood to prevent you from needing to use the terminal. It also allows you to configure your device.
|
||||
1. The [Drag & Drop](/docs/getting-started/flashing-firmware/nrf52/drag-n-drop) firmware installation method is considered the "manual process" and recommended as the easiest solution.
|
||||
2. The [Python Flasher](/docs/software/python/flasher) application does a lot under the hood to prevent you from needing to use the terminal.
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -1,22 +1,33 @@
|
|||
---
|
||||
id: nrf52-erase
|
||||
title: Flash NRF52 Factory Erase
|
||||
sidebar_label: Factory Erase NRF52
|
||||
title: Flash nRF52 Factory Erase
|
||||
sidebar_label: Factory Erase nRF52
|
||||
sidebar_position: 3
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
Meshtastic uses the [littlefs](https://github.com/littlefs-project/littlefs) library to store configuration, logs, and other data in the internal flash of NRF52 devices. Updating the firmware does _not_ erase this additional data, which can cause issues when the format and location of data changes between releases.
|
||||
import Link from "@docusaurus/Link";
|
||||
|
||||
To reset the flash storage on your NRF52 board:
|
||||
Meshtastic uses the [littlefs](https://github.com/littlefs-project/littlefs) library to store configuration, logs, and other data in the internal flash of nRF52 devices. Updating the firmware does _not_ erase this additional data, which can cause issues when the format and location of data changes between releases.
|
||||
|
||||
To reset the flash storage on your nRF52 board:
|
||||
|
||||
Download and unzip the latest firmware from [Meshtastic Downloads](https://meshtastic.org/downloads).
|
||||
|
||||
1. Connect your device to your computer with a USB data cable.
|
||||
2. Double click the reset button on your device (this will put it into bootloader mode)
|
||||
2. Double click the reset button on your device (this will put it into bootloader mode)
|
||||
3. Notice a new drive will be mounted on your computer (Windows, Mac, or Linux)
|
||||
4. Open this drive and you should see three files: `CURRENT.UF2`, `INDEX.HTM`, and `INFO_UF2.TXT`
|
||||
5. Copy the included file named `Meshtastic_nRF52_factory_erase.uf2` onto the virtual disk device. The device should reboot.
|
||||
6. Connect to the device via serial console using the [Meshtastic CLI `--noproto`](/docs/software/python/cli/#--noproto) mode or a standalone serial client like `minicom`.
|
||||
6. Connect to the device via serial console using the [Meshtastic CLI `--noproto`](/docs/software/python/cli/#--noproto) mode or a standalone serial client like `minicom`.
|
||||
7. Press any key, you should see the message: `Formatting... Done`.
|
||||
|
||||
Once the device has been erased, you can proceed to install the latest Meshtastic firmware on a clean storage filesystem by following the [flash firmware](/docs/getting-started/flashing-firmware/nrf52/drag-n-drop#flash-firmware) steps.
|
||||
Once the device has been erased, you can proceed to install the latest Meshtastic firmware on a clean storage filesystem by clicking the link below.
|
||||
|
||||
<div className="indexCtasBody">
|
||||
<Link
|
||||
className={"button button--outline button--lg cta--button"}
|
||||
to={"/docs/getting-started/flashing-firmware/nrf52/"}
|
||||
>
|
||||
Flash nRF52 Firmware
|
||||
</Link>
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -5,6 +5,7 @@ sidebar_label: Python Flasher
|
|||
sidebar_position: 2
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
import MFlasher from '../../../software/python-flasher.mdx'
|
||||
import Link from "@docusaurus/Link";
|
||||
import MFlasher from "../../../software/python-flasher.mdx";
|
||||
|
||||
<MFlasher components={props.components} />
|
||||
<MFlasher components={props.components} />
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -6,192 +6,116 @@ slug: /getting-started
|
|||
sidebar_position: 2
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
import Link from '@docusaurus/Link';
|
||||
import Tabs from '@theme/Tabs';
|
||||
import TabItem from '@theme/TabItem';
|
||||
import Link from "@docusaurus/Link";
|
||||
import Tabs from "@theme/Tabs";
|
||||
import TabItem from "@theme/TabItem";
|
||||
|
||||
## Identify Hardware
|
||||
|
||||
The first order of business in getting started is determining what type of hardware you will be working with. Meshtastic currently supports devices with either of the two Micro-Controller Units (MCU):
|
||||
:::note
|
||||
|
||||
This guide assumes that you have already purchased the devices you will be using with Meshtastic. If you haven't, you can check out our list of [supported hardware](/docs/supported-hardware/)
|
||||
to see your options.
