| .. | ||
| img | ||
| locales | ||
| index.ts | ||
| README.md | ||
i18n in n8n
Scope
n8n allows for internalization of the majority of UI text:
- base text, e.g. menu display items in the left-hand sidebar menu,
- node text, e.g. parameter display names and placeholders in the node view,
- header text, e.g. node display names and descriptions in the nodes panel.
Currently, n8n does not allow for internalization of:
- messages from outside the
editor-uipackage, e.g.No active database connection, - node subtitles, e.g.
create: userorgetAll: postbelow the node name on the canvas, - new version notification contents in the updates panel, e.g.
Includes node enhancements.
Locale identifiers
A locale identifier is a language code compatible with the Accept-Language header, e.g. de (German), es (Spanish), ja (Japanese). Regional variants of locale identifiers are not supported, i.e. use de, not de-AT. For a list of all locale identifiers, refer to the 639-1 column in the ISO 639-1 codes article.
By default, n8n runs in the en (English) locale. To have it to run in a different locale, set the N8N_DEFAULT_LOCALE environment variable. If it has been set and is not en, n8n will use the UI strings for that locale - for any untranslated UI strings, n8n fall back to en.
export N8N_DEFAULT_LOCALE=de
npm run start
Base text
Base text is directly rendered with no dependencies. Base text is supplied by the user in one file per locale in the /editor-ui package.
Locating base text
Each base text file is located at /packages/editor-ui/src/i18n/locales/{localeIdentifier}.ts and exports an object where keys are Vue component names (and their containing dirs if any) and references to parts of those Vue components.
export default {
nodeCreator: {
categoryNames: {
coreNodes: '🇩🇪 Core Nodes',
analytics: '🇩🇪 Analytics',
communication: '🇩🇪 Communication',
},
// ...
Translating base text
- For the new locale identifier, e.g.
de, copy theenbase text and rename it:
cp ./packages/editor-ui/src/i18n/locales/en.ts ./packages/editor-ui/src/i18n/locales/de.ts
- Check in the UI for a base text string to translate, and find it in the newly created base text file.
Note
: If you cannot find a string in the new base text file, either it does not belong to base text (i.e., the string might be part of header text, credential text, or node text), or the string might belong to the backend, where i18n is currently unsupported.
- Translate the string value - do not change the key. In the examples below, a string starting with 🇩🇪 stands for a translated string.
Optionally, remove any untranslated strings from the new base text file. Untranslated strings in the new base text file will automatically fall back to the en base text file.
Reusable base text
As a convenience, the base text file may contain the special key reusableBaseText, allowing for a string to be translated once and reused elsewhere in the base text file:
export default {
reusableBaseText: {
save: '🇩🇪 Save',
},
duplicateWorkflowDialog: {
enterWorkflowName: '🇩🇪 Enter workflow name',
save: '@:reusableBaseText.save',
},
saveButton: {
save: '@:reusableBaseText.save',
saving: '🇩🇪 Saving',
saved: '🇩🇪 Saved',
},
To localize decimal values, add this key to the base text:
export default {
numberFormats: {
decimal: {
style: 'decimal',
},
},
// ...
}
Interpolation
Some base text strings feature interpolation with a variable in curly braces, e.g. Execution ID {activeExecutionId} was stopped. In case of interpolation, the translated string must not modify the variable: Die Ausführung mit der ID {activeExecutionId} wurde gestoppt.
Dynamic text
Dynamic text is text that relies on node-related data in order to be rendered. Node-related data is supplied by the user in multiple files in the /nodes-base package. Dynamic text is mostly visible in the node view, i.e. the node on the canvas and the node parameters modal.
Locating dynamic text
Dynamic text is divided into files located in /translations dirs alongside the translated nodes:
GitHub
├── GitHub.node.ts
├── GitHubTrigger.node.ts
└── translations
├── de.ts
├── es.ts
└── ja.ts
Each translation file may contain the translations for one or both (regular and trigger) nodes.
In the examples below, the node source is located at /packages/nodes-base/nodes/Github/GitHub.node.ts and the node translation is located at /packages/nodes-base/nodes/Github/translations/de.ts.
