6.9 KiB
TC²-BBS Meshtastic Version
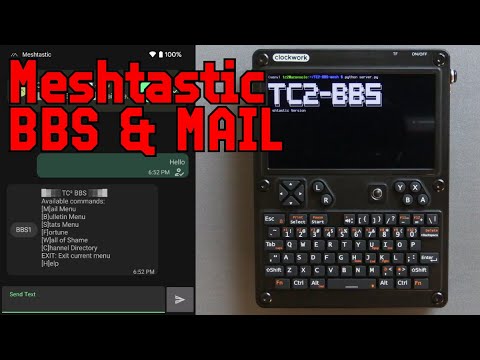
This is the TC²-BBS system integrated with Meshtastic devices. The system allows for message handling,bulletin boards, mail systems, and a channel directory.
Docker available
If you're a Docker user, TC²-BBS Meshtastic is available on Docker Hub!
Docker Automatic Script Deployment
With this single command, TC²-BBS Meshtastic can be easily installed on Debian and all Debian-based Linux distributions, including Raspbian OS.
curl -fsSL https://raw.githubusercontent.com/TheCommsChannel/TC2-BBS-mesh/main/docker/auto_docker_install_debian.sh | bash
Docker configuration:
After executing the Automatic Script Deployment command, TC²-BBS Meshtastic still needs to be configured. First, navigate to the installation directory where the Docker Compose definition is stored:
cd ./TC2-BBS-mesh-docker
This step is optional: if the mestastic node is connected to the system via USB, we need to pass it through to the newly created Docker container so that it can control the USB device:
nano docker-compose.yaml
# devices: <- uncomment if one of the two is needed
# - /dev/ttyUSB0:/dev/ttyUSB0 <- uncomment if needed
# - /dev/ttyACM0:/dev/ttyACM0 <- uncomment if needed
To customize the config file of the TC²-BBS server software itself:
nano ./config/config.ini
After that, the TC²-BBS Meshtastic can simply be started as a service in the background:
docker compose up -d
#for debugging use:
docker compose up
#for stopping use:
docker compose down
Setup manually
Requirements
- Python 3.x
- Meshtastic
- pypubsub
Installation
-
Clone the repository:
cd ~ git clone https://github.com/TheCommsChannel/TC2-BBS-mesh.git cd TC2-BBS-mesh -
Set up a Python virtual environment:
python -m venv venv -
Activate the virtual environment:
- On Windows:
venv\Scripts\activate- On macOS and Linux:
source venv/bin/activate -
Install the required packages:
pip install -r requirements.txt
Configure config.ini
Set up the configuration in config.ini:
[interface]
If using type = serial and you have multiple devices connected, you will need to uncomment the port = line and enter the port of your device.
Linux Example:
port = /dev/ttyUSB0
Windows Example:
port = COM3
If using type = tcp you will need to uncomment the hostname = 192.168.x.x line and put in the IP address of your Meshtastic device.
[sync]
Enter a list of other BBS nodes you would like to sync messages and bulletins with. Separate each by comma and no spaces as shown in the example below.
You can find the nodeID in the menu under Radio Configuration > User for each node, or use this script for getting nodedb data from a device:
Example Config:
[interface]
type = serial
# port = /dev/ttyUSB0
# hostname = 192.168.x.x
[sync]
bbs_nodes = !f53f4abc,!f3abc123
Running the Server manually
Run the server with:
python server.py```
Be sure you've followed the Python virtual environment steps above and activated it before running.
Automatically run at boot
If you would like to have the script automatically run at boot, follow the steps below:
-
Edit the service file
First, edit the mesh-bbs.service file using your preferred text editor. The 3 following lines in that file are what we need to edit:
User=pi WorkingDirectory=/home/pi/TC2-BBS-mesh ExecStart=/home/pi/TC2-BBS-mesh/venv/bin/python3 /home/pi/TC2-BBS-mesh/server.pyThe file is currently setup for a user named 'pi' and assumes that the TC2-BBS-mesh directory is located in the home directory (which it should be if the earlier directions were followed)
We just need to replace the 4 parts that have "pi" in those 3 lines with your username.
-
Configuring systemd
From the TC2-BBS-mesh directory, run the following commands:
sudo cp mesh-bbs.service /etc/systemd/system/sudo systemctl enable mesh-bbs.servicesudo systemctl start mesh-bbs.serviceThe service should be started now and should start anytime your device is powered on or rebooted. You can check the status ofk the service by running the following command:
sudo systemctl status mesh-bbs.serviceIf you need to stop the service, you can run the following:
sudo systemctl stop mesh-bbs.serviceIf you make changes to the watchlist.txt file, you will need to restart the service with the following command:
sudo systemctl restart mesh-bbs.service
Features
- Mail System: Send and receive mail messages.
- Bulletin Boards: Post and view bulletins on various boards.
- Channel Directory: Add and view channels in the directory.
- Statistics: View statistics about nodes, hardware, and roles.
- Wall of Shame: View devices with low battery levels.
- Fortune Teller: Get a random fortune. Pulls from the fortunes.txt file. Feel free to edit this file remove or add more if you like.
Usage
You interact with the BBS by sending direct messages to the node that's connected to the system running the Python script. Sending any message to it will get a response with the main menu.
Make selections by sending messages based on the letter or number in brackets - Send M for [M]ail Menu for example.
A video of it in use is available on our YouTube channel:
Thanks
Big thanks to Meshtastic and pdxlocations for the great Python examples:
python/examples at master · meshtastic/python (github.com)
pdxlocations/Meshtastic-Python-Examples (github.com)
License
GNU General Public License v3.0