|
||||
:::
|
||||
|
||||
Before you begin, it's important to determine which kind of hardware you're using. Meshtastic works with devices that have either of these two types of Micro-Controller Units (MCU):
|
||||
|
||||
### ESP32
|
||||
|
||||
The ESP32 is older and consumes more power than the nrf52, but is equipped with both WiFi and Bluetooth. Supported ESP32 devices:
|
||||
The ESP32 chip is older and consumes more power than the nRF52 chip, but is equipped with both WiFi and Bluetooth. Supported ESP32 devices:
|
||||
|
||||
- LILYGO® TTGO T-Beam
|
||||
- LILYGO® TTGO Lora
|
||||
- Nano G1
|
||||
- Station G1
|
||||
- Heltec V3 and Wireless Stick Lite V3
|
||||
|
||||
### NRF52
|
||||
### nRF52
|
||||
|
||||
The NRF52 is much more power efficient than the esp32 and easier to update, but is only equipped with Bluetooth. Supported NRF52 devices:
|
||||
The nRF52 chip is much more power efficient than the ESP32 chip and easier to update, but is only equipped with Bluetooth. Supported nRF52 devices:
|
||||
|
||||
- RAK WisBlock
|
||||
- LILYGO® TTGO T-Echo
|
||||
|
||||
:::info
|
||||
|
||||
If your device is not listed above, please review our [supported devices](/docs/supported-hardware) to determine which MCU your device has or contact us in [Discord](https://discord.gg/ktMAKGBnBs) with any questions.
|
||||
|
||||
:::
|
||||
|
||||
## Setup Working Environment
|
||||
:::danger STOP! Put The Power Cable Down!
|
||||
|
||||
Never power on the radio without attaching an antenna! _It_ could damage the radio chip.
|
||||
|
||||
:::danger STOP! Put the power cable down!
|
||||
Never power on the radio without attaching an antenna! _it could damage the radio chip._
|
||||
:::
|
||||
|
||||
Prior to connecting your Meshtastic device to the computer, you should perform the following basic checks.
|
||||
|
||||
### Verify data cable
|
||||
### Verify Data Cable
|
||||
|
||||
Some cables only provide _charging_, verify that your cable is also capable of _transferring data_ before proceeding.
|
||||
Some cables only provide _charging_, verify that your cable is also capable of _transferring data_ before proceeding. To check if your cable can also transfer data, try connecting it to another device (like a phone) and see if you can copy a file to or from it. If the file transfer works, then your cable is also able to transfer data and you can continue.
|
||||
|
||||
There is no definitive way to determine the difference in cables if you aren't willing to pull it apart. Trying out a few cables will be the best way to verify.
|
||||
### Install Serial Drivers
|
||||
|
||||
Once you've located a working data cable, [install the correct serial driver](#install-serial-drivers) and [test for driver installation](#test-driver-installation).
|
||||
|
||||
### Install serial drivers
|
||||
If you don't have serial drivers installed on your computer, please choose one of the options below and install it before continuing.