In case of grouping dirs, e.g. Google, Aws, and Microsoft, the /translations dir must also be located alongside the *.node.ts file:
Google
└── Drive
├── GoogleDrive.node.ts
└── translations
├── de.js
├── es.ts
└── ja.ts
And same for nodes in versioned dirs:
Mattermost
└── Mattermost.node.ts
└── v1
├── Mattermost.node.ts
├── actions
├── methods
├── transport
└── translations
├── de.js
├── es.ts
└── ja.ts
Translating dynamic text
Each node translation is an object with a key that matches the node's description.name:
export class Github implements INodeType {
description: INodeTypeDescription = {
displayName: 'GitHub',
description: 'Consume GitHub API',
name: 'github', // ← key to use in translation
icon: 'file:github.svg',
group: ['input'],
version: 1,
// ...
module.exports = {
github: {}, // ↑ key from node's description.name
githubTrigger: {}, // ↑ key from node's description.name
};
The object inside allows for three keys: header, credentialsModal and nodeView. These are the sections of each node translation:
module.exports = {
github: {
header: {},
credentialsModal: {},
nodeView: {},
},
githubTrigger: {
header: {},
credentialsModal: {},
nodeView: {},
},
};
Note: These three keys as well as all keys described below are optional. Remember that, in case of missing sections or keys pointing to missing translations, n8n will fall back to the
enlocale.
header section
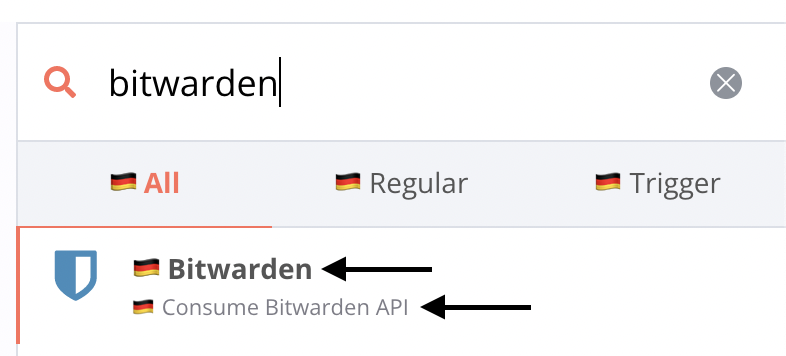
The header section points to an object that may contain only two keys, displayName and description, matching the node's description.displayName and description.description. These are used in the nodes panel, in the node view and in the node credentials modal.
export class Github implements INodeType {
description: INodeTypeDescription = {
displayName: 'GitHub',
description: 'Consume GitHub API',
name: 'github',
icon: 'file:github.svg',
group: ['input'],
version: 1,
// ...
module.exports = {
github: {
header: {
displayName: '🇩🇪 GitHub',
description: '🇩🇪 Consume GitHub API',
},
},
};
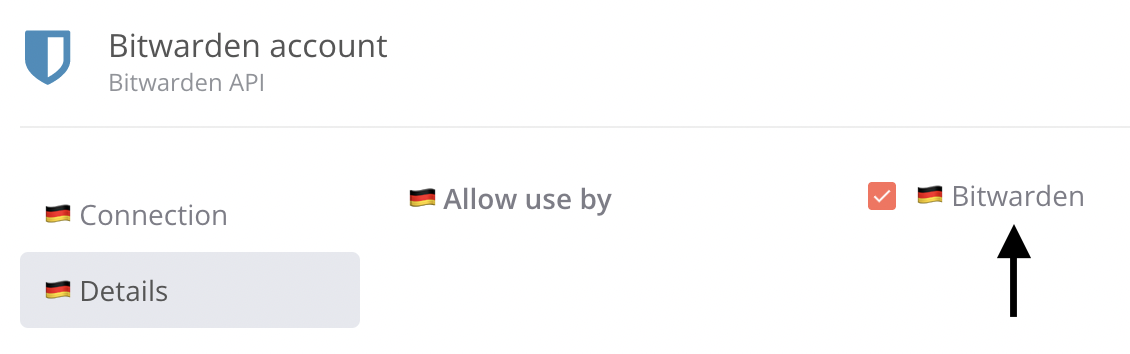
credentialsModal section
The credentialsModal section points to an object having a key that matches the node credential name:
In the examples below, the node credential source is located at /packages/nodes-base/credentials/GithubApi.credentials.ts.