|
||||
|
||||
<div className="indexCtasBody">
|
||||
<div class="split left">
|
||||
<div class="centered">
|
||||
<Link target="_blank"
|
||||
className={'button button--outline button--lg cta--button'}
|
||||
to={'/docs/getting-started/serial-drivers/esp32'}
|
||||
>
|
||||
Install ESP32 Drivers
|
||||
</Link>
|
||||
<div className="split-container">
|
||||
<div className="split-item">
|
||||
<Link
|
||||
className={'button button--outline button--lg cta--button'}
|
||||
to={'/docs/getting-started/serial-drivers/esp32'}
|
||||
>
|
||||
Install ESP32 Drivers
|
||||
</Link>
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
|
||||
<div className="split-item">
|
||||
<Link
|
||||
className={'button button--outline button--lg cta--button'}
|
||||
to={'/docs/getting-started/serial-drivers/nrf52'}
|
||||
>
|
||||
Install NRF52 Drivers
|
||||
</Link>
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
|
||||
<div class="split right">
|
||||
<div class="centered">
|
||||
<Link target="_blank"
|
||||
className={'button button--outline button--lg cta--button'}
|
||||
to={'/docs/getting-started/serial-drivers/nrf52'}
|
||||
>
|
||||
Install NRF52 Drivers
|
||||
</Link>
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
### Flash Firmware
|
||||
|
||||
### Test driver installation
|
||||
|
||||
You can verify that you have a proper data cable (rather than a charge-only type cable) and that the appropriate drivers for your system are installed by performing the following test:
|
||||
|
||||
<Tabs
|
||||
groupId="operating-system"
|
||||
defaultValue="linux"
|
||||
values={[
|
||||
{label: 'Linux', value: 'linux'},
|
||||
{label: 'macOS', value: 'macos'},
|
||||
{label: 'Windows', value: 'windows'},
|
||||
]}>
|
||||
<TabItem value="linux">
|
||||
|
||||
1. Connect your Meshtastic device to your USB port
|
||||
2. Open a **Terminal** and enter the following command:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
lsusb
|
||||
```
|
||||
3. You should see something like:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
ID xxxx:xxxx Silicon Labs CP210x UART Bridge
|
||||
# or
|
||||
ID xxxx:xxxx QinHeng Electronics USB Single Serial
|
||||
# or
|
||||
FIXME (WISBLOCK OUTPUT)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
</TabItem>
|
||||
<TabItem value="macos">
|
||||
|
||||
1. Navigate to `Apple Menu > About This Mac > System Report... > Hardware > USB`.
|
||||
2. You should see similar to one of the following entries:
|
||||
- `CP210X USB to UART Bridge Controller`
|
||||
- `CH9102 USB to UART Bridge Controller`
|
||||
- `WisCore RAK4631 Board`
|
||||
|
||||
</TabItem>
|
||||
<TabItem value="windows">
|
||||
|
||||
1. Navigate to `Device Manager > Ports (COM & LPT)`
|
||||
2. You should see similar to one of the following entries:
|
||||
- `Silicon Labs CP210X USB to UART Bridge (COM5)`
|
||||
- `Silicon Labs CH9102 USB to UART Bridge (COM5)`
|
||||
- `FIXME (WISBLOCK OUTPUT)`
|
||||
|
||||
</TabItem>
|
||||
</Tabs>
|
||||
|
||||
:::info
|
||||
If you do not see your device:
|
||||
|
||||
1. You may be using a charging-only cable, [verify your cable](#verify-data-cable).
|
||||
2. You may need to [install the USB serial driver](/docs/getting-started/serial-drivers)).
|
||||
:::
|
||||
|
||||
## Flash Firmware
|
||||
|
||||
:::info
|
||||
If you have a RAK4631-R (the RUI3 bootloader version of the RAK4631), you must [convert the bootloader](/docs/getting-started/flashing-firmware/nrf52/convert-rak4631r) for use with the Arduino before flashing Meshtastic firmware.
|
||||
:::
|
||||
After completing the previous steps, you can now flash the Meshtastic firmware onto your device. To proceed, select the appropriate device type for your device.
|
||||
|
||||
<div className="indexCtasBody">
|
||||
<div class="split left">
|
||||
<div class="centered">
|
||||
<Link target="_blank"
|
||||
className={'button button--outline button--lg cta--button'}
|
||||
to={'/docs/getting-started/flashing-firmware/esp32/'}
|
||||
>
|
||||
Flash ESP32 Firmware
|
||||
</Link>
|
||||
<div className="split-container">
|
||||
<div className="split-item">
|
||||
<Link
|
||||
className={"button button--outline button--lg cta--button"}
|
||||
to={"/docs/getting-started/flashing-firmware/esp32/"}
|
||||
>
|
||||
Flash ESP32 Firmware
|
||||
</Link>
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
|
||||
<div className="split-item">
|
||||
<Link
|
||||
className={"button button--outline button--lg cta--button"}
|
||||
to={"/docs/getting-started/flashing-firmware/nrf52/"}
|
||||
>
|
||||
Flash nRF52 Firmware
|
||||
</Link>
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
|
||||
<div class="split right">
|
||||
<div class="centered">
|
||||
<Link target="_blank"
|
||||
className={'button button--outline button--lg cta--button'}
|
||||
to={'/docs/getting-started/flashing-firmware/nrf52/'}
|
||||
>
|
||||
Flash NRF52 Firmware
|
||||
</Link>
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
### Connect and Configure Device
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
## Connect and Configure Device
|
||||
|
||||
After connecting to the device for the first time, you should set the regional settings for the radio as well as other optional settings such as the name of the device.
|
||||
After flashing the Meshtastic firmware onto your device, you can now move on to initial configuration.
|
||||
|
||||
<div className="indexCtasBody">
|
||||
<Link target="_blank"
|
||||
className={'button button--outline button--lg cta--button'}
|
||||
to={'/docs/getting-started/initial-config'}
|
||||
<Link
|
||||
className={"button button--outline button--lg cta--button"}
|
||||
to={"/docs/getting-started/initial-config"}
|
||||
>
|
||||
Connect and Configure Device
|
||||
</Link>
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
|
||||
## Use Meshtastic
|
||||
|
||||
### with Command Line Tools
|
||||
- [Python CLI](/docs/software/python/cli)
|
||||
|
||||
### with mobile apps
|
||||
- [Android](/docs/category/android-app)
|
||||
- [Apple](/docs/category/apple-apps)
|
||||
|
||||
### with a browser
|
||||
- https://client.meshtastic.org
|
||||
- [Meshtastic Web](/docs/software/web-client)
|
||||
|
||||
### over the internet with MQTT
|
||||
- [MQTT](/docs/software/mqtt/)
|
||||
|
||||
There are many ways to interact with and use Meshtastic, please visit the [Software](/docs/software) page for more information.
|
||||
|
|
@ -6,10 +6,10 @@ slug: /getting-started/initial-config
|
|||
sidebar_position: 4
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
import Tabs from '@theme/Tabs';
|
||||
import TabItem from '@theme/TabItem';
|
||||
import LoRaRegions from '../blocks/_lora-regions.mdx';
|
||||
|
||||
import Tabs from "@theme/Tabs";
|
||||
import TabItem from "@theme/TabItem";
|
||||
import LoRaRegions from "../blocks/_lora-regions.mdx";
|
||||
import Link from "@docusaurus/Link";
|
||||
|
||||
## Supported Clients per Connection Type
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -17,7 +17,7 @@ Depending on your connection, some configuration options are not fully supported
|
|||
|
||||
<Tabs
|
||||
groupId="settings"
|
||||
defaultValue="serial"
|
||||
defaultValue="ble"
|
||||
values={[
|
||||
{label: 'Serial', value: 'serial'},
|
||||
{label: 'Bluetooth', value: 'ble'},
|
||||
|
|
@ -36,7 +36,6 @@ values={[
|
|||
- [Web Client](https://client.meshtastic.org)
|
||||
- [iOS App](/docs/category/apple-apps)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
</TabItem>
|
||||
<TabItem value="network">
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -49,7 +48,6 @@ Connecting over network is only supported on ESP32 devices.
|
|||
- [iOS App](/docs/category/apple-apps)
|
||||
- [Python CLI](/docs/software/python/cli/)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
</TabItem>
|
||||
</Tabs>
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -57,7 +55,6 @@ Connecting over network is only supported on ESP32 devices.
|
|||
|
||||
In order to start communicating over the mesh, you must set your region. This setting controls which frequency range your device uses and should be set according to your regional location.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
<Tabs
|
||||
groupId="settings"
|
||||
defaultValue="apple"
|
||||
|
|
@ -85,14 +82,14 @@ Configuration of Region, Modem Preset and Hop Limit is available on iOS, iPadOS
|
|||
<TabItem value="cli">
|
||||
|
||||
1. Install [Meshtastic PythonCLI](/docs/software/python/cli/installation)
|
||||
```sh
|
||||
pip3 install --upgrade pytap2
|
||||
pip3 install --upgrade meshtastic
|
||||
```
|
||||
```sh
|
||||
pip3 install --upgrade pytap2
|
||||
pip3 install --upgrade meshtastic
|
||||
```
|
||||
2. Run the following command, replacing `<REGION-CODE>` with the region code listed above according to your regional location.