export class GithubApi implements ICredentialType {
name = 'githubApi'; // ← key to use in translation
displayName = 'Github API';
documentationUrl = 'github';
properties: INodeProperties[] = [
// ...
module.exports = {
github: {
header: {},
credentialsModal: {
githubApi: {} // ↑ key from node credential name
},
nodeView: {},
},
};
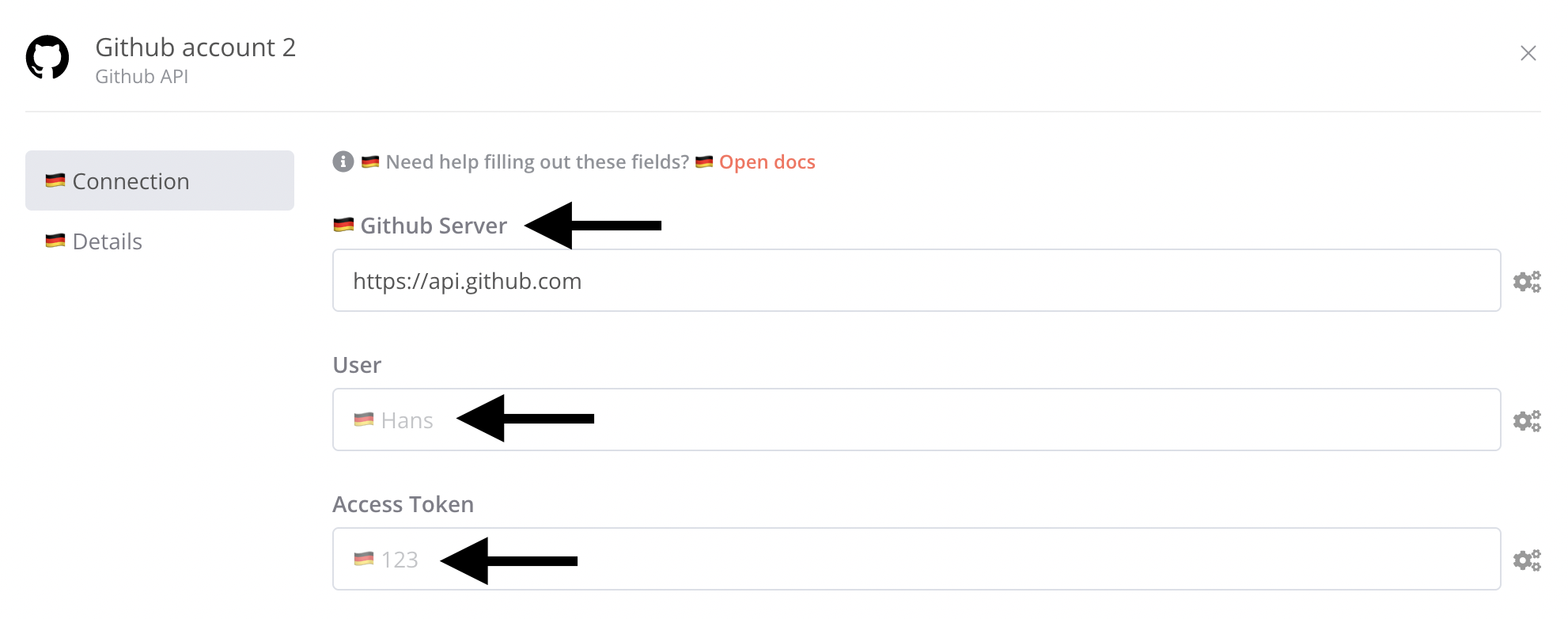
The node credential name key points to an object containing translation keys that match the node's credential parameter names:
export class GithubApi implements ICredentialType {
name = 'githubApi';
displayName = 'Github API';
documentationUrl = 'github';
properties: INodeProperties[] = [
{
displayName: 'Github Server',
name: 'server', // ← key to use in translation
type: 'string',
default: 'https://api.github.com',
description: 'The server to connect to. Only has to be set if Github Enterprise is used.',
},
{
displayName: 'User',
name: 'user', // ← key to use in translation
type: 'string',
default: '',
},
{
displayName: 'Access Token',
name: 'accessToken', // ← key to use in translation
type: 'string',
default: '',
},
];
}
module.exports = {
github: {
header: {
// ...