|
||||
```sh
|
||||
meshtastic --set lora.region <REGION-CODE>
|
||||
```
|
||||
```sh
|
||||
meshtastic --set lora.region <REGION-CODE>
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
</TabItem>
|
||||
<TabItem value="web">
|
||||
|
|
@ -109,6 +106,15 @@ Configuration of Region, Modem Preset and Hop Limit is available on iOS, iPadOS
|
|||
|
||||
<LoRaRegions />
|
||||
|
||||
## Continue Configuration
|
||||
|
||||
Now that you have set the LoRa region on your device, you can continue with configuring any additional configs to suit your needs.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
<div className="indexCtasBody">
|
||||
<Link
|
||||
className={"button button--outline button--lg cta--button"}
|
||||
to={"/docs/settings/"}
|
||||
>
|
||||
Device Configuration
|
||||
</Link>
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -4,4 +4,4 @@ position: 1
|
|||
link:
|
||||
type: generated-index
|
||||
title: Installing Serial Drivers
|
||||
slug: /getting-started/serial-drivers
|
||||
slug: /getting-started/serial-drivers
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -5,8 +5,9 @@ sidebar_label: ESP32 Drivers
|
|||
sidebar_position: 1
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
import Tabs from '@theme/Tabs';
|
||||
import TabItem from '@theme/TabItem';
|
||||
import Tabs from "@theme/Tabs";
|
||||
import TabItem from "@theme/TabItem";
|
||||
import Link from "@docusaurus/Link";
|
||||
|
||||
## Install ESP32 USB to Serial Drivers
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -16,7 +17,7 @@ Some newer boards may require the CH9102 (CH340/CH341) Driver.
|
|||
|
||||
<Tabs
|
||||
groupId="operating-system"
|
||||
defaultValue="linux"
|
||||
defaultValue="windows"
|
||||
values={[
|
||||
{label: 'Linux', value: 'linux'},
|
||||
{label: 'macOS', value: 'macos'},
|
||||
|
|
@ -48,5 +49,22 @@ values={[
|
|||
</Tabs>
|
||||
|
||||
:::important
|
||||
Reboot your computer after you have installed the driver to complete the installation.
|
||||
:::
|
||||
|
||||
After installing the driver, make sure to reboot your computer to finish the installation process.
|
||||
|
||||
You can also [test your serial driver installation](/docs/getting-started/serial-drivers/test-serial-driver-installation) at this step if required.
|
||||
|
||||
:::
|
||||
|
||||
### Flash Firmware
|
||||
|
||||
After installing the serial drivers, you can now flash the Meshtastic firmware onto your device. To proceed, select the appropriate device type for your device.
|
||||
|
||||
<div className="indexCtasBody">
|
||||
<Link
|
||||
className={"button button--outline button--lg cta--button"}
|
||||
to={"/docs/getting-started/flashing-firmware/esp32/"}
|
||||
>
|
||||
Flash ESP32 Firmware
|
||||
</Link>
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -1,18 +1,19 @@
|
|||
---
|
||||
id: nrf52
|
||||
title: NRF52 Serial Drivers
|
||||
sidebar_label: NRF52 Drivers
|
||||
title: nRF52 Serial Drivers
|
||||
sidebar_label: nRF52 Drivers
|
||||
sidebar_position: 2
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
import Tabs from '@theme/Tabs';
|
||||
import TabItem from '@theme/TabItem';
|
||||
import Tabs from "@theme/Tabs";
|
||||
import TabItem from "@theme/TabItem";
|
||||
import Link from "@docusaurus/Link";
|
||||
|
||||
## Install NRF52 USB to Serial Drivers
|
||||
## Install nRF52 USB to Serial Drivers
|
||||
|
||||
<Tabs
|
||||
groupId="operating-system"
|
||||
defaultValue="linux"
|
||||
defaultValue="windows"
|
||||
values={[
|
||||
{label: 'Linux', value: 'linux'},
|
||||
{label: 'macOS', value: 'macos'},
|
||||
|
|
@ -23,22 +24,16 @@ values={[
|
|||
|
||||
- [CH9102 Driver - Linux Download](http://www.wch-ic.com/downloads/CH341SER_LINUX_ZIP.html)
|
||||
|
||||
:::important
|
||||
Reboot your computer after you have installed the driver to complete the installation.
|
||||
:::
|
||||
|
||||
</TabItem>
|
||||
|
||||
<TabItem value="macos">
|
||||
|
||||
- [CH9102 Driver - macOS Download](https://github.com/WCHSoftGroup/ch34xser_macos)
|
||||
|
||||
:::important
|
||||
Reboot your computer after you have installed the driver to complete the installation.
|
||||
:::
|
||||
|
||||
:::caution
|
||||
|
||||
With the latest versions of MacOS, the USB Serial driver is built-in. Do _NOT_ download the USB device drivers unless required. If you downloaded/installed any already, please remove them.
|
||||
|
||||
:::
|
||||
|
||||
### Remove the CH34x USB Driver (macOS)
|
||||
|
|
@ -58,10 +53,27 @@ Uninstall the kernel extension:
|
|||
|
||||
- [CH9102 Driver - Windows Download](http://www.wch-ic.com/downloads/CH341SER_EXE.html)
|
||||
|
||||
:::important
|
||||
Reboot your computer after you have installed the driver to complete the installation.
|
||||
:::
|
||||
|
||||
</TabItem>
|
||||
|
||||
</Tabs>
|
||||
</Tabs>
|
||||
|
||||
:::important
|
||||
|
||||
After installing the driver, make sure to reboot your computer to finish the installation process.
|
||||
|
||||
You can also [test your serial driver installation](/docs/getting-started/serial-drivers/test-serial-driver-installation) at this step if required.
|
||||
|
||||
:::
|
||||
|
||||
### Flash Firmware
|
||||
|
||||
After installing the serial drivers, you can now flash the Meshtastic firmware onto your device. To proceed, select the appropriate device type for your device.
|
||||
|
||||
<div className="indexCtasBody">
|
||||
<Link
|
||||
className={"button button--outline button--lg cta--button"}
|
||||
to={"/docs/getting-started/flashing-firmware/nrf52/"}
|
||||
>
|
||||
Flash nRF52 Firmware
|
||||
</Link>
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -0,0 +1,99 @@
|
|||
---
|
||||
id: test-serial-driver-installation
|
||||
title: Test Serial Driver Installation
|
||||
sidebar_label: Test Serial Driver Installation
|
||||
sidebar_position: 3
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
import Link from "@docusaurus/Link";
|
||||
import Tabs from "@theme/Tabs";
|
||||
import TabItem from "@theme/TabItem";
|
||||
|
||||
### Test Serial Driver Installation
|
||||
|
||||
You can verify that you have a proper data cable (rather than a charge-only type cable) and that the appropriate drivers for your system are installed by performing the following test:
|
||||
|
||||
<Tabs
|
||||
groupId="operating-system"
|
||||
defaultValue="linux"
|
||||
values={[
|
||||
{label: 'Linux', value: 'linux'},
|
||||
{label: 'macOS', value: 'macos'},
|
||||
{label: 'Windows', value: 'windows'},
|
||||
]}>
|
||||
<TabItem value="linux">
|
||||
|
||||
1. Connect your Meshtastic device to your USB port
|
||||
2. Open a **Terminal** and enter the following command:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
lsusb
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
3. You should see something like:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
ID xxxx:xxxx Silicon Labs CP210x UART Bridge
|
||||
# or
|
||||
ID xxxx:xxxx QinHeng Electronics USB Single Serial
|
||||
# or
|
||||
FIXME (WISBLOCK OUTPUT)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
</TabItem>
|
||||
<TabItem value="macos">
|
||||
|
||||
1. Navigate to `Apple Menu > About This Mac > System Report... > Hardware > USB`.
|
||||
2. You should see similar to one of the following entries:
|
||||
|
||||
- `CP210X USB to UART Bridge Controller`
|
||||
- `CH9102 USB to UART Bridge Controller`
|
||||
- `WisCore RAK4631 Board`
|
||||
|
||||
</TabItem>
|
||||
<TabItem value="windows">
|
||||
|
||||
1. Navigate to `Device Manager > Ports (COM & LPT)`
|
||||
2. You should see similar to one of the following entries:
|
||||
|
||||
- `Silicon Labs CP210X USB to UART Bridge (COM5)`
|
||||
- `Silicon Labs CH9102 USB to UART Bridge (COM5)`
|
||||
- `FIXME (WISBLOCK OUTPUT)`
|
||||
|
||||
</TabItem>
|
||||
</Tabs>
|
||||
|
||||
:::info
|
||||
|
||||
If you are unable to see your device:
|
||||
|
||||
- Make sure that your cable is not only for charging but also for [data transfer](/docs/getting-started/#verify-data-cable).