},
credentialsModal: {
githubApi: {
server: {} // ↑ key from node credential parameter name
user: {} // ↑ key from node credential parameter name
accessToken: {} // ↑ key from node credential parameter name
},
},
nodeView: {
// ...
},
},
};
The object for each node credential parameter allows for the keys displayName, description, and placeholder. Their values will be rendered instead of the English text.
module.exports = {
github: {
header: {},
credentialsModal: {
githubApi: {
server: {
displayName: '🇩🇪 Github Server',
description: '🇩🇪 The server to connect to. Only has to be set if Github Enterprise is used.',
},
user: {
placeholder: '🇩🇪 Hans',
},
accessToken: {
placeholder: '🇩🇪 123',
},
},
},
nodeView: {},
},
};
nodeView section
The nodeView section points to an object containing translation keys that match the node's operational parameters.
export class Github implements INodeType {
description: INodeTypeDescription = {
displayName: 'GitHub',
name: 'github',
// ...
properties: [
{
displayName: 'Resource',
name: 'resource', // ← key to use in translation
type: 'options',
options: [],
default: 'issue',
description: 'The resource to operate on.',
},
// ...
module.exports = {
github: {
header: {},
credentialsModal: {},
nodeView: {
resource: {}, // ↑ key from node parameter name
},
},
};
Note: Other than in the
*.node.tsfile, operational parameters may also be found in*Description.tsfiles in the same dir, e.g.UserDescription.ts.
A node parameter allows for different translation keys depending on parameter type.
string, number and boolean parameters
Allowed keys: displayName, description, and placeholder.
{
displayName: 'Repository Owner', // translatable
name: 'owner',
type: 'string',
required: true,
// ...
placeholder: 'n8n-io', // translatable
description: 'Owner of the repository.', // translatable
},
module.exports = {
github: {
header: {},
credentialsModal: {},
nodeView: {
owner: {
displayName: '🇩🇪 Repository Owner',
placeholder: '🇩🇪 n8n-io',
description: '🇩🇪 Owner of the repository.',
},
},
},
};

TODO i18n
[IMAGE OF NODE VIEW MODAL WHERE string parameter IS USED]
options parameter
Allowed keys: displayName, description, and placeholder.
Allows subkeys: options.{optionName}.displayName and options.{optionName}.description.
{
displayName: 'Resource', // translatable
name: 'resource',
type: 'options',
options: [
{
name: 'File', // translatable
value: 'file',
},
{
name: 'Issue', // translatable
value: 'issue',
},
],
default: 'issue',
description: 'The resource to operate on.', // translatable
},
module.exports = {
github: {
header: {},
credentialsModal: {},
nodeView: {
resource: {
displayName: '🇩🇪 Resource',
description: '🇩🇪 The resource to operate on.',
options: {
file: {
displayName: '🇩🇪 File',
},
issue: {
displayName: '🇩🇪 Issue',
},
},
},
},
},
};
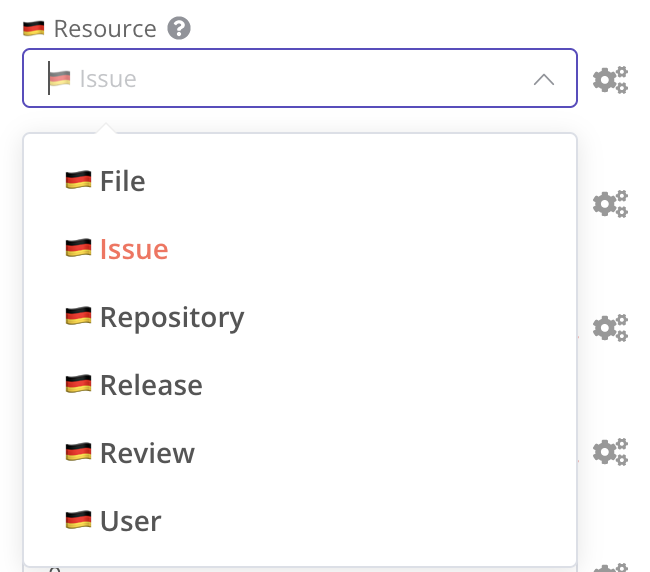
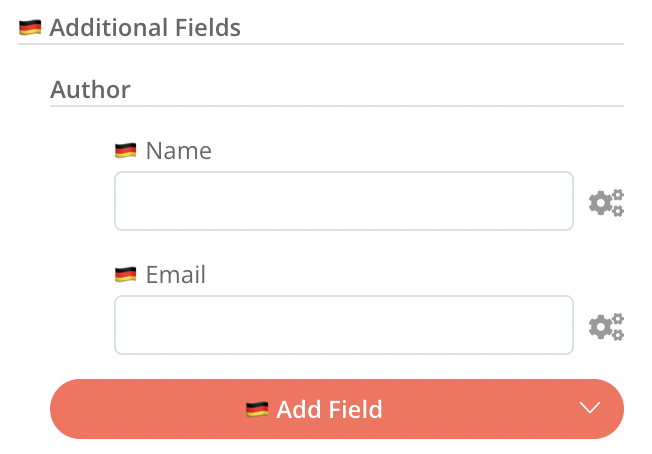
collection and fixedCollection parameters
Allowed keys: displayName, description, placeholder, and multipleValueButtonText.
{
displayName: 'Labels', // translatable
name: 'labels',
type: 'collection',
typeOptions: {
multipleValues: true,
multipleValueButtonText: 'Add Label', // translatable
},
displayOptions: {
show: {
operation: [
'create',
],
resource: [
'issue',
],
},
},
default: { 'label': '' },
options: [
{
displayName: 'Label', // translatable
name: 'label',
type: 'string',
default: '',
description: 'Label to add to issue.', // translatable
},
],
},
module.exports = {
github: {
header: {},
credentialsModal: {},
nodeView: {
// collection
labels: {
displayName: '🇩🇪 Labels',
multipleValueButtonText: '🇩🇪 Add Label',
},
// collection item - same level of nesting
label: {
displayName: '🇩🇪 Label',
description: '🇩🇪 Label to add to issue.',
},
// fixed collection
additionalParameters: {
displayName: '🇩🇪 Additional Fields',
options: {
author: {
displayName: '🇩🇪 Author',
},
},
},
// fixed collection item - same level of nesting
author: {
displayName: '🇩🇪 Author',
},
},
},
};
To reduce nesting and to share translations, a parameter inside a collection's or fixed collection's options parameter sits at the same level of nesting as the containing collection in the nodeView section.
Note
: In case of deep nesting, i.e. a child of a child of a
collectionandfixedCollectionparameter, the deeply nested child in principle should be translatable at the same level of nesting as thecollectionandfixedCollectionparameter, but this has not been fully tested for this first release.
Reusable dynamic text
Also, the base text file may contain the special key reusableDynamicText, allowing for a node parameter to be translated once and reused elsewhere in other node parameter translations.
Currently only the keys oauth.clientId and oauth.clientSecret are supported - these two translations to be reused in all node credential parameters.
export default {
reusableDynamicText: {
oauth2: {
clientId: '🇩🇪 Client ID',
clientSecret: '🇩🇪 Client Secret',
},
},
Building translations
Base text
When translating a base text file at /packages/editor-ui/src/i18n/locales/{localeIdentifier}.ts:
- Open a terminal:
export N8N_DEFAULT_LOCALE=de
npm run start
- Open another terminal:
export N8N_DEFAULT_LOCALE=de
cd packages/editor-ui
npm run dev
Changing the base text file will trigger a rebuild of the client at http://localhost:8080.
Dynamic text
When translating a dynamic text file at /packages/nodes-base/nodes/{node}/translations/{localeIdentifier}.ts,
- Open a terminal:
export N8N_DEFAULT_LOCALE=de
npm run start
- Open another terminal:
export N8N_DEFAULT_LOCALE=de
cd packages/nodes-base
npm run build:translations
npm run watch
After changing the dynamic text file:
- Stop and restart the first terminal.
- Refresh the browser at
http://localhost:5678
If a headerText section was changed, run npm run build:translations again.
Note
: To translate base and dynamic text simultaneously, open three terminals following the steps in both sections (opening the first terminal only once) and browse at
http://localhost:8080.