|
||||
- It's possible that you need to [reinstall the USB serial driver](/docs/getting-started/serial-drivers).
|
||||
|
||||
:::
|
||||
|
||||
## Flash Firmware
|
||||
|
||||
After completing the previous steps, you can now flash the Meshtastic firmware onto your device. To proceed, select the appropriate device type for your device.
|
||||
|
||||
<div className="indexCtasBody">
|
||||
<div className="split-container">
|
||||
<div className="split-item">
|
||||
<Link
|
||||
className={"button button--outline button--lg cta--button"}
|
||||
to={"/docs/getting-started/flashing-firmware/esp32/"}
|
||||
>
|
||||
Flash ESP32 Firmware
|
||||
</Link>
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
|
||||
<div className="split-item">
|
||||
<Link
|
||||
className={"button button--outline button--lg cta--button"}
|
||||
to={"/docs/getting-started/flashing-firmware/nrf52/"}
|
||||
>
|
||||
Flash nRF52 Firmware
|
||||
</Link>
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
|
|
@ -4,4 +4,4 @@ position: 5
|
|||
link:
|
||||
type: generated-index
|
||||
title: Supported Hardware
|
||||
slug: hardware
|
||||
slug: hardware
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -4,4 +4,4 @@ position: 2
|
|||
link:
|
||||
type: generated-index
|
||||
title: Antennas
|
||||
slug: antenna
|
||||
slug: antenna
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -7,6 +7,6 @@ sidebar_position: 2
|
|||
|
||||
## RicInNewMexico
|
||||
|
||||
[_RicInNewMexico_](https://github.com/RicInNewMexico) has gone through the trouble of testing a number of commonly purchased antennas in the Meshtastic community and given an opinion on whether or not a given antenna is performing optimally.
|
||||
[_RicInNewMexico_](https://github.com/RicInNewMexico) has gone through the trouble of testing a number of commonly purchased antennas in the Meshtastic community and given an opinion on whether or not a given antenna is performing optimally.
|
||||
|
||||
Please check out the project on Github: [Meshtastic-Antenna-Reports](https://github.com/RicInNewMexico/Meshtastic-Antenna-Reports)
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -28,7 +28,7 @@ Devices on another frequency will not be able to interact with yours. See this l
|
|||
|
||||
### How will you be carrying / transporting the radio?
|
||||
|
||||
A large directional antenna will transmit over significantly greater distance than an omni-directional antenna. However, it must be pointed at its target - so it is not optimal for mobile use.
|
||||
A large directional antenna will transmit over significantly greater distance than an omni-directional antenna. However, it must be pointed at its target - so it is not optimal for mobile use.
|
||||
|
||||
A tuned half-wave whip antenna may have more omni-directional range than the quarter wave stubby; but it will be conspicuous in your pocket.
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -50,7 +50,7 @@ The perfect antenna on paper, sourced from the other side of the world with mixe
|
|||
|
||||
### How close will the antenna be to my Meshtastic device?
|
||||
|
||||
Most cables will significantly degrade the signal strength over any significant distance. It is often more effective to place a node outside than to have it indoors with the antenna outside. The exception might be if there is extreme heat, cold, or humidity, and if the shortest possible low loss cable is used.
|
||||
Most cables will significantly degrade the signal strength over any significant distance. It is often more effective to place a node outside than to have it indoors with the antenna outside. The exception might be if there is extreme heat, cold, or humidity, and if the shortest possible low loss cable is used.
|
||||
|
||||
Still, a proper enclosure should mitigate bad weather.
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -58,4 +58,4 @@ Still, a proper enclosure should mitigate bad weather.
|
|||
|
||||
You could do a lot worse than reading the [Wikipedia entry for Antenna](<https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Antenna_(radio)>), along with the [Wikipedia entry for LoRa](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/LoRa).
|
||||
|
||||
Instead of listing the terms, let us recommend this superb [tutorial](https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=J3PBL9oLPX8) by Andreas Spiess (the 'guy with the Swiss accent').
|
||||
Instead of listing the terms, let us recommend this superb [tutorial](https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=J3PBL9oLPX8) by Andreas Spiess (the 'guy with the Swiss accent').
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -10,35 +10,32 @@ sidebar_position: 4
|
|||
- [Hackaday's Introduction to Antenna Basics](https://www.youtube.com/playlist?list=PL_tws4AXg7authztKFg5ZN5qWGtq3N_nI)
|
||||
- An excellent series of presentations on the basics of antenna design and function, presented by spacecraft radio engineer Karen Rucker.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
### Coverage prediction
|
||||
|
||||
- [Tower Coverage.com](https://www.towercoverage.com)
|
||||
|
||||
- Commercial, but has free options
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
- [HeyWhat'sThat](http://www.heywhatsthat.com)
|
||||
- Free with path profiling options
|
||||
|
||||
- Free with path profiling options
|
||||
|
||||
- [Radio Mobile Online](https://www.ve2dbe.com/rmonline_s.asp)
|
||||
- Radio Mobile Online is a radio wave propagation prediction tool dedicated to amateur radio
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
### RF Tools
|
||||
|
||||
- [Times Microwave Systems](https://www.timesmicrowave.com/calculator/?Product=RG-6&RunLength=10&Frequency=868)
|
||||
|
||||
- Coaxial Cable Attenuation & Power Handling Calculator
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
- [Solwise Link Budget Calculator](https://www.solwise.co.uk/link-budget.htm)
|
||||
- Predict the received signal strength
|
||||
|
||||
- Predict the received signal strength
|
||||
|
||||
- [Amateur Radio Toolkit](https://play.google.com/store/apps/details?id=com.daveyhollenberg.amateurradiotoolkit)
|
||||
- Android app with lots of antenna information
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
### Antenna designs
|
||||
|
||||
- [1/4 Wave Ground Plane Antenna Calculator](https://m0ukd.com/calculators/quarter-wave-ground-plane-antenna-calculator)
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -32,7 +32,6 @@ While the LoRa devices we are using for Meshtastic are relatively low power radi
|
|||
|
||||
The information collected here is by no means definitive, and necessarily abbreviated (it's a huge topic).
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
## Range Testing
|
||||
|
||||
As mentioned, while stating the obvious, the simplest way of performing a test is:
|
||||
|
|
@ -63,7 +62,6 @@ One of the first things to ensure, is that the antenna you have is tuned to the
|
|||
|
||||
Andreas Spiess also gives a great explanation of [how to use Vector Network Analyzers](https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=ZpKoLvqOWyc) to correctly tune your antennas, as well as a more [in depth tutorial of how to use VNAs](https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=_pjcEKQY_Tk). It is important to remember however, that VNAs can only tell you if the antenna is well-matched, not how well it is transmitting. A 50 ohm resistor across the transmitter output would show as ideally matched, but it would be useless at transmitting a signal. There are a number of VNAs now available for less than $100, making this no longer out of reach for most hobbyists, unlike expensive spectrum analyzers.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
## Non-aerial Factors Affecting Transmission
|
||||
|
||||
Unless you're using your devices in a vacuum, with clear line of sight between aerials the following will have an effect:
|
||||
|
|
@ -87,11 +85,8 @@ For a bit of light reading on environmental research:
|
|||
|
||||
In summary - wavelengths in Europe fair well in plain sight, curve over not-so-tall obstacles (including trees), and they reflect off surfaces at low angles of incidence. They go through humans without much attenuation; but not brick, stone, or anything with more attenuation than glass / Kevlar. Oh, and don’t sit under an LTE tower and expect it to be plain sailing. RF emissions at adjacent frequencies can interfere at a high enough power.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
## Discussion
|
||||
|
||||
To comment on / join in antenna range [Meshtastic discourse](https://meshtastic.discourse.group/t/antenna-improved-range/227/35?u=sens8tion)
|
||||
|
||||
There, you will also find reference to Meshtastic range achievements and aerial recommendations. (Note we've stopped short of making specific supplier aerial recommendations in this wiki.)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
Some files were not shown because too many files have changed in this diff Show more
Loading…
Reference in a new issue